
Threaded rod
Encyclopedia
A threaded rod, also known as a stud, is a relatively long rod that is threaded
on both ends; the thread may extend along the complete length of the rod. They are designed to be used in tension. Threaded rod in bar stock
form is often called all-thread.
studs have a shank equal to the pitch diameter of the screw thread. Undercut studs are designed to better distribute axial stresses. In a full-bodied stud the stresses are greater in the threads than in the shank.
Undercut studs (rolled thread) are also stronger because the metal is "rolled" up to the major diameter, not removed. This preserves the grain of the steel, and in some cases even enhances it. Full bodied studs (cut thread) are weaker because metal is removed to create the thread, disturbing the grain of the steel.
Undercut studs are only required in applications where the stud is exposed to fatigue. Cut threads are entirely suitable for many applications, even when rolled threads might be slightly stronger. Mass-produced fasteners (standard bolts and studs) are usually rolled, but jobbed
parts with custom features and small lot sizes are likely to be cut.
(AISC) as: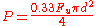
where d is the nominal diameter and Fu is the ultimate tensile strength of the material. For undercut threaded rods the allowable tensile stress is defined as: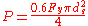
where ds is the diameter of the shank and Fy is the yield strength of the material.
. The color codes are:
Screw thread
A screw thread, often shortened to thread, is a helical structure used to convert between rotational and linear movement or force. A screw thread is a ridge wrapped around a cylinder or cone in the form of a helix, with the former being called a straight thread and the latter called a tapered thread...
on both ends; the thread may extend along the complete length of the rod. They are designed to be used in tension. Threaded rod in bar stock
Bar stock
Bar stock, also colloquially known as billet, is a common form of raw purified metal, used by industry to manufacture metal parts and products....
form is often called all-thread.
Studs
Studs may have a drive slot in one end to facilitate installing the stud.Types
For studs that are not completely threaded, there are two types of studs: full-bodied studs, and undercut studs. Full-bodied studs have a shank equal to the major diameter of the thread. UndercutUndercut (manufacturing)
In manufacturing, an undercut is a special type of recessed surface. In turning it refers to a recess in a diameter. In machining it refers to a recess in a corner. In molding it refers to a feature that cannot be molded using only a single pull mold...
studs have a shank equal to the pitch diameter of the screw thread. Undercut studs are designed to better distribute axial stresses. In a full-bodied stud the stresses are greater in the threads than in the shank.
Undercut studs (rolled thread) are also stronger because the metal is "rolled" up to the major diameter, not removed. This preserves the grain of the steel, and in some cases even enhances it. Full bodied studs (cut thread) are weaker because metal is removed to create the thread, disturbing the grain of the steel.
Undercut studs are only required in applications where the stud is exposed to fatigue. Cut threads are entirely suitable for many applications, even when rolled threads might be slightly stronger. Mass-produced fasteners (standard bolts and studs) are usually rolled, but jobbed
Job production
Job production, sometimes called jobbing, involves producing a one-off product for a specific customer. Job production is most often associated with small firms but large firms use job production too...
parts with custom features and small lot sizes are likely to be cut.
Strength
The allowable tensile force for a non-undercut threaded rod is defined by the American Institute of Steel ConstructionAmerican Institute of Steel Construction
The American Institute of Steel Construction, often abbreviated AISC, is a not-for-profit technical institute and trade association for the use of structural steel in the construction industry of the United States. It is headquartered in Chicago, IL. Their mission is to make structural steel the...
(AISC) as:
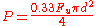
where d is the nominal diameter and Fu is the ultimate tensile strength of the material. For undercut threaded rods the allowable tensile stress is defined as:
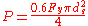
where ds is the diameter of the shank and Fy is the yield strength of the material.
Class
Metric threaded rods are marked on the end with a color code to define the classClass
- General :* Class , a group of students attending a specific course or lesson** Lessons, in education** Classroom* Class , an analytical concept used differently to group phenomena from grouping as 'types' or 'kinds'...
. The color codes are:
- Unmarked — 4.6 class
- Yellow — 8.8 class
- Green — A2 stainless steel (304)
- Red — A4 stainless steel (316)
- White — 10.9 class

