
TrueSkill
Encyclopedia
TrueSkill is a Bayesian
ranking algorithm developed by Microsoft Research
and used in the Xbox matchmaking system built to address some perceived flaws in the Elo rating system
. It is an extension of the Glicko rating system
to multiplayer games.
In layman's terms, TrueSkill maintains a belief on the skill of each player; every time a player plays a game, the system accordingly changes the perceived skill of the player and acquires more confidence about this perception.
A player's skill is represented as a normal distribution characterized by a mean value of
characterized by a mean value of 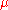 (mu, representing perceived skill) and a variance of
(mu, representing perceived skill) and a variance of  (sigma, representing how much "confidence" the system has in the player's
(sigma, representing how much "confidence" the system has in the player's 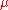 value). As such
value). As such 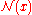 can be interpreted as the probability that the player's "true" skill is
can be interpreted as the probability that the player's "true" skill is  .
.
On Xbox Live, players start with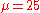 and
and 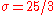 ;
; 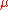 always increases after a win and always decreases after a loss. The extent of actual updates depends on each player's
always increases after a win and always decreases after a loss. The extent of actual updates depends on each player's  and on how "surprising" the outcome is to the system. Unbalanced games, for example, result in either negligible updates when the favorite wins, or huge updates when the favorite loses surprisingly
and on how "surprising" the outcome is to the system. Unbalanced games, for example, result in either negligible updates when the favorite wins, or huge updates when the favorite loses surprisingly
.
Factor graph
s are used to "pack up" each team into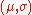 pairs on which the update formulas are run; the skill updates are then correctly distributed to each player.
pairs on which the update formulas are run; the skill updates are then correctly distributed to each player.
Player ranks are displayed as the conservative estimate of their skill,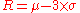 . This is conservative, because the system is 99% sure that the player's skill is actually higher than what is displayed as their rank.
. This is conservative, because the system is 99% sure that the player's skill is actually higher than what is displayed as their rank.
The system can be used with arbitrary scales, but Microsoft uses a scale from 0 to 50 for Xbox Live. Hence, players start with a rank of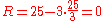 . This means that a new player's defeat results in a large sigma loss, which partially or completely compensates their mu loss. This explains why people may gain ranks from losses.
. This means that a new player's defeat results in a large sigma loss, which partially or completely compensates their mu loss. This explains why people may gain ranks from losses.
Bayesian inference
In statistics, Bayesian inference is a method of statistical inference. It is often used in science and engineering to determine model parameters, make predictions about unknown variables, and to perform model selection...
ranking algorithm developed by Microsoft Research
Microsoft Research
Microsoft Research is the research division of Microsoft created in 1991 for developing various computer science ideas and integrating them into Microsoft products. It currently employs Turing Award winners C.A.R. Hoare, Butler Lampson, and Charles P...
and used in the Xbox matchmaking system built to address some perceived flaws in the Elo rating system
Elo rating system
The Elo rating system is a method for calculating the relative skill levels of players in two-player games such as chess. It is named after its creator Arpad Elo, a Hungarian-born American physics professor....
. It is an extension of the Glicko rating system
Glicko rating system
The Glicko rating system and the Glicko-2 rating system are chess rating systems similar to the Elo rating system: a method for assessing a player's strength in games of skill such as chess. It was invented by Mark Glickman as an improvement of the Elo rating system...
to multiplayer games.
In layman's terms, TrueSkill maintains a belief on the skill of each player; every time a player plays a game, the system accordingly changes the perceived skill of the player and acquires more confidence about this perception.
A player's skill is represented as a normal distribution
 characterized by a mean value of
characterized by a mean value of  (mu, representing perceived skill) and a variance of
(mu, representing perceived skill) and a variance of  (sigma, representing how much "confidence" the system has in the player's
(sigma, representing how much "confidence" the system has in the player's  value). As such
value). As such 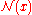 can be interpreted as the probability that the player's "true" skill is
can be interpreted as the probability that the player's "true" skill is  .
.On Xbox Live, players start with
 and
and 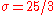 ;
;  always increases after a win and always decreases after a loss. The extent of actual updates depends on each player's
always increases after a win and always decreases after a loss. The extent of actual updates depends on each player's  and on how "surprising" the outcome is to the system. Unbalanced games, for example, result in either negligible updates when the favorite wins, or huge updates when the favorite loses surprisingly
and on how "surprising" the outcome is to the system. Unbalanced games, for example, result in either negligible updates when the favorite wins, or huge updates when the favorite loses surprisinglyUpset
An upset occurs in a competition, frequently in electoral politics or sports, when the party popularly expected to win , is defeated by an underdog whom the majority expects to lose, defying the conventional wisdom...
.
Factor graph
Factor graph
In probability theory and its applications, a factor graph is a particular type of graphical model, with applications in Bayesian inference, that enables efficient computation of marginal distributions through the sum-product algorithm...
s are used to "pack up" each team into
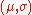 pairs on which the update formulas are run; the skill updates are then correctly distributed to each player.
pairs on which the update formulas are run; the skill updates are then correctly distributed to each player.Player ranks are displayed as the conservative estimate of their skill,
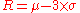 . This is conservative, because the system is 99% sure that the player's skill is actually higher than what is displayed as their rank.
. This is conservative, because the system is 99% sure that the player's skill is actually higher than what is displayed as their rank.The system can be used with arbitrary scales, but Microsoft uses a scale from 0 to 50 for Xbox Live. Hence, players start with a rank of
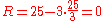 . This means that a new player's defeat results in a large sigma loss, which partially or completely compensates their mu loss. This explains why people may gain ranks from losses.
. This means that a new player's defeat results in a large sigma loss, which partially or completely compensates their mu loss. This explains why people may gain ranks from losses.
