
Split normal distribution
Encyclopedia
In probability theory
and statistics
, the split normal distribution also known as the two-piece normal distribution results from joining at the mode the corresponding halves of two normal distributions with the same mode but different variances. The split normal distribution was introduced by Gibbons and Mylroie and by John.
of the split normal distribution is given by
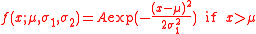
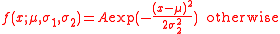
where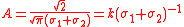
where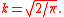
The split-normal distribution has the following moments:
mean: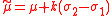
variance: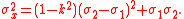
The third central moment is given by: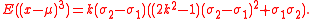
The sign of the third central moment is determined by the dfference in sigmas (the second factor in the formula above). If this difference is positive, the distribution is skewed to the right and if it is negative, to the left.
In a special case where , the split normal density collapses to the density of the Normal distribution.
, the split normal density collapses to the density of the Normal distribution.
Other properties of the split normal density have been discussed by Johnson et al. and Julio.
, a representation of the inflation
forecast distribution reported by inflation targeting
central banks around the globe.
Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with analysis of random phenomena. The central objects of probability theory are random variables, stochastic processes, and events: mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic events or measured quantities that may either be single...
and statistics
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, the split normal distribution also known as the two-piece normal distribution results from joining at the mode the corresponding halves of two normal distributions with the same mode but different variances. The split normal distribution was introduced by Gibbons and Mylroie and by John.
Definition
The probability density functionProbability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
of the split normal distribution is given by
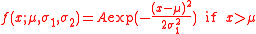
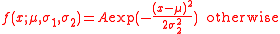
where
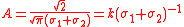
where
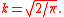
Moments and other properties
The parameter μ is the mode of the distribution (unlike for the Normal distribution, where μ is both mode, mean and median).The split-normal distribution has the following moments:
mean:
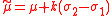
variance:
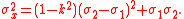
The third central moment is given by:
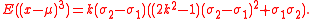
The sign of the third central moment is determined by the dfference in sigmas (the second factor in the formula above). If this difference is positive, the distribution is skewed to the right and if it is negative, to the left.
In a special case where
 , the split normal density collapses to the density of the Normal distribution.
, the split normal density collapses to the density of the Normal distribution.Other properties of the split normal density have been discussed by Johnson et al. and Julio.
Applications
The split normal distribution has been used mainly in econometrics and time series. A remarkable area of application is the construction of the fan chartFan chart (time series)
In time series analysis, a fan chart is a chart that joins a simple line chart for observed past data, by showing ranges for possible values of future data together with a line showing a central estimate or most likely value for the future outcomes...
, a representation of the inflation
Inflation
In economics, inflation is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation also reflects an erosion in the purchasing power of money – a...
forecast distribution reported by inflation targeting
Inflation targeting
Inflation targeting is an economic policy in which a central bank estimates and makes public a projected, or "target", inflation rate and then attempts to steer actual inflation towards the target through the use of interest rate changes and other monetary tools.Because interest rates and the...
central banks around the globe.

