.gif)
USS Casco (1864)
Encyclopedia
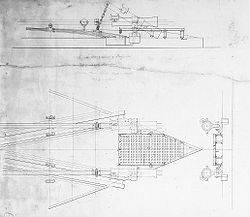
The first USS Casco was the first of a class of twenty 1,175-ton light-draft monitors
built by Atlantic Works, Boston, MA for the Union Navy
during the American Civil War
.
vessel, without a turret or heavy guns. Casco was commissioned 4 December 1864, Acting Master C. A. Crooker in command.
 John Ericsson
John Ericsson
developed the original design for the Casco class monitors, but Chief Engineer Alban C. Stimers
, the General Inspector of Ironclads, elaborated it. When bids were requested for the ships, Assistant Secretary of the Navy Gustavus Fox
wrote to Ericsson to confirm that Stimers had arranged the details with Ericsson’s approval. Ericsson replied that he had been kept in the dark and that Stimers had “frittered away” Ericsson’s principles, but in March 1863, Fox began to award contracts anyway. The vessels received another redesign in the aftermath of Rear Admiral
Samuel F. Du Pont's failed attack on Charleston, SC, on 7 April 1863. Twenty vessels were ordered without serious scrutiny of the design. $14 million US was allocated for the construction of these vessels. It was discovered that Stimers and his assistant Theodore Allen had failed to compensate properly for the weight his revisions added to the original plan and this resulted in excessive stress on the hull and a freeboard of only 3 inches (76.2 mm). In June 1864, Stimers was removed from control of the project and Ericsson was called in to undo the damage. He was forced to raise the hulls of the monitors under construction by nearly two feet and the first few completed vessels had their turrets removed and a single pivot-mount 11 in (279.4 mm) Dahlgren
cannon mounted. These same few vessels had a retractable spar torpedo
added as well.
in March 1865. She assisted in the removal of mines in the James River
which made possible the advance of naval forces to Richmond, VA
. In mid-April she was transferred to the Potomac Flotilla, with whom she served until the end of May. Casco was decommissioned 10 June 1865 at Washington Navy Yard
. In the widespread ship-renamings that took place in June 1869, Casco was given the new name Hero. She saw no further active service, and she was broken up in April 1875.
Monitor (warship)
A monitor was a class of relatively small warship which was neither fast nor strongly armoured but carried disproportionately large guns. They were used by some navies from the 1860s until the end of World War II, and saw their final use by the United States Navy during the Vietnam War.The monitors...
built by Atlantic Works, Boston, MA for the Union Navy
Union Navy
The Union Navy is the label applied to the United States Navy during the American Civil War, to contrast it from its direct opponent, the Confederate States Navy...
during the American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
.
Launch and refitting
Upon her launching in May 1864, it was found that the design of these ships was seriously flawed. She was pronounced unseaworthy when nearly completed and on 25 June 1864 she was ordered to be converted to a torpedoTorpedo
The modern torpedo is a self-propelled missile weapon with an explosive warhead, launched above or below the water surface, propelled underwater towards a target, and designed to detonate either on contact with it or in proximity to it.The term torpedo was originally employed for...
vessel, without a turret or heavy guns. Casco was commissioned 4 December 1864, Acting Master C. A. Crooker in command.

John Ericsson
John Ericsson was a Swedish-American inventor and mechanical engineer, as was his brother Nils Ericson. He was born at Långbanshyttan in Värmland, Sweden, but primarily came to be active in England and the United States...
developed the original design for the Casco class monitors, but Chief Engineer Alban C. Stimers
Alban C. Stimers
Alban Crocker Stimers was a Chief Engineer with the United States Navy. He assisted with the design of the Navy's first ironclad, the , and later with the design of the Passaic-class monitors...
, the General Inspector of Ironclads, elaborated it. When bids were requested for the ships, Assistant Secretary of the Navy Gustavus Fox
Gustavus Fox
Gustavus Vasa Fox was an officer of the United States Navy, who served during the Mexican-American War, and as Assistant Secretary of the Navy during the Civil War.-Biography:...
wrote to Ericsson to confirm that Stimers had arranged the details with Ericsson’s approval. Ericsson replied that he had been kept in the dark and that Stimers had “frittered away” Ericsson’s principles, but in March 1863, Fox began to award contracts anyway. The vessels received another redesign in the aftermath of Rear Admiral
Rear Admiral
Rear admiral is a naval commissioned officer rank above that of a commodore and captain, and below that of a vice admiral. It is generally regarded as the lowest of the "admiral" ranks, which are also sometimes referred to as "flag officers" or "flag ranks"...
Samuel F. Du Pont's failed attack on Charleston, SC, on 7 April 1863. Twenty vessels were ordered without serious scrutiny of the design. $14 million US was allocated for the construction of these vessels. It was discovered that Stimers and his assistant Theodore Allen had failed to compensate properly for the weight his revisions added to the original plan and this resulted in excessive stress on the hull and a freeboard of only 3 inches (76.2 mm). In June 1864, Stimers was removed from control of the project and Ericsson was called in to undo the damage. He was forced to raise the hulls of the monitors under construction by nearly two feet and the first few completed vessels had their turrets removed and a single pivot-mount 11 in (279.4 mm) Dahlgren
Dahlgren gun
Dahlgren guns were muzzle loading naval artillery designed by Rear Admiral John A. Dahlgren USN, mostly used in the period of the American Civil War. Dahlgren's design philosophy evolved from an accidental explosion in 1849 of a 32-pounder being tested for accuracy, killing a gunner...
cannon mounted. These same few vessels had a retractable spar torpedo
Spar torpedo
A spar torpedo is a weapon consisting of a bomb placed at the end of a long pole, or spar, and attached to a boat. The weapon is used by running the end of the spar into the enemy ship. Spar torpedoes were often equipped with a barbed spear at the end, so it would stick to wooden hulls...
added as well.
Potomac Flotilla
After completion of the additional yard work, Casco was towed to Hampton RoadsHampton Roads
Hampton Roads is the name for both a body of water and the Norfolk–Virginia Beach metropolitan area which surrounds it in southeastern Virginia, United States...
in March 1865. She assisted in the removal of mines in the James River
James River (Virginia)
The James River is a river in the U.S. state of Virginia. It is long, extending to if one includes the Jackson River, the longer of its two source tributaries. The James River drains a catchment comprising . The watershed includes about 4% open water and an area with a population of 2.5 million...
which made possible the advance of naval forces to Richmond, VA
Richmond, Virginia
Richmond is the capital of the Commonwealth of Virginia, in the United States. It is an independent city and not part of any county. Richmond is the center of the Richmond Metropolitan Statistical Area and the Greater Richmond area...
. In mid-April she was transferred to the Potomac Flotilla, with whom she served until the end of May. Casco was decommissioned 10 June 1865 at Washington Navy Yard
Washington Navy Yard
The Washington Navy Yard is the former shipyard and ordnance plant of the United States Navy in Southeast Washington, D.C. It is the oldest shore establishment of the U.S. Navy...
. In the widespread ship-renamings that took place in June 1869, Casco was given the new name Hero. She saw no further active service, and she was broken up in April 1875.

