
Transversality theorem
Encyclopedia
In differential topology
, the transversality theorem, also known as the Thom
Transversality Theorem, is a major result that describes the transversal intersection properties of a smooth family of smooth maps. It says that transversality is a generic property
: any smooth map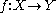 , may be deformed by an arbitrary small amount into a map that is transversal to a given submanifold
, may be deformed by an arbitrary small amount into a map that is transversal to a given submanifold 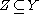 . Together with the Pontryagin-Thom construction, it is the technical heart of cobordism theory, and the starting point for surgery theory
. Together with the Pontryagin-Thom construction, it is the technical heart of cobordism theory, and the starting point for surgery theory
. The finite dimensional version of the transversality theorem is also a very useful tool for establishing the genericity of a property which is dependent on a finite number of real parameters and which is expressible using a system of nonlinear equations. This can be extended to an infinite dimensional parametrization using the infinite dimensional version of the transversality theorem.
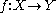 be a smooth map between manifolds, and let
be a smooth map between manifolds, and let 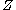 be a submanifold of
be a submanifold of 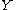 . We say that
. We say that 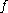 is transversal to
is transversal to 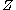 , denoted as
, denoted as 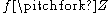 , if and only if for every
, if and only if for every 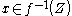 we have
we have 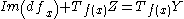 .
.
An important result about transversality states that if a smooth map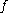 is transversal to
is transversal to 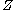 , then
, then 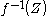 is a regular submanifold of
is a regular submanifold of 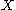 .
.
If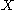 is a manifold with boundary, then we can define the restriction of the map
is a manifold with boundary, then we can define the restriction of the map 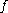 to the boundary, as
to the boundary, as 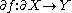 . The map
. The map 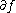 is smooth, and it allow us to state an extension of the previous result: if both
is smooth, and it allow us to state an extension of the previous result: if both 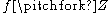 and
and 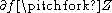 , then
, then 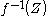 is a regular submanifold of
is a regular submanifold of 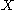 with boundary, and
with boundary, and 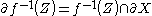 .
.
The key to transversality is families of mappings. Consider the map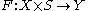 and define
and define 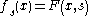 . This generates a family of mappings
. This generates a family of mappings 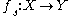 . We require that the family vary smoothly by assuming
. We require that the family vary smoothly by assuming 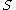 to be a manifold and
to be a manifold and 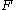 to be smooth.
to be smooth.
Suppose that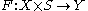 is a smooth map of manifolds, where only
is a smooth map of manifolds, where only 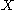 has boundary, and let
has boundary, and let 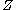 be any submanifold of
be any submanifold of 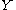 without boundary. If both
without boundary. If both 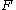 and
and 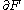 are transversal to
are transversal to 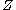 , then for almost every
, then for almost every 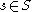 , both
, both 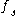 and
and 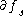 are transversal to
are transversal to 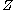 .
.
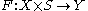 is a
is a 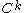 map of
map of 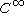 -Banach manifolds. Assume that
-Banach manifolds. Assume that
i-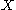 ,
, 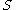 and
and 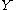 are nonempty, metrizable
are nonempty, metrizable 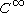 -Banach manifols with chart spaces over a field
-Banach manifols with chart spaces over a field 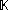 .
.
ii- The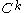 -map
-map 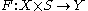 with
with 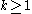 has
has 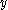 as a regular value.
as a regular value.
iii- For each parameter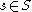 , the map
, the map 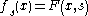 is a Fredholm map
is a Fredholm map
, where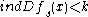 for every
for every 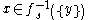 .
.
iv- The convergence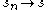 on
on 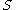 as
as 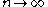 and
and 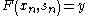 for all
for all  implies the existence of a convergent subsequence
implies the existence of a convergent subsequence 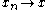 as
as 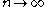 with
with 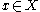 .
.
If Assumptions i-iv hold, then there exists an open, dense subset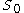 of
of 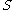 such that
such that 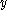 is a regular value of
is a regular value of 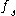 for each parameter
for each parameter 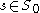 .
.
Now, fix an element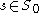 . If there exists a number
. If there exists a number 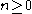 with
with 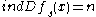 for all solutions
for all solutions 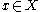 of
of 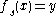 , then the solution set
, then the solution set 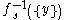 consists of an
consists of an  -dimensional
-dimensional 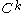 -Banach manifold or the solution set is empty.
-Banach manifold or the solution set is empty.
Note that if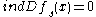 for all the solutions of
for all the solutions of 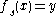 , then there exists an open dense subset
, then there exists an open dense subset 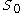 of
of 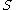 such that there are at most finitely many solutions for each fixed parameter
such that there are at most finitely many solutions for each fixed parameter 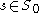 . In addition, all these solutions are regular.
. In addition, all these solutions are regular.
Differential topology
In mathematics, differential topology is the field dealing with differentiable functions on differentiable manifolds. It is closely related to differential geometry and together they make up the geometric theory of differentiable manifolds.- Description :...
, the transversality theorem, also known as the Thom
René Thom
René Frédéric Thom was a French mathematician. He made his reputation as a topologist, moving on to aspects of what would be called singularity theory; he became world-famous among the wider academic community and the educated general public for one aspect of this latter interest, his work as...
Transversality Theorem, is a major result that describes the transversal intersection properties of a smooth family of smooth maps. It says that transversality is a generic property
Generic property
In mathematics, properties that hold for "typical" examples are called generic properties. For instance, a generic property of a class of functions is one that is true of "almost all" of those functions, as in the statements, "A generic polynomial does not have a root at zero," or "A generic...
: any smooth map
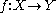 , may be deformed by an arbitrary small amount into a map that is transversal to a given submanifold
, may be deformed by an arbitrary small amount into a map that is transversal to a given submanifold 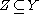 . Together with the Pontryagin-Thom construction, it is the technical heart of cobordism theory, and the starting point for surgery theory
. Together with the Pontryagin-Thom construction, it is the technical heart of cobordism theory, and the starting point for surgery theorySurgery theory
In mathematics, specifically in geometric topology, surgery theory is a collection of techniques used to produce one manifold from another in a 'controlled' way, introduced by . Surgery refers to cutting out parts of the manifold and replacing it with a part of another manifold, matching up along...
. The finite dimensional version of the transversality theorem is also a very useful tool for establishing the genericity of a property which is dependent on a finite number of real parameters and which is expressible using a system of nonlinear equations. This can be extended to an infinite dimensional parametrization using the infinite dimensional version of the transversality theorem.
Previous definitions
Let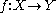 be a smooth map between manifolds, and let
be a smooth map between manifolds, and let 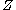 be a submanifold of
be a submanifold of 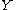 . We say that
. We say that 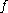 is transversal to
is transversal to 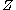 , denoted as
, denoted as 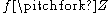 , if and only if for every
, if and only if for every 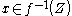 we have
we have 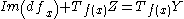 .
.An important result about transversality states that if a smooth map
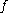 is transversal to
is transversal to 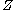 , then
, then 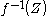 is a regular submanifold of
is a regular submanifold of 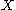 .
.If
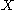 is a manifold with boundary, then we can define the restriction of the map
is a manifold with boundary, then we can define the restriction of the map 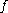 to the boundary, as
to the boundary, as 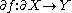 . The map
. The map 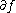 is smooth, and it allow us to state an extension of the previous result: if both
is smooth, and it allow us to state an extension of the previous result: if both 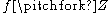 and
and 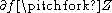 , then
, then 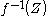 is a regular submanifold of
is a regular submanifold of 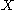 with boundary, and
with boundary, and 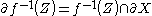 .
.The key to transversality is families of mappings. Consider the map
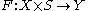 and define
and define 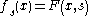 . This generates a family of mappings
. This generates a family of mappings 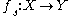 . We require that the family vary smoothly by assuming
. We require that the family vary smoothly by assuming 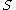 to be a manifold and
to be a manifold and 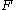 to be smooth.
to be smooth.Formal statement
The formal statement of the transversality theorem is:Suppose that
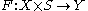 is a smooth map of manifolds, where only
is a smooth map of manifolds, where only 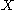 has boundary, and let
has boundary, and let 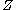 be any submanifold of
be any submanifold of 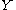 without boundary. If both
without boundary. If both 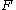 and
and 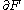 are transversal to
are transversal to 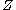 , then for almost every
, then for almost every 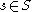 , both
, both 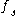 and
and 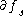 are transversal to
are transversal to 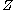 .
.Infinite dimensional version
The infinite dimensional version of the transversality theorem takes into account that the manifolds may be modeled in Banach spaces.Formal statement
Suppose that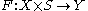 is a
is a 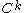 map of
map of 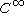 -Banach manifolds. Assume that
-Banach manifolds. Assume thati-
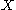 ,
, 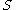 and
and 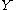 are nonempty, metrizable
are nonempty, metrizable 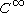 -Banach manifols with chart spaces over a field
-Banach manifols with chart spaces over a field 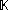 .
.ii- The
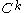 -map
-map 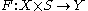 with
with 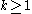 has
has 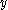 as a regular value.
as a regular value.iii- For each parameter
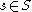 , the map
, the map 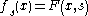 is a Fredholm map
is a Fredholm mapFredholm operator
In mathematics, a Fredholm operator is an operator that arises in the Fredholm theory of integral equations. It is named in honour of Erik Ivar Fredholm....
, where
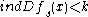 for every
for every 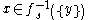 .
.iv- The convergence
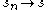 on
on 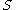 as
as 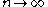 and
and 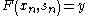 for all
for all  implies the existence of a convergent subsequence
implies the existence of a convergent subsequence 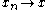 as
as 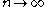 with
with 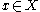 .
.If Assumptions i-iv hold, then there exists an open, dense subset
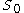 of
of 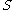 such that
such that 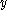 is a regular value of
is a regular value of 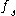 for each parameter
for each parameter 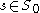 .
.Now, fix an element
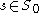 . If there exists a number
. If there exists a number 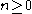 with
with 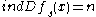 for all solutions
for all solutions 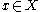 of
of 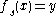 , then the solution set
, then the solution set 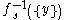 consists of an
consists of an  -dimensional
-dimensional 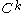 -Banach manifold or the solution set is empty.
-Banach manifold or the solution set is empty.Note that if
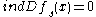 for all the solutions of
for all the solutions of 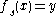 , then there exists an open dense subset
, then there exists an open dense subset 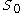 of
of 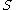 such that there are at most finitely many solutions for each fixed parameter
such that there are at most finitely many solutions for each fixed parameter 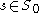 . In addition, all these solutions are regular.
. In addition, all these solutions are regular.

