
Topness
Encyclopedia
Topness a flavour quantum number, represents the difference between the number of top quark
s (t) and number of top antiquarks that are present in a particle: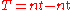
By convention, top quarks have a topness of +1 and top antiquarks have a topness of −1.The term "topness" is rarely used; most physicists simply refer to "the number of top quarks" and "the number of top antiquarks".
and electromagnetic interactions, but not under weak interaction
. However the top quark is extremely unstable, with a half life under 10−23 s, which is the required time for the strong interaction to take place. For that reason the top quark doesn't hadronize
, that is it never forms any meson
or baryon
. By the time it can interact strongly it has already decayed to another flavour of quark (usually to a bottom quark
).
Top quark
The top quark, also known as the t quark or truth quark, is an elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Like all quarks, the top quark is an elementary fermion with spin-, and experiences all four fundamental interactions: gravitation, electromagnetism, weak interactions, and...
s (t) and number of top antiquarks that are present in a particle:
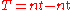
By convention, top quarks have a topness of +1 and top antiquarks have a topness of −1.The term "topness" is rarely used; most physicists simply refer to "the number of top quarks" and "the number of top antiquarks".
Conservation
Like all flavour quantum numbers, topness is preserved under strongStrong interaction
In particle physics, the strong interaction is one of the four fundamental interactions of nature, the others being electromagnetism, the weak interaction and gravitation. As with the other fundamental interactions, it is a non-contact force...
and electromagnetic interactions, but not under weak interaction
Weak interaction
Weak interaction , is one of the four fundamental forces of nature, alongside the strong nuclear force, electromagnetism, and gravity. It is responsible for the radioactive decay of subatomic particles and initiates the process known as hydrogen fusion in stars...
. However the top quark is extremely unstable, with a half life under 10−23 s, which is the required time for the strong interaction to take place. For that reason the top quark doesn't hadronize
Hadronization
In particle physics, hadronization is the process of the formation of hadrons out of quarks and gluons. This occurs after high-energy collisions in a particle collider in which free quarks or gluons are created. Due to postulated colour confinement, these cannot exist individually...
, that is it never forms any meson
Meson
In particle physics, mesons are subatomic particles composed of one quark and one antiquark, bound together by the strong interaction. Because mesons are composed of sub-particles, they have a physical size, with a radius roughly one femtometer: 10−15 m, which is about the size of a proton...
or baryon
Baryon
A baryon is a composite particle made up of three quarks . Baryons and mesons belong to the hadron family, which are the quark-based particles...
. By the time it can interact strongly it has already decayed to another flavour of quark (usually to a bottom quark
Bottom quark
The bottom quark, also known as the beauty quark, is a third-generation quark with a charge of − e. Although all quarks are described in a similar way by the quantum chromodynamics, the bottom quark's large bare mass , combined with low values of the CKM matrix elements Vub and Vcb, gives it a...
).
Further reading
- Lessons in Particle Physics Luis Anchordoqui and Francis Halzen, University of Wisconsin, 18th Dec. 2009

