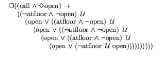
Temporal logic in finite-state verification
Encyclopedia
In finite-state verification
, model checkers
examine finite-state machines representing concurrent software systems looking for errors in design
. Errors are defined as violations of requirements expressed as properties of the system. In the event that the finite-state machine fails to satisfy the property, a model checker is in some cases capable of producing a counterexample – an execution of the system demonstrating how the error occurs.
Property specifications are often written as Linear Temporal Logic
(LTL) expressions. Once a requirement is expressed as an LTL formula
, a model checker can automatically verify this property against the model.
Between the time an elevator is called at a floor and the time it opens its doors at that floor, the elevator can arrive at that floor at most twice. The authors of "Patterns in Property Specification for Finite-State Verification" translate this requirement into the following LTL formula:

Verification
The word verification may refer to:* Verification and validation, in engineering or quality management systems, it is the act of reviewing, inspecting or testing, in order to establish and document that a product, service or system meets regulatory or technical standards.* Verification , in the...
, model checkers
Model checking
In computer science, model checking refers to the following problem:Given a model of a system, test automatically whether this model meets a given specification....
examine finite-state machines representing concurrent software systems looking for errors in design
Design
Design as a noun informally refers to a plan or convention for the construction of an object or a system while “to design” refers to making this plan...
. Errors are defined as violations of requirements expressed as properties of the system. In the event that the finite-state machine fails to satisfy the property, a model checker is in some cases capable of producing a counterexample – an execution of the system demonstrating how the error occurs.
Property specifications are often written as Linear Temporal Logic
Linear temporal logic
In logic, Linear temporal logic is a modal temporal logic with modalities referring to time. In LTL, one can encode formulae about the future of paths such as that a condition will eventually be true, that a condition will be true until another fact becomes true, etc. It is a fragment of the more...
(LTL) expressions. Once a requirement is expressed as an LTL formula
Formula
In mathematics, a formula is an entity constructed using the symbols and formation rules of a given logical language....
, a model checker can automatically verify this property against the model.
Example
One example of such a system requirement:Between the time an elevator is called at a floor and the time it opens its doors at that floor, the elevator can arrive at that floor at most twice. The authors of "Patterns in Property Specification for Finite-State Verification" translate this requirement into the following LTL formula:

See also
- Finite-state machines
- Formal methodsFormal methodsIn computer science and software engineering, formal methods are a particular kind of mathematically-based techniques for the specification, development and verification of software and hardware systems...
- Formal verificationFormal verificationIn the context of hardware and software systems, formal verification is the act of proving or disproving the correctness of intended algorithms underlying a system with respect to a certain formal specification or property, using formal methods of mathematics .- Usage :Formal verification can be...
- Kripke structureKripke structureA Kripke structure is a type of nondeterministic finite state machine proposed by Saul Kripke , used in model checking to represent the behavior of a system.It is a simple abstract machine to capture an idea of a computing machine,...
- Linear temporal logicLinear temporal logicIn logic, Linear temporal logic is a modal temporal logic with modalities referring to time. In LTL, one can encode formulae about the future of paths such as that a condition will eventually be true, that a condition will be true until another fact becomes true, etc. It is a fragment of the more...
- Model checkingModel checkingIn computer science, model checking refers to the following problem:Given a model of a system, test automatically whether this model meets a given specification....
- Temporal logicTemporal logicIn logic, the term temporal logic is used to describe any system of rules and symbolism for representing, and reasoning about, propositions qualified in terms of time. In a temporal logic we can then express statements like "I am always hungry", "I will eventually be hungry", or "I will be hungry...

