
Syntactic predicate
Encyclopedia
A syntactic predicate specifies the syntactic validity of applying a production in a formal grammar
and is analogous to a semantic predicate
that specifies the semantic validity of applying a production. It is a simple and effective means of dramatically improving the recognition strength of an LL parser
by providing arbitrary lookahead. In their original implementation, syntactic predicates had the form “( α )?” and could only appear on the left edge of a production. The required syntactic condition α could be any valid context-free grammar fragment.
More formally, a syntactic predicate is a form of production intersection
, used in parser
specifications or in formal grammar
s. In this sense, the term predicate has the meaning of a mathematical indicator function. If p1 and p2, are production rules, the language
generated by both p1 and p2 is their set intersection.
As typically defined or implemented, syntactic predicates implicitly order the productions so that predicated productions specified earlier have higher precedence than predicated productions specified later within the same decision. This conveys an ability to disambiguate ambiguous productions because the programmer can simply specify which production should match.
Parsing expression grammar
s (PEGs), invented by Bryan Ford, extend these simple predicates by allowing "not predicates" and permitting a predicate to appear anywhere within a production. Morever, Ford invented packrat parsing to handle these grammars in linear time by employing memoization
, at the cost of heap space.
It is possible to support linear-time parsing of predicates as general as those allowed by PEGs, but reduce the memory cost associated with memoization by avoiding backtracking where some more efficient implementation of lookahead suffices. This approach is implemented by ANTLR
version 3, which uses Deterministic Finite Automata for lookahead; this may require testing a predicate in order to choose between transitions of the DFA (called "pred-LL(*)" parsing).
Syntactic predicates have been called multi-step matching, parse constraints, and simply predicates in various literature. (See References section below.) This article uses the term syntactic predicate throughout for consistency and to distinguish them from semantic predicates.
et al. show that the intersection of two regular language
s is also a regular language, which is to say that the regular languages are closed
under intersection
.
The intersection of a regular language
and a context-free language is also closed, and it has been known at least since Hartmanis that the intersection of two context-free languages is not necessarily a context-free language (and is thus not closed). This can be demonstrated easily using the canonical Type 1
language,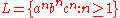 :
:
Let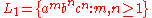 (Type 2)
(Type 2)
Let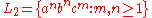 (Type 2)
(Type 2)
Let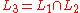
Given the strings
abcc, aabbc, and aaabbbccc, it is clear that the only string that belongs to both L1 and L2 (that is, the only one that produces a non-empty
intersection) is aaabbbccc.
Y also satisfies predicate Z":
S ::= a X
X ::= Y PRED Z
Y ::= a+ BNCN
Z ::= ANBN c+
BNCN ::= b [BNCN] c
ANBN ::= a [ANBN] b
Given the string aaaabbbccc, in the case where Y must be satisfied first (and assuming a greedy implementation), S will generate aX and X in turn will generate aaabbbccc, thereby generating aaaabbbccc. In the case where Z must be satisfied first, ANBN will fail to generate aaaabbb, and thus aaaabbbccc is not generated by the grammar. Moreover, if either Y or Z (or both) specify any action to be taken upon reduction (as would be the case in many parsers), the order that these productions match determines the order in which those side-effects occur. Formalisms that vary over time (such as adaptive grammar
s) may rely on these side effects
.
Parr & Quong give this example of a syntactic predicate:
stat: (declaration)? declaration
| expression
;
which is intended to satisfy the following informally stated constraints of C++
:
In the first production of rule stat, the syntactic predicate (declaration)? indicates
that declaration is the syntactic context that must be present for the rest of that production to succeed. We can interpret the use of (declaration)? as "I am not sure if
declaration will match; let me try it out and, if it does not match, I shall try the next
alternative." Thus, when encountering a valid declaration, the rule declaration will be
recognized twice—once as syntactic predicate and once during the actual parse to execute semantic actions.
Of note in the above example is the fact that any code triggered by the acceptance of the declaration production will only occur if the predicate is satisfied.
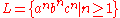 can be represented in various grammars and formalisms as follows:
can be represented in various grammars and formalisms as follows:
Parsing Expression Grammars
S ← &(A !b) a+ B !c
A ← a A? b
B ← b B? c
§-Calculus
Using a bound predicate:
S → {A}B
A → X 'c+'
X → 'a' [X] 'b'
B → 'a+' Y
Y → 'b' [Y] 'c'
Using two free predicates:
A → <'a+'>a <'b+'>b Ψ(a b)X <'c+'>c Ψ(b c)Y
X → 'a' [X] 'b'
Y → 'b' [Y] 'c'
Conjunctive Grammars
(Note: the following example actually generates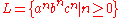 , but is included here because it is the example given by the inventor of conjunctive grammars.):
, but is included here because it is the example given by the inventor of conjunctive grammars.):
S → AB&DC
A → aA | ε
B → bBc | ε
C → cC | ε
D → aDb | ε
Perl 6 rules
rule S { > a+ <B> }
rule A { a ? b }
rule B { b <B>? c }
and grammar
formalisms
employ syntactic predicates:
ANTLR
(Parr & Quong)
Augmented Pattern Matcher (Balmas)
Parsing expression grammar
s (Ford)
§-Calculus (Jackson)
Perl 6 rules
ProGrammar (NorKen Technologies)
Conjunctive and Boolean
Grammars (Okhotin)
Formal grammar
A formal grammar is a set of formation rules for strings in a formal language. The rules describe how to form strings from the language's alphabet that are valid according to the language's syntax...
and is analogous to a semantic predicate
Predicate (grammar)
There are two competing notions of the predicate in theories of grammar. Traditional grammar tends to view a predicate as one of two main parts of a sentence, the other being the subject, which the predicate modifies. The other understanding of predicates is inspired from work in predicate calculus...
that specifies the semantic validity of applying a production. It is a simple and effective means of dramatically improving the recognition strength of an LL parser
LL parser
An LL parser is a top-down parser for a subset of the context-free grammars. It parses the input from Left to right, and constructs a Leftmost derivation of the sentence...
by providing arbitrary lookahead. In their original implementation, syntactic predicates had the form “( α )?” and could only appear on the left edge of a production. The required syntactic condition α could be any valid context-free grammar fragment.
More formally, a syntactic predicate is a form of production intersection
Intersection (set theory)
In mathematics, the intersection of two sets A and B is the set that contains all elements of A that also belong to B , but no other elements....
, used in parser
Parsing
In computer science and linguistics, parsing, or, more formally, syntactic analysis, is the process of analyzing a text, made of a sequence of tokens , to determine its grammatical structure with respect to a given formal grammar...
specifications or in formal grammar
Formal grammar
A formal grammar is a set of formation rules for strings in a formal language. The rules describe how to form strings from the language's alphabet that are valid according to the language's syntax...
s. In this sense, the term predicate has the meaning of a mathematical indicator function. If p1 and p2, are production rules, the language
Formal language
A formal language is a set of words—that is, finite strings of letters, symbols, or tokens that are defined in the language. The set from which these letters are taken is the alphabet over which the language is defined. A formal language is often defined by means of a formal grammar...
generated by both p1 and p2 is their set intersection.
As typically defined or implemented, syntactic predicates implicitly order the productions so that predicated productions specified earlier have higher precedence than predicated productions specified later within the same decision. This conveys an ability to disambiguate ambiguous productions because the programmer can simply specify which production should match.
Parsing expression grammar
Parsing expression grammar
A parsing expression grammar, or PEG, is a type of analytic formal grammar, i.e. it describes a formal language in terms of a set of rules for recognizing strings in the language...
s (PEGs), invented by Bryan Ford, extend these simple predicates by allowing "not predicates" and permitting a predicate to appear anywhere within a production. Morever, Ford invented packrat parsing to handle these grammars in linear time by employing memoization
Memoization
In computing, memoization is an optimization technique used primarily to speed up computer programs by having function calls avoid repeating the calculation of results for previously processed inputs...
, at the cost of heap space.
It is possible to support linear-time parsing of predicates as general as those allowed by PEGs, but reduce the memory cost associated with memoization by avoiding backtracking where some more efficient implementation of lookahead suffices. This approach is implemented by ANTLR
ANTLR
In computer-based language recognition, ANTLR , or ANother Tool for Language Recognition, is a parser generator that uses LL parsing. ANTLR is the successor to the Purdue Compiler Construction Tool Set , first developed in 1989, and is under active development...
version 3, which uses Deterministic Finite Automata for lookahead; this may require testing a predicate in order to choose between transitions of the DFA (called "pred-LL(*)" parsing).
Terminology
The term syntactic predicate was coined by Parr & Quong and differentiates this form of predicate from semantic predicates (also discussed in that paper).Syntactic predicates have been called multi-step matching, parse constraints, and simply predicates in various literature. (See References section below.) This article uses the term syntactic predicate throughout for consistency and to distinguish them from semantic predicates.
Formal Closure Properties
Bar-HillelYehoshua Bar-Hillel
Yehoshua Bar-Hillel was an Israeli philosopher, mathematician, and linguist at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, best known for his pioneering work in machine translation and formal linguistics.- Biography :...
et al. show that the intersection of two regular language
Regular language
In theoretical computer science and formal language theory, a regular language is a formal language that can be expressed using regular expression....
s is also a regular language, which is to say that the regular languages are closed
Closure (mathematics)
In mathematics, a set is said to be closed under some operation if performance of that operation on members of the set always produces a unique member of the same set. For example, the real numbers are closed under subtraction, but the natural numbers are not: 3 and 8 are both natural numbers, but...
under intersection
Intersection (set theory)
In mathematics, the intersection of two sets A and B is the set that contains all elements of A that also belong to B , but no other elements....
.
The intersection of a regular language
Regular language
In theoretical computer science and formal language theory, a regular language is a formal language that can be expressed using regular expression....
and a context-free language is also closed, and it has been known at least since Hartmanis that the intersection of two context-free languages is not necessarily a context-free language (and is thus not closed). This can be demonstrated easily using the canonical Type 1
Chomsky hierarchy
Within the field of computer science, specifically in the area of formal languages, the Chomsky hierarchy is a containment hierarchy of classes of formal grammars....
language,
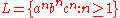 :
:Let
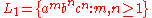 (Type 2)
(Type 2)Let
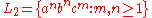 (Type 2)
(Type 2)Let
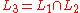
Given the strings
String (computer science)
In formal languages, which are used in mathematical logic and theoretical computer science, a string is a finite sequence of symbols that are chosen from a set or alphabet....
abcc, aabbc, and aaabbbccc, it is clear that the only string that belongs to both L1 and L2 (that is, the only one that produces a non-empty
Empty string
In computer science and formal language theory, the empty string is the unique string of length zero. It is denoted with λ or sometimes Λ or ε....
intersection) is aaabbbccc.
Other Considerations
In most formalisms that use syntactic predicates, the syntax of the predicate is noncommutative, which is to say that the operation of predication is ordered. For instance, using the above example, consider the following pseudo-grammar, where X ::= Y PRED Z is understood to mean: "Y produces X if and only ifIf and only if
In logic and related fields such as mathematics and philosophy, if and only if is a biconditional logical connective between statements....
Y also satisfies predicate Z":
S ::= a X
X ::= Y PRED Z
Y ::= a+ BNCN
Z ::= ANBN c+
BNCN ::= b [BNCN] c
ANBN ::= a [ANBN] b
Given the string aaaabbbccc, in the case where Y must be satisfied first (and assuming a greedy implementation), S will generate aX and X in turn will generate aaabbbccc, thereby generating aaaabbbccc. In the case where Z must be satisfied first, ANBN will fail to generate aaaabbb, and thus aaaabbbccc is not generated by the grammar. Moreover, if either Y or Z (or both) specify any action to be taken upon reduction (as would be the case in many parsers), the order that these productions match determines the order in which those side-effects occur. Formalisms that vary over time (such as adaptive grammar
Adaptive grammar
An adaptive grammar is a formal grammar that explicitly provides mechanisms within the formalism to allow its own production rules to be manipulated.-Overview:John N...
s) may rely on these side effects
Side effect (computer science)
In computer science, a function or expression is said to have a side effect if, in addition to returning a value, it also modifies some state or has an observable interaction with calling functions or the outside world...
.
Examples of Use
ANTLRParr & Quong give this example of a syntactic predicate:
stat: (declaration)? declaration
| expression
;
which is intended to satisfy the following informally stated constraints of C++
C++
C++ is a statically typed, free-form, multi-paradigm, compiled, general-purpose programming language. It is regarded as an intermediate-level language, as it comprises a combination of both high-level and low-level language features. It was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup starting in 1979 at Bell...
:
- If it looks like a declaration, it is; otherwise
- if it looks like an expression, it is; otherwise
- it is a syntax error.
In the first production of rule stat, the syntactic predicate (declaration)? indicates
that declaration is the syntactic context that must be present for the rest of that production to succeed. We can interpret the use of (declaration)? as "I am not sure if
declaration will match; let me try it out and, if it does not match, I shall try the next
alternative." Thus, when encountering a valid declaration, the rule declaration will be
recognized twice—once as syntactic predicate and once during the actual parse to execute semantic actions.
Of note in the above example is the fact that any code triggered by the acceptance of the declaration production will only occur if the predicate is satisfied.
Canonical Examples
The language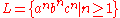 can be represented in various grammars and formalisms as follows:
can be represented in various grammars and formalisms as follows:Parsing Expression Grammars
S ← &(A !b) a+ B !c
A ← a A? b
B ← b B? c
§-Calculus
Using a bound predicate:
S → {A}B
A → X 'c+'
X → 'a' [X] 'b'
B → 'a+' Y
Y → 'b' [Y] 'c'
Using two free predicates:
A → <'a+'>a <'b+'>b Ψ(a b)X <'c+'>c Ψ(b c)Y
X → 'a' [X] 'b'
Y → 'b' [Y] 'c'
Conjunctive Grammars
(Note: the following example actually generates
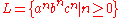 , but is included here because it is the example given by the inventor of conjunctive grammars.):
, but is included here because it is the example given by the inventor of conjunctive grammars.):S → AB&DC
A → aA | ε
B → bBc | ε
C → cC | ε
D → aDb | ε
Perl 6 rules
rule S {
rule A { a ? b }
rule B { b <B>? c }
Parsers/Formalisms Using Some Form of Syntactic Predicate
Although by no means an exhaustive list, the following parsersParsing
In computer science and linguistics, parsing, or, more formally, syntactic analysis, is the process of analyzing a text, made of a sequence of tokens , to determine its grammatical structure with respect to a given formal grammar...
and grammar
Formal grammar
A formal grammar is a set of formation rules for strings in a formal language. The rules describe how to form strings from the language's alphabet that are valid according to the language's syntax...
formalisms
Formal system
In formal logic, a formal system consists of a formal language and a set of inference rules, used to derive an expression from one or more other premises that are antecedently supposed or derived . The axioms and rules may be called a deductive apparatus...
employ syntactic predicates:
ANTLR
ANTLR
In computer-based language recognition, ANTLR , or ANother Tool for Language Recognition, is a parser generator that uses LL parsing. ANTLR is the successor to the Purdue Compiler Construction Tool Set , first developed in 1989, and is under active development...
(Parr & Quong)
- As originally implemented, syntactic predicates sit on the leftmost edge of a production such that the productionFormal grammarA formal grammar is a set of formation rules for strings in a formal language. The rules describe how to form strings from the language's alphabet that are valid according to the language's syntax...
to the right of the predicate is attempted if and only if the syntactic predicate first accepts the next portion of the input stream. Although ordered, the predicates are checked first, with parsing of a clause continuing if and only if the predicate is satisified, and semantic actions only occurring in non-predicates.
Augmented Pattern Matcher (Balmas)
- Balmas refers to syntactic predicates as "multi-step matching" in her paper on APM. As an APM parser parses, it can bind substrings to a variable, and later check this variable against other rules, continuing to parse if and only if that substring is acceptable to further rules.
Parsing expression grammar
Parsing expression grammar
A parsing expression grammar, or PEG, is a type of analytic formal grammar, i.e. it describes a formal language in terms of a set of rules for recognizing strings in the language...
s (Ford)
- Ford's PEGs have syntactic predicates expressed as the and-predicate and the not-predicate.
§-Calculus (Jackson)
- In the §-Calculus, syntactic predicates are originally called simply predicates, but are later divided into bound and free forms, each with different input properties.
Perl 6 rules
Perl 6 rules
Perl 6 rules are the regular expression, pattern matching and general-purpose parsing facility of Perl 6, and are a core part of the language. Since Perl's pattern-matching constructs have exceeded the capabilities of formal regular expressions for some time, Perl 6 documentation refers to them...
- Perl 6Perl 6Perl 6 is a major revision to the Perl programming language. It is still in development, as a specification from which several interpreter and compiler implementations are being written. It is introducing elements of many modern and historical languages. Perl 6 is intended to have many...
introduces a generalized tool for describing a grammar called rules, which are an extension of PerlPerlPerl is a high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming language. Perl was originally developed by Larry Wall in 1987 as a general-purpose Unix scripting language to make report processing easier. Since then, it has undergone many changes and revisions and become widely popular...
5's regular expression syntax. Predicates are introduced via a lookahead mechanism called before, either with "
ProGrammar (NorKen Technologies)
- ProGrammar's GDL (Grammar Definition Language) makes use of syntactic predicates in a form called parse constraints.
Conjunctive and Boolean
Boolean grammar
Boolean grammars are a class of formal grammars studied in formal language theory. They extend the basic type of grammars, the context-free grammars, with conjunction and negation operations...
Grammars (Okhotin)
- Conjunctive grammars, first introduced by Okhotin, introduce the explicit notion of conjunctionLogical conjunctionIn logic and mathematics, a two-place logical operator and, also known as logical conjunction, results in true if both of its operands are true, otherwise the value of false....
-as-predication. Later treatment of conjunctive and boolean grammars is the most thorough treatment of this formalism to date.
External links
- ANTLR site
- Paper: "ANTLR: A Predicated Parser-Generator" (PDF)
- Alexander Okhotin's Conjunctive Grammars Page
- Alexander Okhotin's Boolean Grammars Page
- The Packrat Parsing and Parsing Expression Grammars Page
- Thesis: Packrat Parsing: a Practical Linear-Time Algorithm with Backtracking (PDF and Postscript, as well as various source files)

