
Swain equation
Encyclopedia
The Swain equation relates the kinetic isotope effect
for the proton
/tritium
combination with that of the proton
/deuterium
combination according to:
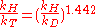
where kH,D,T are the reaction rate constants for the protonated, deuterated and tritiated reactants respectively.The Swain equation relates the kinetic isotope effect for the proton/tritium combination with that of the proton/deuterium combination according to: where kH,D,T is the reaction rate constant for the protonated, deuterated and tritiated reactants.
Kinetic isotope effect
The kinetic isotope effect is the ratio of reaction rates of two different isotopically labeled molecules in a chemical reaction. It is also called "isotope fractionation," although this term is somewhat broader in meaning...
for the proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
/tritium
Tritium
Tritium is a radioactive isotope of hydrogen. The nucleus of tritium contains one proton and two neutrons, whereas the nucleus of protium contains one proton and no neutrons...
combination with that of the proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
/deuterium
Deuterium
Deuterium, also called heavy hydrogen, is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen. It has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom in of hydrogen . Deuterium accounts for approximately 0.0156% of all naturally occurring hydrogen in Earth's oceans, while the most common isotope ...
combination according to:
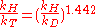
where kH,D,T are the reaction rate constants for the protonated, deuterated and tritiated reactants respectively.The Swain equation relates the kinetic isotope effect for the proton/tritium combination with that of the proton/deuterium combination according to: where kH,D,T is the reaction rate constant for the protonated, deuterated and tritiated reactants.

