Tarsal tunnel syndrome
Encyclopedia
Tarsal tunnel syndrome also known as posterior tibial neuralgia, is compression neuropathy and a painful foot condition in which the tibial nerve
is impinged and compressed as it travels through the tarsal tunnel
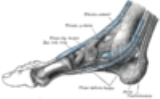
. TTS is a compression syndrome of the tibial nerve within the tarsal tunnel. This tunnel is found along the inner leg behind the medial malleolus (bump on the inside of the ankle). The posterior tibial artery, tibial nerve, and tendons of the tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, and flexor hallucis longus muscles travel in a bundle along this pathway, through the tarsal tunnel. In the tunnel, the nerve splits into three different paths. One nerve (calcaneal) continues to the heel, the other two (medial and lateral plantar nerves) continue on to the bottom of the foot. The tarsal tunnel is made up of bone on the inside and the flexor retinaculum on the outside.
Patients complain typically of numbness in the foot, radiating to the big toe and the first 3 toes, pain
, burning, electrical sensations, and tingling over the base of the foot and the heel. Depending on the area of entrapment, other areas can be affected. If the entrapment is high, the entire foot can be affected as varying branches of the tibial nerve can become involved. Ankle pain is also present in patients who have high level entrapments. Inflammation or swelling can occur within this tunnel for a number of reasons. The flexor retinaculum has a limited ability to stretch, so increased pressure will eventually cause compression on the nerve within the tunnel. As pressure increases on the nerves, the blood flow decreases. Nerves respond with altered sensations like tingling and numbness. Fluid collects in the foot when standing and walking and this makes the condition worse. As small muscles lose their nerve supply they can create a cramping feeling.
Tinel's sign
is a tingling electric shock sensation that occurs when you tap over an affected nerve. The sensation usually travels into the foot but can also travel up the inner leg as well.
, Orthopedist, Physiatrist, Chiropractor
, podiatrist, physical therapist, or athletic trainer
. Patients' pain history and a positive Tinel's sign
are the first steps in evaluating the possibility of tarsal tunnel syndrome. X-ray
can rule out fracture. MRI can assess for space occupying lesions or other causes of nerve compression. Ultrasound
can assess for synovitis or ganglia. Nerve conduction studies alone are not diagnostic, but they may be used to confirm the suspected clinical diagnosis. Common causes include trauma, varicose veins
, neuropathy and space occupying anomalies within the tarsal tunnel.
A fellowship trained Neurologist or a Physiatrist usually administers nerve conduction tests. During this test, electrodes are placed at various spots along the nerves in the legs and feet. Both sensory and motor nerves are tested at different locations. Electrical impulses are sent through the nerve and the speed and intensity at which they travel is measured. If there is compression in the tunnel, this can be confirmed and pinpointed with this test. Many doctors do not feel that this test is necessarily a reliable way to rule out TTS. Some research indicates that nerve conduction tests will be normal in at least 50% of the cases. It is possible to have TTS without a positive nerve conduction test.
, peroneus and short toe flexors, casting with a walker boot, corticosteroid
and anesthetic injections, hot wax baths, wrapping, compression hose, and orthotics
. Medications may include various anti-inflammatories, Anaprox, Ultracet, and Neurontin and Lyrica. Lidocaine
patches are also a treatment that helps some patients. If non-invasive treatment measures fail, surgery may be recommended to decompress the area.
The patient may not respond to conservative treatment and may need surgical treatment or tarsal tunnel release surgery. The incision is made behind the ankle bone and then down towards but not as far as the bottom of foot. The Posterior Tibial nerve is identified above the ankle. It is separated from the accompanying artery and vein and then followed into the tunnel. The nerves are released. Cysts or other space-occupying problems may be corrected at this time. If there is scarring within the nerve or branches, this is relieved by internal neurolysis. Neurolysis is when the outer layer of nerve wrapping is opened and the scar tissue is removed from within nerve. Following surgery, a large bulky cotton wrapping immobilizes the ankle joint without plaster. The dressing may be removed at the one week point and sutures at about three weeks.
Complications may include bleeding, infection, and unpredictable healing. The incision may open from swelling. There may be considerable pain and cramping. Regenerating nerve fibers may create shooting pains. Patients may have hot or cold sensations and may feel worse than before surgery. Crutches are usually recommended for the first two weeks, as well as elevation to minimize swelling. The nerve will grow at about one inch per month. One can expect to continue the healing process over the course of about one year.
Many patients report good results. Some, however, experience no improvement or a worsening of symptoms. In the Pfeiffer article (Los Angeles, 1996), fewer than 50% of the patients reported improvement, and there was a 13% complication rate. This is a staggering percentage of complications for what is a fairly superficial and minor surgical procedure.
Tarsal tunnel can greatly impact patients' quality of life. Depending on the severity, the ability to walk distances people normally take for granted (such as grocery shopping) may become compromised. Proper pain management and counseling is often required.
Tibial nerve
The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.In the popliteal fossa the nerve gives off branches to gastrocnemius, popliteus, soleus and plantaris muscles, an articular branch to the knee joint, and a...
is impinged and compressed as it travels through the tarsal tunnel
Tarsal tunnel
The tarsal tunnel is found along the inner leg behind the medial malleolus.The tarsal tunnel is made up of bone on the inside and the flexor retinaculum on the outside.-Nerve distribution:...
. TTS is a compression syndrome of the tibial nerve within the tarsal tunnel. This tunnel is found along the inner leg behind the medial malleolus (bump on the inside of the ankle). The posterior tibial artery, tibial nerve, and tendons of the tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, and flexor hallucis longus muscles travel in a bundle along this pathway, through the tarsal tunnel. In the tunnel, the nerve splits into three different paths. One nerve (calcaneal) continues to the heel, the other two (medial and lateral plantar nerves) continue on to the bottom of the foot. The tarsal tunnel is made up of bone on the inside and the flexor retinaculum on the outside.
Patients complain typically of numbness in the foot, radiating to the big toe and the first 3 toes, pain
Pain
Pain is an unpleasant sensation often caused by intense or damaging stimuli such as stubbing a toe, burning a finger, putting iodine on a cut, and bumping the "funny bone."...
, burning, electrical sensations, and tingling over the base of the foot and the heel. Depending on the area of entrapment, other areas can be affected. If the entrapment is high, the entire foot can be affected as varying branches of the tibial nerve can become involved. Ankle pain is also present in patients who have high level entrapments. Inflammation or swelling can occur within this tunnel for a number of reasons. The flexor retinaculum has a limited ability to stretch, so increased pressure will eventually cause compression on the nerve within the tunnel. As pressure increases on the nerves, the blood flow decreases. Nerves respond with altered sensations like tingling and numbness. Fluid collects in the foot when standing and walking and this makes the condition worse. As small muscles lose their nerve supply they can create a cramping feeling.
Symptoms
Some of the symptoms are:- Pain and tingling in and around ankles and sometimes the toes
- Swelling of the feet
- Painful burning, tingling, or numb sensations in the lower legs. Pain worsens and spreads after standing for long periods; pain is worse with activity and is relieved by rest.
- Electric shock sensations
- Pain radiating up into the leg, and down into the arch, heel, and toes
- Hot and cold sensations in the feet
- A feeling as though the feet do not have enough padding
- Pain while operating automobiles
- Pain along the Posterior Tibial nerve path
- Burning sensation on the bottom of foot that radiates upward reaching the knee
- "Pins and needles"-type feeling and increased sensation on the feet
- A positive Tinel's sign
Tinel's sign
Tinel's sign
Tinel's sign is a way to detect irritated nerves. It is performed by lightly tapping over the nerve to elicit a sensation of tingling or "pins and needles" in the distribution of the nerve.It takes its name from French neurologist Jules Tinel .For example, in carpal tunnel syndrome where the...
is a tingling electric shock sensation that occurs when you tap over an affected nerve. The sensation usually travels into the foot but can also travel up the inner leg as well.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is based upon physical examination findings, which is typically diagnosed by a Family Physician, NeurologistNeurologist
A neurologist is a physician who specializes in neurology, and is trained to investigate, or diagnose and treat neurological disorders.Neurology is the medical specialty related to the human nervous system. The nervous system encompasses the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. A specialist...
, Orthopedist, Physiatrist, Chiropractor
Chiropractor
A Chiropractor, according to the Association of Chiropractic Colleges , "focuses on the relationship between the body's main structures – the skeleton, the muscles and the nerves – and the patient's health. Chiropractors believe that health can be improved and preserved by making adjustments to...
, podiatrist, physical therapist, or athletic trainer
Athletic trainer
An athletic trainer is a certified, health care professional who practices in the field of sports medicine. Athletic training has been recognized by the American Medical Association as an allied health care profession since 1990....
. Patients' pain history and a positive Tinel's sign
Tinel's sign
Tinel's sign is a way to detect irritated nerves. It is performed by lightly tapping over the nerve to elicit a sensation of tingling or "pins and needles" in the distribution of the nerve.It takes its name from French neurologist Jules Tinel .For example, in carpal tunnel syndrome where the...
are the first steps in evaluating the possibility of tarsal tunnel syndrome. X-ray
X-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
can rule out fracture. MRI can assess for space occupying lesions or other causes of nerve compression. Ultrasound
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is cyclic sound pressure with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is thus not separated from "normal" sound based on differences in physical properties, only the fact that humans cannot hear it. Although this limit varies from person to person, it is...
can assess for synovitis or ganglia. Nerve conduction studies alone are not diagnostic, but they may be used to confirm the suspected clinical diagnosis. Common causes include trauma, varicose veins
Varicose veins
Varicose veins are veins that have become enlarged and tortuous. The term commonly refers to the veins on the leg, although varicose veins can occur elsewhere. Veins have leaflet valves to prevent blood from flowing backwards . Leg muscles pump the veins to return blood to the heart, against the...
, neuropathy and space occupying anomalies within the tarsal tunnel.
A fellowship trained Neurologist or a Physiatrist usually administers nerve conduction tests. During this test, electrodes are placed at various spots along the nerves in the legs and feet. Both sensory and motor nerves are tested at different locations. Electrical impulses are sent through the nerve and the speed and intensity at which they travel is measured. If there is compression in the tunnel, this can be confirmed and pinpointed with this test. Many doctors do not feel that this test is necessarily a reliable way to rule out TTS. Some research indicates that nerve conduction tests will be normal in at least 50% of the cases. It is possible to have TTS without a positive nerve conduction test.
Cause
It is difficult to determine the exact cause of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome. It is important to attempt to determine the source of the problem. Treatment and the potential outcome of the treatment may depend on the cause. Anything that creates pressure in the Tarsal Tunnel can cause TTS. This would include benign tumors or cysts, bone spurs, inflammation of the tendon sheath, nerve ganglions, or swelling from a broken or sprained ankle. Varicose veins (that may or may not be visible) can also cause compression of the nerve. TTS is more common in athletes and other active people. These people put more stress on the tarsal tunnel area. Flat feet may cause an increase in pressure in the tunnel region and this can cause nerve compression. Those with lower back problems may have symptoms. Back problems with the L4, L5 and S1 regions are suspect and might suggest a "Double Crush" issue: one "crush" (nerve pinch or entrapment) in the lower back, and the second in the tunnel area. In some cases, TTS can simply be idiopathic.Treatment
Treatments typically include rest, manipulation, strengthening of tibialis anterior, tibialis posteriorTibialis posterior muscle
The Tibialis posterior is the most central of all the leg muscles, and is located in the posterior compartment of the leg.It is the key stabilizing muscle of the lower leg....
, peroneus and short toe flexors, casting with a walker boot, corticosteroid
Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex. Corticosteroids are involved in a wide range of physiologic systems such as stress response, immune response and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte...
and anesthetic injections, hot wax baths, wrapping, compression hose, and orthotics
Orthotics
Orthotics is a specialty within the medical field concerned with the design, manufacture and application of orthoses. An orthosis is an orthopedic device that supports or corrects the function of a limb or the torso...
. Medications may include various anti-inflammatories, Anaprox, Ultracet, and Neurontin and Lyrica. Lidocaine
Lidocaine
Lidocaine , Xylocaine, or lignocaine is a common local anesthetic and antiarrhythmic drug. Lidocaine is used topically to relieve itching, burning and pain from skin inflammations, injected as a dental anesthetic or as a local anesthetic for minor surgery.- History :Lidocaine, the first amino...
patches are also a treatment that helps some patients. If non-invasive treatment measures fail, surgery may be recommended to decompress the area.
The patient may not respond to conservative treatment and may need surgical treatment or tarsal tunnel release surgery. The incision is made behind the ankle bone and then down towards but not as far as the bottom of foot. The Posterior Tibial nerve is identified above the ankle. It is separated from the accompanying artery and vein and then followed into the tunnel. The nerves are released. Cysts or other space-occupying problems may be corrected at this time. If there is scarring within the nerve or branches, this is relieved by internal neurolysis. Neurolysis is when the outer layer of nerve wrapping is opened and the scar tissue is removed from within nerve. Following surgery, a large bulky cotton wrapping immobilizes the ankle joint without plaster. The dressing may be removed at the one week point and sutures at about three weeks.
Complications may include bleeding, infection, and unpredictable healing. The incision may open from swelling. There may be considerable pain and cramping. Regenerating nerve fibers may create shooting pains. Patients may have hot or cold sensations and may feel worse than before surgery. Crutches are usually recommended for the first two weeks, as well as elevation to minimize swelling. The nerve will grow at about one inch per month. One can expect to continue the healing process over the course of about one year.
Many patients report good results. Some, however, experience no improvement or a worsening of symptoms. In the Pfeiffer article (Los Angeles, 1996), fewer than 50% of the patients reported improvement, and there was a 13% complication rate. This is a staggering percentage of complications for what is a fairly superficial and minor surgical procedure.
Tarsal tunnel can greatly impact patients' quality of life. Depending on the severity, the ability to walk distances people normally take for granted (such as grocery shopping) may become compromised. Proper pain management and counseling is often required.

