
String galvanometer
Encyclopedia
The string galvanometer was one of the earliest instruments capable of detecting and recording the very small electrical
currents produced by the human heart
and provided the first practical Electrocardiogram
(ECG). The original machines achieved "such amazing technical perfection that many modern day electrocardiographs do not attain equally reliable and undistorted recordings".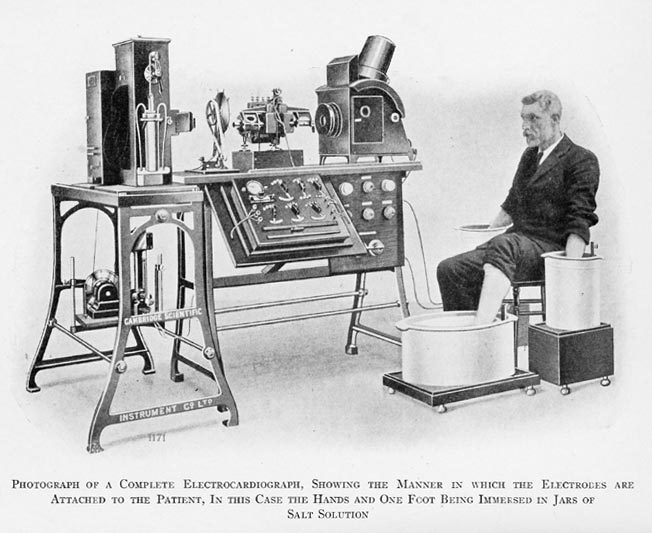
to measure the heart’s electrical activity, but this device was unable to produce results of a diagnostic level. Willem Einthoven
invented the string galvanometer in the early 20th century, publishing the first registration of its use to record an electrocardiogram in a Festschrift
book in 1902. The first human electrocardiogram was recorded in 1887, however it was not until 1901 that a quantifiable result was obtained from the string galvanometer . He was awarded the Nobel prize in Physiology or Medicine
in 1924 for his work.
filament of negligible
mass that conducted the electrical currents from the heart. This filament was acted upon by powerful electromagnet
s positioned either side of it, which caused sideways displacement of the filament in proportion to the current carried due to the electromagnetic field
. The movement in the filament was heavily magnified and projected through a thin slot onto a moving photographic plate .
The filament was originally made by drawing out a filament of glass from a crucible of molten glass. To produce a sufficiently thin and long filament an arrow
was fired across the room so that it dragged the filament from the molten glass. The filament so produced was then coated with silver
to provide the conductive pathway for the current. By tightening or loosening the filament it is possible to very accurately regulate the sensitivity of the galvanometer.
The original machine required water cooling for the powerful electromagnets, required 5 operators and weighed some 600 lb.
Electricity
Electricity is a general term encompassing a variety of phenomena resulting from the presence and flow of electric charge. These include many easily recognizable phenomena, such as lightning, static electricity, and the flow of electrical current in an electrical wire...
currents produced by the human heart
Heart
The heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
and provided the first practical Electrocardiogram
Electrocardiogram
Electrocardiography is a transthoracic interpretation of the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time, as detected by electrodes attached to the outer surface of the skin and recorded by a device external to the body...
(ECG). The original machines achieved "such amazing technical perfection that many modern day electrocardiographs do not attain equally reliable and undistorted recordings".

History
Previous to the string galvanometer, scientists were using a machine called the capillary electrometerElectrometer
An electrometer is an electrical instrument for measuring electric charge or electrical potential difference. There are many different types, ranging from historical hand-made mechanical instruments to high-precision electronic devices...
to measure the heart’s electrical activity, but this device was unable to produce results of a diagnostic level. Willem Einthoven
Willem Einthoven
Willem Einthoven was a Dutch doctor and physiologist. He invented the first practical electrocardiogram in 1903 and received the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1924 for it....
invented the string galvanometer in the early 20th century, publishing the first registration of its use to record an electrocardiogram in a Festschrift
Festschrift
In academia, a Festschrift , is a book honoring a respected person, especially an academic, and presented during his or her lifetime. The term, borrowed from German, could be translated as celebration publication or celebratory writing...
book in 1902. The first human electrocardiogram was recorded in 1887, however it was not until 1901 that a quantifiable result was obtained from the string galvanometer . He was awarded the Nobel prize in Physiology or Medicine
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine administered by the Nobel Foundation, is awarded once a year for outstanding discoveries in the field of life science and medicine. It is one of five Nobel Prizes established in 1895 by Swedish chemist Alfred Nobel, the inventor of dynamite, in his will...
in 1924 for his work.
How the string galvanometer works
Einthoven's invention consisted of a very long (several meters) silver-coated quartzQuartz
Quartz is the second-most-abundant mineral in the Earth's continental crust, after feldspar. It is made up of a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall formula SiO2. There are many different varieties of quartz,...
filament of negligible
Negligible
Negligible refers to the quantities so small that they can be ignored when studying the larger effect. Although related to the more mathematical concepts of infinitesimal, the idea of negligibility is particularly useful in practical disciplines like physics, chemistry, mechanical and electronic...
mass that conducted the electrical currents from the heart. This filament was acted upon by powerful electromagnet
Electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by the flow of electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off...
s positioned either side of it, which caused sideways displacement of the filament in proportion to the current carried due to the electromagnetic field
Electromagnetic field
An electromagnetic field is a physical field produced by moving electrically charged objects. It affects the behavior of charged objects in the vicinity of the field. The electromagnetic field extends indefinitely throughout space and describes the electromagnetic interaction...
. The movement in the filament was heavily magnified and projected through a thin slot onto a moving photographic plate .
The filament was originally made by drawing out a filament of glass from a crucible of molten glass. To produce a sufficiently thin and long filament an arrow
Arrow
An arrow is a shafted projectile that is shot with a bow. It predates recorded history and is common to most cultures.An arrow usually consists of a shaft with an arrowhead attached to the front end, with fletchings and a nock at the other.- History:...
was fired across the room so that it dragged the filament from the molten glass. The filament so produced was then coated with silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
to provide the conductive pathway for the current. By tightening or loosening the filament it is possible to very accurately regulate the sensitivity of the galvanometer.
The original machine required water cooling for the powerful electromagnets, required 5 operators and weighed some 600 lb.

