
Tonicity
Encyclopedia
Osmotic pressure
Osmotic pressure is the pressure which needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of water across a semipermeable membrane....
gradient (as defined by the water potential of the two solutions) of two solutions separated by a semipermeable membrane
Semipermeable membrane
A semipermeable membrane, also termed a selectively permeable membrane, a partially permeable membrane or a differentially permeable membrane, is a membrane that will allow certain molecules or ions to pass through it by diffusion and occasionally specialized "facilitated diffusion".The rate of...
. It is commonly used when describing the response of cells
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
immersed in an external solution. Like osmotic pressure, tonicity is influenced only by solute
Solution
In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
s that cannot cross the membrane, as only these exert an osmotic pressure. Solutes able to freely cross the membrane do not affect tonicity because they will always be in equal concentrations on both sides of the membrane.
Classification
There are three classifications of tonicity that one solution can have relative to another. The three are hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic.Hypertonicity
A hypertonic solution is a solution having a greater effective osmole concentration than the cytosolCytosol
The cytosol or intracellular fluid is the liquid found inside cells, that is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into compartments....
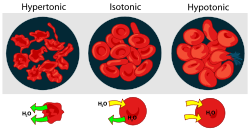
. It contains a greater concentration of impermeable solutes on the external side of the membrane. When a cell’s cytoplasm is bathed in a hypertonic solution, water will be drawn into the solution and out of the cell by osmosis. If water molecules continue to diffuse out of the cell, it will cause the cell to shrink, or crenate.
A hypertonic solution is used in osmotherapy
Osmotherapy
Osmotherapy is a medical treatment, using intravenous injection or oral administration of an agent to induce dehydration. The goal of dehydration is to reduce the amount of accumulated fluid in the brain. The earliest description in medical literature dates back to 1919.- Treatment :Osmotherapy can...
to treat cerebral hemorrhage.
Hypotonicity
A hypotonic solution is a solution having a lower effective osmole concentration than the cytosolCytosol
The cytosol or intracellular fluid is the liquid found inside cells, that is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into compartments....
. It contains a lesser concentration of impermeable solutes on the external side of the membrane. When a cell’s cytoplasm is bathed in a hypotonic solution the water will be drawn out of the solution and into the cell by osmosis. If water molecules continue to diffuse into the cell, it will cause the cell to swell, up to the point that cytolysis
Cytolysis
Cytolysis, or osmotic lysis, occurs when a cell bursts due to an osmotic imbalance that has caused excess water to move into the cell. It occurs in a hypotonic environment, where water diffuses into the cell and causes its volume to increase. If the volume of water exceeds the cell membrane's...
(rupture) may occur. In plant cells, the cell will not always rupture. When placed in a hypotonic solution, the cell will have Turgor Pressure
Turgor pressure
Turgor Pressure or turgidity is the main pressure of the cell contents against the cell wall in plant cells and bacteria cells, determined by the water content of the vacuole, resulting from osmotic pressure, i.e...
and proceed with its normal functions.
Isotonicity
A condition or property of a solution in which its effective osmole concentration is the same as the solute concentration of another solution with which it is compared. It is a concentration of both water and total solute molecules are the same in an external solution as in the cell content. Water molecules diffuse through the plasma membrane in both direction. The rate of water diffusion is the same in both direction that cell will neither gain nor lose water.Effect on cells
In animalAnimal
Animals are a major group of multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their life. Most animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and...
cells, a hypertonic environment forces water to leave the cell so that the shape of the cell becomes distorted and wrinkled, a state known as crenation
Crenation
Crenation is the contraction of a cell after exposure to a hypertonic solution, due to the loss of water through osmosis. The word is from the Latin "crenatus" meaning scalloped or notched, and is named for the scalloped-edged shape the cells take on when crenated.Crenation occurs because in a...
. In plant cell
Plant cell
Plant cells are eukaryotic cells that differ in several key respects from the cells of other eukaryotic organisms. Their distinctive features include:...
s, the effect is more dramatic. The flexible cell membrane
Cell membrane
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell...
pulls away from the rigid cell wall
Cell wall
The cell wall is the tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to...
, but remains joined to the cell wall at points called plasmodesmata
Plasmodesmata
Plasmodesmata are microscopic channels which traverse the cell walls of plant cells and some algal cells, enabling transport and communication between them. Species that have plasmodesmata include members of the Charophyceae, Charales and Coleochaetales , as well as all embryophytes, better known...
. The cell takes on the appearance of a pincushion
Pincushion
A pincushion is a small cushion, typically 3–5 cm across, which is used in sewing to store pins or needles with their heads protruding so as to take hold of them easily, collect them, and keep them organized....
, and the plasmodesmata almost cease to function because they become constricted — a condition known as plasmolysis
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the process in plant cells where the cytoplasm pulls away from the cell wall due to the loss of water through osmosis. The reverse process, cytolysis, can occur if the cell is in a hypotonic solution resulting in a higher external osmotic pressure and a net flow of water into the cell...
. In plant cells the terms isotonic, hypotonic and hypertonic cannot strictly be used accurately because the pressure exerted by the cell wall significantly affects the osmotic equilibrium point.
Some organisms have evolved intricate methods of circumventing hypertonicity. For example, saltwater
Seawater
Seawater is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% . This means that every kilogram of seawater has approximately of dissolved salts . The average density of seawater at the ocean surface is 1.025 g/ml...
is hypertonic to the fish
Fish
Fish are a paraphyletic group of organisms that consist of all gill-bearing aquatic vertebrate animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as various extinct related groups...
that live in it. They need a large surface area in their gill
Gill
A gill is a respiratory organ found in many aquatic organisms that extracts dissolved oxygen from water, afterward excreting carbon dioxide. The gills of some species such as hermit crabs have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are kept moist...
s in contact with seawater for gas exchange
Gas exchange
Gas exchange is a process in biology where gases contained in an organism and atmosphere transfer or exchange. In human gas-exchange, gases contained in the blood of human bodies exchange with gases contained in the atmosphere. Human gas-exchange occurs in the lungs...
, thus they lose water osmotically to the sea from gill cells. They respond to the loss by drinking large amounts of saltwater, and actively excreting
Excretion
Excretion is the process by which waste products of metabolism and other non-useful materials are eliminated from an organism. This is primarily carried out by the lungs, kidneys and skin. This is in contrast with secretion, where the substance may have specific tasks after leaving the cell...
the excess salt. This process is called osmoregulation
Osmoregulation
Osmoregulation is the active regulation of the osmotic pressure of an organism's fluids to maintain the homeostasis of the organism's water content; that is it keeps the organism's fluids from becoming too diluted or too concentrated. Osmotic pressure is a measure of the tendency of water to move...
.
In a hypotonic environment, animal cells will swell until they burst, a process known as cytolysis
Cytolysis
Cytolysis, or osmotic lysis, occurs when a cell bursts due to an osmotic imbalance that has caused excess water to move into the cell. It occurs in a hypotonic environment, where water diffuses into the cell and causes its volume to increase. If the volume of water exceeds the cell membrane's...
. Fresh water fish urinate constantly to prevent cytolysis. Plant cells tend to resist bursting, due to the reinforcement of their cell wall, which provides effective osmolarity or osmolality.
In some cases of suspensions intended for intramuscular injection
Intramuscular injection
Intramuscular injection is the injection of a substance directly into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several alternative methods for the administration of medications . It is used for particular forms of medication that are administered in small amounts...
, a slightly hypotonic solution is preferred in order to increase the dissolution and absorption of the drug by absorbing water from the surrounding tissues.

