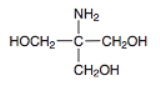
Tris
Overview
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
known as tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, with the formula (HOCH2)3CNH2. Tris is extensively used in biochemistry
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
and molecular biology
Molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that deals with the molecular basis of biological activity. This field overlaps with other areas of biology and chemistry, particularly genetics and biochemistry...
. In biochemistry
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
, tris is widely used as a component of buffer solution
Buffer solution
A buffer solution is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. It has the property that the pH of the solution changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. Buffer solutions are used as a...
s, such as in TAE
TAE buffer
TAE buffer is a buffer solution containing a mixture of Tris base, acetic acid and EDTA.In molecular biology it is used in agarose electrophoresis typically for the separation of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. It is made up of Tris-acetate buffer, usually at pH 8.0, and EDTA, which sequesters...
and TBE buffer
TBE Buffer
TBE or Tris/Borate/EDTA, is a buffer solution containing a mixture of Tris base, boric acid and EDTA.In molecular biology, TBE and TAE buffers are often used in procedures involving nucleic acids, the most common being electrophoresis. Tris-acid solutions are effective buffers for slightly basic...
, especially for solutions of nucleic acid
Nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biological molecules essential for life, and include DNA and RNA . Together with proteins, nucleic acids make up the most important macromolecules; each is found in abundance in all living things, where they function in encoding, transmitting and expressing genetic information...
s. It is a primary amine and thus undergoes the reactions associated with typical amines, e.g. condensations with aldehydes.
Tris has a pKa
Acid dissociation constant
An acid dissociation constant, Ka, is a quantitative measure of the strength of an acid in solution. It is the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction known as dissociation in the context of acid-base reactions...
of 8.06 at 25°C , which implies that the buffer has an effective pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
range between 7.1 and 9.0.
- The pKa declines approximately 0.03 units per degree Celsius rise in temperature.
- SilverSilverSilver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
-containing single-junction pH electrodes (e.g., silver chloride electrodeSilver chloride electrodeA silver chloride electrode is a type of reference electrode, commonly used in electrochemical measurements. For example, it is usually the internal reference electrode in pH meters...
) are incompatible with Tris (Ag-tris precipitation clogs the junction).
Unanswered Questions

