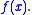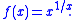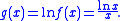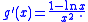Steiner's problem
Encyclopedia
Steiner's problem is the problem of finding the maximum
of the function
It is named after Jakob Steiner
.
The maximum is at , where e denotes the base of natural logarithms
, where e denotes the base of natural logarithms
. One can determine that by solving the equivalent problem of maximizing
The derivative
of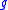 can be calculated to be
can be calculated to be
It follows that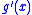 is positive for
is positive for 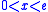 and negative for
and negative for 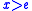 , which implies that
, which implies that 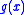 (and therefore
(and therefore 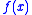 ) increases for
) increases for 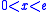 and decreases for
and decreases for 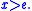 Thus,
Thus,  is the unique global maximum of
is the unique global maximum of 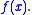
Maxima and minima
In mathematics, the maximum and minimum of a function, known collectively as extrema , are the largest and smallest value that the function takes at a point either within a given neighborhood or on the function domain in its entirety .More generally, the...
of the function
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function associates one quantity, the argument of the function, also known as the input, with another quantity, the value of the function, also known as the output. A function assigns exactly one output to each input. The argument and the value may be real numbers, but they can...
It is named after Jakob Steiner
Jakob Steiner
Jakob Steiner was a Swiss mathematician who worked primarily in geometry.-Personal and professional life:...
.
The maximum is at
 , where e denotes the base of natural logarithms
, where e denotes the base of natural logarithmsE (mathematical constant)
The mathematical constant ' is the unique real number such that the value of the derivative of the function at the point is equal to 1. The function so defined is called the exponential function, and its inverse is the natural logarithm, or logarithm to base...
. One can determine that by solving the equivalent problem of maximizing
The derivative
Derivative
In calculus, a branch of mathematics, the derivative is a measure of how a function changes as its input changes. Loosely speaking, a derivative can be thought of as how much one quantity is changing in response to changes in some other quantity; for example, the derivative of the position of a...
of
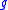 can be calculated to be
can be calculated to beIt follows that
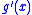 is positive for
is positive for 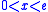 and negative for
and negative for  , which implies that
, which implies that 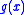 (and therefore
(and therefore 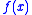 ) increases for
) increases for 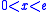 and decreases for
and decreases for  Thus,
Thus,  is the unique global maximum of
is the unique global maximum of