
Tupan Patera
Encyclopedia
Volcano
2. Bedrock3. Conduit 4. Base5. Sill6. Dike7. Layers of ash emitted by the volcano8. Flank| 9. Layers of lava emitted by the volcano10. Throat11. Parasitic cone12. Lava flow13. Vent14. Crater15...
on Jupiter's
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet within the Solar System. It is a gas giant with mass one-thousandth that of the Sun but is two and a half times the mass of all the other planets in our Solar System combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn,...
moon
Natural satellite
A natural satellite or moon is a celestial body that orbits a planet or smaller body, which is called its primary. The two terms are used synonymously for non-artificial satellites of planets, of dwarf planets, and of minor planets....
Io
Io (moon)
Io ) is the innermost of the four Galilean moons of the planet Jupiter and, with a diameter of , the fourth-largest moon in the Solar System. It was named after the mythological character of Io, a priestess of Hera who became one of the lovers of Zeus....
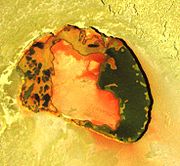
. It is located on Io's anti-Jupiter hemisphere at 18.73°S 141.13°W. Tupan consists of a volcanic crater, known as a patera, 79 kilometers across and 900 meters deep. The volcano was first seen in low-resolution observations by the two Voyager
Voyager program
The Voyager program is a U.S program that launched two unmanned space missions, scientific probes Voyager 1 and Voyager 2. They were launched in 1977 to take advantage of a favorable planetary alignment of the late 1970s...
spacecraft in 1979, but volcanic activity was not seen at this volcano until June 1996 during the Galileo spacecraft's first orbit. Following this first detection of near-infrared thermal emission and subsequent detections by Galileo during the next few orbits, this volcano was formally named
Planetary nomenclature
Planetary nomenclature, like terrestrial nomenclature, is a system of uniquely identifying features on the surface of a planet or natural satellite so that the features can be easily located, described, and discussed. The task of assigning official names to features is taken up by the International...
Tupan Patera, after the thunder god of the Tupí-Guaraní indigenous peoples in Brazil
Indigenous peoples in Brazil
The Indigenous peoples in Brazil comprise a large number of distinct ethnic groups who inhabited the country prior to the European invasion around 1500...
, by the International Astronomical Union
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union IAU is a collection of professional astronomers, at the Ph.D. level and beyond, active in professional research and education in astronomy...
in 1997.
Additional observations by Galileo's Near-Infrared Mapping Spectrometer (NIMS) between 1996 and 2001 revealed Tupan to be a persistently active volcano, visible during most NIMS observations of Io's anti-Jupiter hemisphere. Galileo acquired high-resolution color images and near-infrared spectra of Tupan Patera during an encounter on October 16, 2001. This data revealed warm, dark silicate lava on the eastern and western sides of the patera floor with an "island" of bright, cool material in the middle. Reddish material was observed along the margins of the bright island as well as on the bright plains to the southeast of the volcano. This is indicative of short-chain sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
being emitted from vents on the patera floor by recent volcanic activity. The island as well as a shelf of material at the base of the patera wall is outlined by a "strand" of dark material. This strand line may result from lava filling the patera floor, then deflating due to either degassing of the cooling lava or drainage back into the magma chamber. Alternatively, the strand line may have been created from limited volcanic activity along the edge of the patera floor. The mix of red-orange and dark material on the volcano's western side possibly resulted from sulfur melting from the central island and the patera wall and covering the dark material in this area. This theory is supported by the cooler temperatures seen on the western side of Tupan, cool enough perhaps to support the melting and solidification of sulfur, compared to the much darker eastern side. The morphology of Tupan Patera may also be consistent with a sill
Sill (geology)
In geology, a sill is a tabular sheet intrusion that has intruded between older layers of sedimentary rock, beds of volcanic lava or tuff, or even along the direction of foliation in metamorphic rock. The term sill is synonymous with concordant intrusive sheet...
that is still exhuming itself.
After the last Galileo flyby of Io in January 2002, Tupan remained active with observations of a thermal emission from the volcano by ground-based observers using the Keck Telescope and by the New Horizons
New Horizons
New Horizons is a NASA robotic spacecraft mission currently en route to the dwarf planet Pluto. It is expected to be the first spacecraft to fly by and study Pluto and its moons, Charon, Nix, Hydra and S/2011 P 1. Its estimated arrival date at the Pluto-Charon system is July 14th, 2015...
spacecraft. A large eruption at Tupan was observed by astronomers using the 10-meter adaptive optics
Adaptive optics
Adaptive optics is a technology used to improve the performance of optical systems by reducing the effect of wavefront distortions. It is used in astronomical telescopes and laser communication systems to remove the effects of atmospheric distortion, and in retinal imaging systems to reduce the...
at the Keck Observatory on March 8, 2003. Other than this major eruption, activity at Tupan through the Galileo mission and afterward has been persistent, with variations in power output from the patera floor being episodic, similar to, but at lower energy levels, Loki Patera
Loki Patera
Loki Patera is the largest volcanic depression on Jupiter's moon Io, in diameter. It contains an active lava lake, with an episodically overturning crust. The level of activity seen is similar to a superfast spreading mid-ocean ridge on Earth...
.

