TITAN2D
Encyclopedia
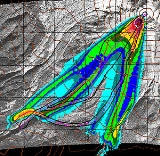
TITAN2D is a geoflow simulation software application, intended for geological researchers. It is distributed as free software
.
TITAN2D was developed for the purpose of simulating granular flows (primarily geological mass
flows such as debris avalanches and landslides) over
digital elevation model
s (DEM)s of natural terrain.
The code is designed to help scientists and civil protection authorities assess the
risk of, and mitigate, hazards due to dry debris flows and avalanches.
TITAN2D combines numerical simulations of a flow with digital elevation data of natural terrain
supported through a Geographical Information System (GIS) interface such as GRASS
.
TITAN2D is capable of multiprocessor runs.
A Message Passing Interface (MPI)
Application
Programming Interface (API)
allows
for parallel computing
on multiple processors, which effectively increases computational power, decreases computing time,
and allows for the use of large data sets.
Adaptive gridding
allows
for the concentration of computing power on regions of special
interest. Mesh refinement captures the complex flow features that occur at the leading edge
of a flow, as well as locations where rapid changes in topography induce large mass and momentum fluxes. Mesh
unrefinement is applied where solution values are relatively constant
or small to further improve computational efficiency.
TITAN2D requires an initial volume and shape estimate for the starting material, a basal friction angle, and an
internal friction angle for the simulated granular flow. The direct outputs of the program are
dynamic representations of a flow's depth and momentum. Secondary or derived outputs include flow velocity, and such field-observable quantities as run-up height, deposit thickness, and inundation area.
Coulomb continuum, a “shallow-water” granular flow. The conservation equations
for mass and momentum are solved with a Coulomb-type friction
term for the interactions between the grains of the media and between the granular material
and the basal surface. The resulting hyperbolic system
of equations is solved using a parallel, adaptive mesh,
Godunov scheme
. The basic form of the depth-averaged governing equations appear as follows.
The depth-averaged conservation of mass is:
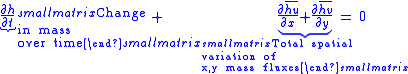
The depth-averaged x,y momentum balances are:
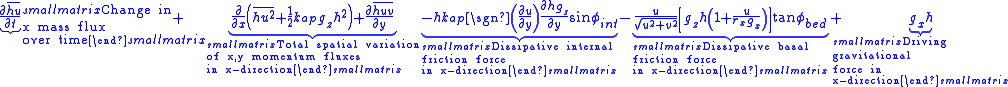

Free software
Free software, software libre or libre software is software that can be used, studied, and modified without restriction, and which can be copied and redistributed in modified or unmodified form either without restriction, or with restrictions that only ensure that further recipients can also do...
.
Overview
TITAN2D is a free software application developed by the Geophysical Mass Flow Group at the State University of New York (SUNY) at Buffalo.TITAN2D was developed for the purpose of simulating granular flows (primarily geological mass
flows such as debris avalanches and landslides) over
digital elevation model
Digital elevation model
A digital elevation model is a digital model or 3-D representation of a terrain's surface — commonly for a planet , moon, or asteroid — created from terrain elevation data....
s (DEM)s of natural terrain.
The code is designed to help scientists and civil protection authorities assess the
risk of, and mitigate, hazards due to dry debris flows and avalanches.
TITAN2D combines numerical simulations of a flow with digital elevation data of natural terrain
supported through a Geographical Information System (GIS) interface such as GRASS
GRASS GIS
GRASS GIS is a free, open source geographical information system capable of handling raster, topological vector, image processing, and graphic data....
.
TITAN2D is capable of multiprocessor runs.
A Message Passing Interface (MPI)
Message Passing Interface
Message Passing Interface is a standardized and portable message-passing system designed by a group of researchers from academia and industry to function on a wide variety of parallel computers...
Application
Programming Interface (API)
Application programming interface
An application programming interface is a source code based specification intended to be used as an interface by software components to communicate with each other...
allows
for parallel computing
Parallel computing
Parallel computing is a form of computation in which many calculations are carried out simultaneously, operating on the principle that large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which are then solved concurrently . There are several different forms of parallel computing: bit-level,...
on multiple processors, which effectively increases computational power, decreases computing time,
and allows for the use of large data sets.
Adaptive gridding
Adaptive mesh refinement
In numerical analysis, adaptive mesh refinement is a method of adaptive meshing. Central to any Eulerian method is the manner in which it discretizes the continuous domain of interest into a grid of many individual elements...
allows
for the concentration of computing power on regions of special
interest. Mesh refinement captures the complex flow features that occur at the leading edge
of a flow, as well as locations where rapid changes in topography induce large mass and momentum fluxes. Mesh
unrefinement is applied where solution values are relatively constant
or small to further improve computational efficiency.
TITAN2D requires an initial volume and shape estimate for the starting material, a basal friction angle, and an
internal friction angle for the simulated granular flow. The direct outputs of the program are
dynamic representations of a flow's depth and momentum. Secondary or derived outputs include flow velocity, and such field-observable quantities as run-up height, deposit thickness, and inundation area.
Mathematical Model
The TITAN2D program is based upon a depth-averaged model for an incompressibleCoulomb continuum, a “shallow-water” granular flow. The conservation equations
for mass and momentum are solved with a Coulomb-type friction
Mohr-Coulomb theory
Mohr–Coulomb theory is a mathematical model describing the response of brittle materials such as concrete, or rubble piles, to shear stress as well as normal stress. Most of the classical engineering materials somehow follow this rule in at least a portion of their shear failure envelope...
term for the interactions between the grains of the media and between the granular material
and the basal surface. The resulting hyperbolic system
Hyperbolic partial differential equation
In mathematics, a hyperbolic partial differential equation of order n is a partial differential equation that, roughly speaking, has a well-posed initial value problem for the first n−1 derivatives. More precisely, the Cauchy problem can be locally solved for arbitrary initial data along...
of equations is solved using a parallel, adaptive mesh,
Godunov scheme
Godunov's scheme
In numerical analysis and computational fluid dynamics, Godunov's scheme is a conservative numerical scheme, suggested by S. K. Godunov in 1959, for solving partial differential equations...
. The basic form of the depth-averaged governing equations appear as follows.
The depth-averaged conservation of mass is:
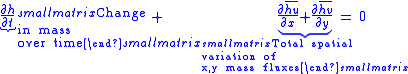
The depth-averaged x,y momentum balances are:
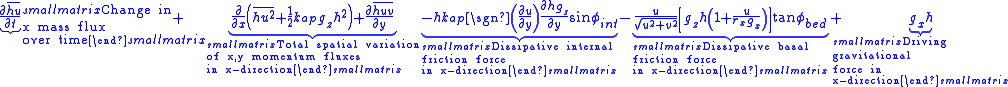

External links
- Geophysical Mass Flow Group (TITAN2D Distribution Site)

