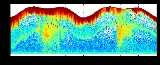
Thin layers
Encyclopedia
Thin layers are congregations of phytoplankton
and zooplankton
in the water column which were discovered with advances in instrumentation and deployment technologies allowed samples at the temporal and spatial scales where patterns were revealed. Although they may extend for kilometers, thin layers are only a few tens of centimeters in vertical
thickness. They have distinct physical, biological
, chemical, optical and acoustical signatures. Thin layers of phytoplankton
or zooplankton
may contain densities of organisms ranging up to 1000 times those found just above, or below the structure.
These extraordinary concentrations of living material must have important implications for many aspects of marine ecology (e.g., phytoplankton growth dynamics, micro- and macrozooplankton grazing, behaviour, life histories, predation, harmful algal blooms), as well as for ocean optics and acoustics.
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton are the autotrophic component of the plankton community. The name comes from the Greek words φυτόν , meaning "plant", and πλαγκτός , meaning "wanderer" or "drifter". Most phytoplankton are too small to be individually seen with the unaided eye...
and zooplankton
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are heterotrophic plankton. Plankton are organisms drifting in oceans, seas, and bodies of fresh water. The word "zooplankton" is derived from the Greek zoon , meaning "animal", and , meaning "wanderer" or "drifter"...
in the water column which were discovered with advances in instrumentation and deployment technologies allowed samples at the temporal and spatial scales where patterns were revealed. Although they may extend for kilometers, thin layers are only a few tens of centimeters in vertical
Vertical direction
In astronomy, geography, geometry and related sciences and contexts, a direction passing by a given point is said to be vertical if it is locally aligned with the gradient of the gravity field, i.e., with the direction of the gravitational force at that point...
thickness. They have distinct physical, biological
Biology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
, chemical, optical and acoustical signatures. Thin layers of phytoplankton
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton are the autotrophic component of the plankton community. The name comes from the Greek words φυτόν , meaning "plant", and πλαγκτός , meaning "wanderer" or "drifter". Most phytoplankton are too small to be individually seen with the unaided eye...
or zooplankton
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are heterotrophic plankton. Plankton are organisms drifting in oceans, seas, and bodies of fresh water. The word "zooplankton" is derived from the Greek zoon , meaning "animal", and , meaning "wanderer" or "drifter"...
may contain densities of organisms ranging up to 1000 times those found just above, or below the structure.
These extraordinary concentrations of living material must have important implications for many aspects of marine ecology (e.g., phytoplankton growth dynamics, micro- and macrozooplankton grazing, behaviour, life histories, predation, harmful algal blooms), as well as for ocean optics and acoustics.

