
Supplee's paradox
Encyclopedia
In relativistic
physics
, Supplee's paradox (also called the submarine paradox) arises when considering the buoyant force exerted on a relativistic bullet immersed in a fluid subject to an ambient gravitational field
. If a bullet with neutral buoyancy passes through a fluid at a relativistic speed, will its increased mass in the fluid's frame of reference cause it to sink, or will the fluid's increased mass in the bullet's frame of reference cause it to rise? The paradox was apparently first discussed by James M. Supplee.
and viscosity
, and even to assume that the fluid has constant density
.
Consider a small object immersed in a container of fluid subject to a uniform gravitational field. Then the object will be subject to a net downward gravitational force. Compare this with the net downward gravitational force on an equal volume of the fluid. If the object is less dense than the fluid, the difference between these two vectors is an upward pointing vector, the buoyant force, and the object will rise. If things are the other way around, it will sink. If the object and the fluid have equal density, we say that the object has neutral buoyancy and it will neither rise nor sink.
In the rest frame of the fluid, if the bullet moves at speed , then according to the kinematic laws of special relativity
, then according to the kinematic laws of special relativity
, its density (as measured in the frame of the fluid) increases by the square of the Lorentz Factor
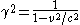 . Therefore, a rapidly moving bullet should sink.
. Therefore, a rapidly moving bullet should sink.
In the rest frame of the bullet, the density of fluid, as measured in the frame of the bullet, increases by the same factor, so the moving bullet should rise.
; when it is treated properly, the paradox disappears.
Supplee himself concluded that the paradox can be resolved by noting that in the frame of the bullet, the shape of the container of fluid is altered (viz. the sea floor is curved upwards). Given certain assumptions about how to treat the gravitational force, he argued that the bullet sinks with acceleration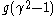 , where g is the acceleration due to gravity (assumed to be uniform over the scale of the thought experiment) and
, where g is the acceleration due to gravity (assumed to be uniform over the scale of the thought experiment) and 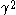 is the factor mentioned above.
is the factor mentioned above.
The paradox has also been studied by George Matsas, who used mathematical methods from general relativity
to remove Supplee's assumptions. In particular, he modeled the situation using a Rindler chart
. Matsas concluded that the paradox can be resolved by noting that in the frame of the fluid, the shape of the bullet is altered, and derived the same result which had been obtained by Supplee. Matsas has applied a similar analysis to shed light on certain questions involving the thermodynamics
of black hole
s.
Theory of relativity
The theory of relativity, or simply relativity, encompasses two theories of Albert Einstein: special relativity and general relativity. However, the word relativity is sometimes used in reference to Galilean invariance....
physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, Supplee's paradox (also called the submarine paradox) arises when considering the buoyant force exerted on a relativistic bullet immersed in a fluid subject to an ambient gravitational field
Gravitational field
The gravitational field is a model used in physics to explain the existence of gravity. In its original concept, gravity was a force between point masses...
. If a bullet with neutral buoyancy passes through a fluid at a relativistic speed, will its increased mass in the fluid's frame of reference cause it to sink, or will the fluid's increased mass in the bullet's frame of reference cause it to rise? The paradox was apparently first discussed by James M. Supplee.
A bit about buoyancy
To simplify the analysis, it is customary to neglect dragDrag (physics)
In fluid dynamics, drag refers to forces which act on a solid object in the direction of the relative fluid flow velocity...
and viscosity
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
, and even to assume that the fluid has constant density
Density
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
.
Consider a small object immersed in a container of fluid subject to a uniform gravitational field. Then the object will be subject to a net downward gravitational force. Compare this with the net downward gravitational force on an equal volume of the fluid. If the object is less dense than the fluid, the difference between these two vectors is an upward pointing vector, the buoyant force, and the object will rise. If things are the other way around, it will sink. If the object and the fluid have equal density, we say that the object has neutral buoyancy and it will neither rise nor sink.
Statement of the paradox
It is simplest to assume that at rest, the bullet has neutral buoyancy.In the rest frame of the fluid, if the bullet moves at speed
 , then according to the kinematic laws of special relativity
, then according to the kinematic laws of special relativitySpecial relativity
Special relativity is the physical theory of measurement in an inertial frame of reference proposed in 1905 by Albert Einstein in the paper "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies".It generalizes Galileo's...
, its density (as measured in the frame of the fluid) increases by the square of the Lorentz Factor
Lorentz factor
The Lorentz factor or Lorentz term appears in several equations in special relativity, including time dilation, length contraction, and the relativistic mass formula. Because of its ubiquity, physicists generally represent it with the shorthand symbol γ . It gets its name from its earlier...
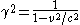 . Therefore, a rapidly moving bullet should sink.
. Therefore, a rapidly moving bullet should sink.In the rest frame of the bullet, the density of fluid, as measured in the frame of the bullet, increases by the same factor, so the moving bullet should rise.
Resolution of the paradox
The resolution comes down to observing that the gravitational force lies outside the domain of kinematicsKinematics
Kinematics is the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of bodies and systems without consideration of the forces that cause the motion....
; when it is treated properly, the paradox disappears.
Supplee himself concluded that the paradox can be resolved by noting that in the frame of the bullet, the shape of the container of fluid is altered (viz. the sea floor is curved upwards). Given certain assumptions about how to treat the gravitational force, he argued that the bullet sinks with acceleration
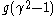 , where g is the acceleration due to gravity (assumed to be uniform over the scale of the thought experiment) and
, where g is the acceleration due to gravity (assumed to be uniform over the scale of the thought experiment) and 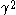 is the factor mentioned above.
is the factor mentioned above.The paradox has also been studied by George Matsas, who used mathematical methods from general relativity
General relativity
General relativity or the general theory of relativity is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1916. It is the current description of gravitation in modern physics...
to remove Supplee's assumptions. In particular, he modeled the situation using a Rindler chart
Rindler coordinates
In relativistic physics, the Rindler coordinate chart is an important and useful coordinate chart representing part of flat spacetime, also called the Minkowski vacuum. The Rindler chart was introduced by Wolfgang Rindler. The Rindler coordinate system or frame describes a uniformly accelerating...
. Matsas concluded that the paradox can be resolved by noting that in the frame of the fluid, the shape of the bullet is altered, and derived the same result which had been obtained by Supplee. Matsas has applied a similar analysis to shed light on certain questions involving the thermodynamics
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a physical science that studies the effects on material bodies, and on radiation in regions of space, of transfer of heat and of work done on or by the bodies or radiation...
of black hole
Black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime from which nothing, not even light, can escape. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass will deform spacetime to form a black hole. Around a black hole there is a mathematically defined surface called an event horizon that...
s.
See also
- Bell's spaceship paradoxBell's spaceship paradoxBell's spaceship paradox is a thought experiment in special relativity involving accelerated spaceships and strings. The results of this thought experiment are for many people paradoxical. While J. S. Bell's 1976 version of the paradox is the most widely known, it was first designed by E. Dewan and M...
- Ehrenfest paradoxEhrenfest paradoxThe Ehrenfest paradox concerns the rotation of a "rigid" disc in the theory of relativity.In its original formulation as presented by Paul Ehrenfest 1909 in the Physikalische Zeitschrift, it discusses an ideally rigid cylinder that is made to rotate about its axis of symmetry...
- Ladder paradoxLadder paradoxThe ladder paradox is a thought experiment in special relativity. It involves a ladder travelling horizontally and undergoing a length contraction, the result of which being that it can fit into a much smaller garage...
- Physical paradoxPhysical paradoxA physical paradox is an apparent contradiction in physical descriptions of the universe. While many physical paradoxes have accepted resolutions, others defy resolution and may indicate flaws in theory...
- Twins paradox
External links
- Light Speed Submarine - article about the paradox in Physical Review Focus

