
Sugar phosphates
Encyclopedia
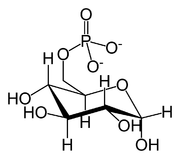
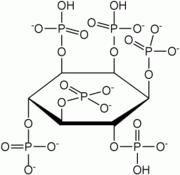
Examples include:
- DihydroxyacetonephosphateDihydroxyacetonephosphateDihydroxyacetone phosphate is a biochemical compound involved in many reactions, from the Calvin cycle in plants to the ether-lipid biosynthesis process in Leishmania mexicana. Its major biochemical role is in the glycolysis metabolic pathway...
- Glucose-6-phosphateGlucose-6-phosphateGlucose 6-phosphate is glucose sugar phosphorylated on carbon 6. This compound is very common in cells as the vast majority of glucose entering a cell will become phosphorylated in this way....
- Phytic acidPhytic acidPhytic acid is the principal storage form of phosphorus in many plant tissues, especially bran and seeds. Phytate is not digestible to humans or nonruminant animals, however, so it is not a source of either inositol or phosphate if eaten directly...
- Teichoic acidTeichoic acidTeichoic acids are bacterial polysaccharides of glycerol phosphate or ribitol phosphate linked via phosphodiester bonds.-Location and structure:...

