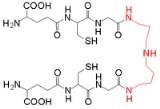
Trypanothione
Encyclopedia
Trypanothione is an unusual form of glutathione
containing two molecules of glutathione joined by a spermidine
(polyamine
) linker. It is found in parasitic protozoa such as leishmania
and trypanosome
s. These protozoal parasites are the cause of leishmaniasis
, sleeping sickness and Chagas' disease. Trypanothione was discovered by Alan Fairlamb
. Its structure was proven by chemical synthesis. It is unique to the Kinetoplastida and not found in other parasitic protozoa such as Entamoeba histolytica
. Since this thiol is absent from humans and is essential for the survival of the parasites, the enzymes that make and use this molecule are targets for the development of new drugs to treat these diseases.
Trypanothione-dependent enzymes include reductase
s, peroxidase
s, glyoxalases and transferase
s. Trypanothione-disulfide reductase
(TryR) was the first trypanothione-dependent enzyme to be discovered (EC 1.8.1.12). It is an NADPH-dependent flavoenzyme that reduces trypanothione disulfide. TryR is essential for survival of these parasites both in vitro and in the human host.
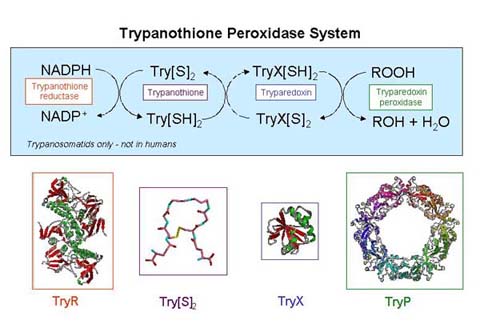
A major function of trypanothione is in the defence against oxidative stress
. Here, trypanothione-dependent enzymes such as tryparedoxin peroxidase (TryP) reduce peroxides using electrons donated either directly from trypanothione, or via the redox intermediate tryparedoxin (TryX). Trypanothione-dependent hydrogen peroxide
metabolism is particularly important in these organisms because they lack catalase
. Since the trypanosomatids also lack an equivalent of thioredoxin reductase
, trypanothione reductase is the sole path that electrons can take from NADPH to these antioxidant enzymes.
Glutathione
Glutathione is a tripeptide that contains an unusual peptide linkage between the amine group of cysteine and the carboxyl group of the glutamate side-chain...
containing two molecules of glutathione joined by a spermidine
Spermidine
Spermidine is a polyamine involved in cellular metabolism. Its known actions include:#Inhibition of neuronal nitric oxide synthase, nNOS#Assisting the in vitro process of transcribing RNA via stimulation of T4 polynucleotide kinase and T7 RNA polymerase activity; it binds to and precipitates DNA...
(polyamine
Polyamine
A polyamine is an organic compound having two or more primary amino groups .This class of compounds includes several synthetic substances that are important feedstocks for the chemical industry, such as ethylene diamine , 1,3-diaminopropane , and hexamethylenediamine...
) linker. It is found in parasitic protozoa such as leishmania
Leishmania
Leishmania is a genus of Trypanosomatid protozoa, and is the parasite responsible for the disease leishmaniasis. It is spread through sandflies of the genus Phlebotomus in the Old World, and of the genus Lutzomyia in the New World. Their primary hosts are vertebrates; Leishmania commonly infects...
and trypanosome
Trypanosoma
Trypanosoma is a genus of kinetoplastids , a monophyletic group of unicellular parasitic flagellate protozoa. The name is derived from the Greek trypano and soma because of their corkscrew-like motion. All trypanosomes are heteroxenous and are transmitted via a vector...
s. These protozoal parasites are the cause of leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is a disease caused by protozoan parasites that belong to the genus Leishmania and is transmitted by the bite of certain species of sand fly...
, sleeping sickness and Chagas' disease. Trypanothione was discovered by Alan Fairlamb
Alan Fairlamb
Alan Hutchison Fairlamb, CBE, FRSE, FLS, FMedSci is a Wellcome Trust Principal Research Fellow, Professor of Biochemistry and Head of the Division of Biological Chemistry and Drug Discovery at the University of Dundee, Scotland...
. Its structure was proven by chemical synthesis. It is unique to the Kinetoplastida and not found in other parasitic protozoa such as Entamoeba histolytica
Entamoeba histolytica
Entamoeba histolytica is an anaerobic parasitic protozoan, part of the genus Entamoeba. Predominantly infecting humans and other primates, E. histolytica is estimated to infect about 50 million people worldwide...
. Since this thiol is absent from humans and is essential for the survival of the parasites, the enzymes that make and use this molecule are targets for the development of new drugs to treat these diseases.
Trypanothione-dependent enzymes include reductase
Reductase
-Examples:* 5-alpha reductase* Dihydrofolate reductase* HMG-CoA reductase* Methemoglobin reductase* Ribonucleotide reductase* Thioredoxin reductase* E. coli nitroreductase* Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase...
s, peroxidase
Peroxidase
Peroxidases are a large family of enzymes that typically catalyze a reaction of the form:For many of these enzymes the optimal substrate is hydrogen peroxide, but others are more active with organic hydroperoxides such as lipid peroxides...
s, glyoxalases and transferase
Transferase
In biochemistry, a transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another . For example, an enzyme that catalyzed this reaction would be a transferase:In this example, A would be the donor, and B would be the acceptor...
s. Trypanothione-disulfide reductase
Trypanothione-disulfide reductase
In enzymology, a trypanothione-disulfide reductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactionThus, the two substrates of this enzyme are trypanothione and NADP+, whereas its 3 products are trypanothione disulfide, NADPH, and H+....
(TryR) was the first trypanothione-dependent enzyme to be discovered (EC 1.8.1.12). It is an NADPH-dependent flavoenzyme that reduces trypanothione disulfide. TryR is essential for survival of these parasites both in vitro and in the human host.
A major function of trypanothione is in the defence against oxidative stress
Oxidative stress
Oxidative stress represents an imbalance between the production and manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage...
. Here, trypanothione-dependent enzymes such as tryparedoxin peroxidase (TryP) reduce peroxides using electrons donated either directly from trypanothione, or via the redox intermediate tryparedoxin (TryX). Trypanothione-dependent hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is the simplest peroxide and an oxidizer. Hydrogen peroxide is a clear liquid, slightly more viscous than water. In dilute solution, it appears colorless. With its oxidizing properties, hydrogen peroxide is often used as a bleach or cleaning agent...
metabolism is particularly important in these organisms because they lack catalase
Catalase
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms that are exposed to oxygen, where it catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen...
. Since the trypanosomatids also lack an equivalent of thioredoxin reductase
Thioredoxin reductase
Thioredoxin Reductases are the only known enzymes to reduce thioredoxin . Two classes of thioredoxin reductase have been identified: one class in bacteria and some eukaryotes and one in animals. Both classes are flavoproteins which function as homodimers...
, trypanothione reductase is the sole path that electrons can take from NADPH to these antioxidant enzymes.


