
TAFIM
Encyclopedia
Technical Architecture Framework for Information Management (TAFIM) is a 1990s reference model for enterprise architecture
development, defined by the United States Department of Defense
(DoD) in 1986.
TAFIM provides enterprise-level guidance for the evolution of the DoD Technical infrastructure
. It identifies the services, standards, concepts, components, and configurations that can be used to guide the development of technical architectures that meet specific mission requirements.
It also subsumes the widely accepted Open Systems Interface (OSI) reference model within the network services and communications area.
This architecture, and associated model, is not a specific system design. Rather, it establishes a common vocabulary and defines a set of services and interfaces common to information systems. It identifies standards and guidelines in terms of the architecture services and interfaces. The architecture serves to facilitate the development of plans that will lead to interoperability between mission area applications, portability across mission areas and cost reductions through the use of common services.
The first draft of TAFIM was completed in 1991 with the TAFIM Technical Reference Model (TAFIM TRM). This technical reference model wanted to use open systems and new technologies available in the commercial market, to develop a DoD
-wide application. The TAFIM project has resulted in an eight-volume Information Technology
Architecture
"how-to" manual
, see image, published in 1996 by the Department of Defense.
The original development of TOGAF
Version 1 in 1995 was based on the Technical Architecture Framework for Information Management. The US Department of Defense gave The Open Group
explicit permission and encouragement to create TOGAF by building on the TAFIM, which itself was the result of many years of development effort and many millions of dollars of US Government investment.
The 1996 US DoD publication on TAFIM was the latest version published. TAFIM has been cancelled as a stand alone document in 1999. In 2000 the whole TAFIM concept and its regulations have been re-evaluated and found inconsistent with the newly developed DoDAF architecture direction. For this reason all references to TAFIM have been removed from DoD documentation since then.
The Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA) is responsible for developing, obtaining from commercial sources, and maintaining the compilation of Defense Information Infrastructure technical standards, and it is responsible for maintaining a Defense data dictionary system as a repository of data requirements and for facilitating the cross-functional coordination and approval of standard formats, definitions, etc. PSAs, the military services, Defense agencies, and Joint Chiefs of Staff are responsible for reaching agreement on the standards and approving them as DOD standard data elements. DISA is then responsible for disseminating the approved standard data elements for use throughout the Department.
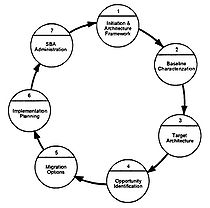 The Standards-Based Architecture (SBA) planning process. defined by the TAFIM, consists of seven distinct, but interdependent, phases. Each phase of the SBA process is intended to create specific deliverable products and or documents, that guide the subsequent phase. The seven phases are briefly outlined below.
The Standards-Based Architecture (SBA) planning process. defined by the TAFIM, consists of seven distinct, but interdependent, phases. Each phase of the SBA process is intended to create specific deliverable products and or documents, that guide the subsequent phase. The seven phases are briefly outlined below.
The entire enterprise, as defined, includes Work organization, Information, Application, and Technology. This leads to the four different views:
This gallery with the four views shows the interrelationship between the four views as mentioned earlier. In the view models of later Enterprise Architecture frameworks, such as the DoDAF the views are presented in layers and no longer interconnected.
Enterprise architecture
An enterprise architecture is a rigorous description of the structure of an enterprise, which comprises enterprise components , the externally visible properties of those components, and the relationships between them...
development, defined by the United States Department of Defense
United States Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense is the U.S...
(DoD) in 1986.
TAFIM provides enterprise-level guidance for the evolution of the DoD Technical infrastructure
Infrastructure
Infrastructure is basic physical and organizational structures needed for the operation of a society or enterprise, or the services and facilities necessary for an economy to function...
. It identifies the services, standards, concepts, components, and configurations that can be used to guide the development of technical architectures that meet specific mission requirements.
Overview
The "Technical Architecture Framework for Information Management" (TAFIM) defined:- a target common conceptual framework or reference modelReference ModelA reference model in systems, enterprise, and software engineering is a model of something that embodies the basic goal or idea of something and can then be looked at as a reference for various purposes.- Overview :...
for an information system infrastructure - and the specific applications that the information system must support.
It also subsumes the widely accepted Open Systems Interface (OSI) reference model within the network services and communications area.
This architecture, and associated model, is not a specific system design. Rather, it establishes a common vocabulary and defines a set of services and interfaces common to information systems. It identifies standards and guidelines in terms of the architecture services and interfaces. The architecture serves to facilitate the development of plans that will lead to interoperability between mission area applications, portability across mission areas and cost reductions through the use of common services.
History
The development of TAFIM started around 1986 at the US Defense Information Systems Agency/Center for Information Management. The first concept of TAFIM was derived from the NIST Application Portability Profile and the IEEE P1003.00SE models.The first draft of TAFIM was completed in 1991 with the TAFIM Technical Reference Model (TAFIM TRM). This technical reference model wanted to use open systems and new technologies available in the commercial market, to develop a DoD
United States Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense is the U.S...
-wide application. The TAFIM project has resulted in an eight-volume Information Technology
Information technology
Information technology is the acquisition, processing, storage and dissemination of vocal, pictorial, textual and numerical information by a microelectronics-based combination of computing and telecommunications...
Architecture
Enterprise architecture
An enterprise architecture is a rigorous description of the structure of an enterprise, which comprises enterprise components , the externally visible properties of those components, and the relationships between them...
"how-to" manual
User guide
A user guide or user's guide, also commonly known as a manual, is a technical communication document intended to give assistance to people using a particular system...
, see image, published in 1996 by the Department of Defense.
The original development of TOGAF
TOGAF
The Open Group Architecture Framework is a framework for enterprise architecture which provides a comprehensive approach for designing, planning, implementation, and governance of an enterprise information architecture...
Version 1 in 1995 was based on the Technical Architecture Framework for Information Management. The US Department of Defense gave The Open Group
The Open Group
The Open Group is a vendor and technology-neutral industry consortium, currently with over three hundred member organizations. It was formed in 1996 when X/Open merged with the Open Software Foundation...
explicit permission and encouragement to create TOGAF by building on the TAFIM, which itself was the result of many years of development effort and many millions of dollars of US Government investment.
The 1996 US DoD publication on TAFIM was the latest version published. TAFIM has been cancelled as a stand alone document in 1999. In 2000 the whole TAFIM concept and its regulations have been re-evaluated and found inconsistent with the newly developed DoDAF architecture direction. For this reason all references to TAFIM have been removed from DoD documentation since then.
DoD technical and data standards
Defense’s technical and data standards are designed to enable systems to easily interoperate and transfer information. Its standard definitions for data elements are intended to ensure that users of all Defense systems define the same data in the same way and have a common understanding of their meaning. Defense has developed or is in the process of defining technical standards in the 1990s with the Technical Architecture Framework for Information Management (TAFIM), the Joint Technical Architecture (JTA), and the Defense Information Infrastructure Common Operating Environment (DII COE).The Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA) is responsible for developing, obtaining from commercial sources, and maintaining the compilation of Defense Information Infrastructure technical standards, and it is responsible for maintaining a Defense data dictionary system as a repository of data requirements and for facilitating the cross-functional coordination and approval of standard formats, definitions, etc. PSAs, the military services, Defense agencies, and Joint Chiefs of Staff are responsible for reaching agreement on the standards and approving them as DOD standard data elements. DISA is then responsible for disseminating the approved standard data elements for use throughout the Department.
DoD Standards-Based Architecture Planning Process

- Phase 1, Initiation and Architecture Framework : The methodology begins with a proper initiation of the process within the host organization. This involves developing a set of strategic drivers for the organization. Further, a business model is reviewed or built to establish a strategic target operation model.
- Phase 2. Baseline Characterization : This grounding phase intends to determine the organization's current architecture. It is an assessment of the current environment, which results in a characterization in four key dimensions or views: work, information, application and technology.
- Phase 3. Target Architecture : The various views of the framework are modeled in terms of a desirable target architecture, usually 3 to 5 years in the future.
- Phase 4. Opportunity Identification : Step from the conceptual reflection to practical realities and implementation, with determination of development projects needed.
- Phase 5. Migration Options : Links the reality of the present with the desirability of the target architecture by establishing one or more plateaus representing practical migration stages.
- Phase 6. Implementation Planning : Phase results in a detailed implementation plan for the first plateau of the migration effort.
- Phase 7. Institutionalizing the ITA Process : This phase is intended to keep the architecture alive and well by continuously improving it.
Integrated Model of Architectural Views
The "Integrated Model of Four Architectural Views" is part of the target architecture, defined in the TAFIM. It gives a vision on the organization in all of its architectural views, especially the work architecture. The model, see figure, depicts an overall framework to develop the target architecture deliverable. Each view of the target architecture has some overlap with aspects of the other views. This overlap supports the argument that the model depicts the developing of a single, integrated architecture.The entire enterprise, as defined, includes Work organization, Information, Application, and Technology. This leads to the four different views:
- Work Organization View : The work view of architecture is developed by identifying specific classes of users within the business environment (e.g. executives, planners, administrators, engineers, recruiters), business location (e.g. headquarters, sales office, plant, warehouse); and the logical representation of the business functions that are required to deliver products and services.
- Information Management View : The information architecture of the enterprise will contain three levels of detail, subject areas, data groups, and data attributes.
- Application View : This view focuses on the opportunities to autonomate aspects of work and or the access to information needed to perform work.
- Technology Infrastructure View : This areas of architecture uses specific component-level models to provide the basic for linking the technology view of the architecture to the work, information, and application views. The linchpin is the generic application environment.
This gallery with the four views shows the interrelationship between the four views as mentioned earlier. In the view models of later Enterprise Architecture frameworks, such as the DoDAF the views are presented in layers and no longer interconnected.
See also
- Enterprise Architecture framework
- Enterprise Architecture PlanningEnterprise Architecture PlanningEnterprise Architecture Planning in Enterprise Architecture is the planning process of defining architectures for the use of information in support of the business and the plan for implementing those architectures.- Overview :...
- GERAM
- Open System Environment Reference ModelOpen System Environment Reference ModelOpen-system environment reference model or OSE reference model is one of the first reference models for enterprise architecture. It provides a framework for describing open system concepts and defining a lexicon of terms, that can be agreed upon generally by all interested parties...
- Technical architectureTechnical architectureTechnical architecture is one of several architecture domains that form the pillars of an enterprise architecture or solution architecture. It describes the structure and behaviour of the technology infrastructure of an enterprise, solution or system...
- Treasury Enterprise Architecture FrameworkTreasury Enterprise Architecture FrameworkTreasury Enterprise Architecture Framework is an Enterprise architecture framework for treasury, based on the Zachman Framework.It was developed by the US Department of the Treasury and published in July 2000.- Overview :...
- TOGAFTOGAFThe Open Group Architecture Framework is a framework for enterprise architecture which provides a comprehensive approach for designing, planning, implementation, and governance of an enterprise information architecture...

