
Split horizon
Encyclopedia
In computer networking, split-horizon route advertisement is a method of preventing routing loop
s in distance-vector routing protocol
s by prohibiting a router from advertising a route back onto the interface from which it was learned.
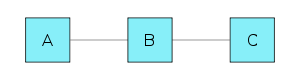 According to the split-horizon rule, node A does not advertise its route for C (namely A to B to C) back to B. On the surface, this seems redundant since B will never route via node A because the route costs more than the direct route from B to C. However, if the link between B and C goes down, and B had received a route from A, B could end up using that route via A. A would send the packet right back to B, creating a loop. With the split-horizon rule in place, this particular loop scenario cannot happen, improving convergence time in complex, highly-redundant environments.
According to the split-horizon rule, node A does not advertise its route for C (namely A to B to C) back to B. On the surface, this seems redundant since B will never route via node A because the route costs more than the direct route from B to C. However, if the link between B and C goes down, and B had received a route from A, B could end up using that route via A. A would send the packet right back to B, creating a loop. With the split-horizon rule in place, this particular loop scenario cannot happen, improving convergence time in complex, highly-redundant environments.
There are scenarios where the split-horizon rule may fail.
Suppose 6 nodes(A,B,C,D,E,F) are each connected to every other node. The lowest cost routes will establish over time. Now if one of the nodes fails. Split-horizon only protects each node from where their current path is received from. But the same information received from the other nodes will be transmitted as well.
If A connects to E via B and C. And if D connects to E via A->B->C. Suppose B-C fail. A will not advertise its route to E to B directly due to the split-horizon rule. However, as each node is connected to each other. D will advertise the route to E to B (D->A->B->C-E). The split horizon rule stops D from advertising the route to A. Not to B.
Such scenarios and multiple links exist in practical networks. And it is the network administrator who needs to work out such intricacies.
The main disadvantage of poison reverse is that it can significantly increase the size of routing announcements in certain fairly common network topologies, but it allows to improve the overall efficiency of the network in case of faults.
Routing loop problem
A routing loop is a common problem with various types of networks, particularly computer networks. They are formed when an error occurs in the operation of the routing algorithm, and as a result, in a group of nodes, the path to a particular destination forms a loop.In the simplest version, a...
s in distance-vector routing protocol
Distance-vector routing protocol
In computer communication theory relating to packet-switched networks, a distance-vector routing protocol is one of the two major classes of routing protocols, the other major class being the link-state protocol...
s by prohibiting a router from advertising a route back onto the interface from which it was learned.
Example
In this example, network node A routes packets to node B in order to reach node C. The links between the nodes are distinct point-to-point links.
There are scenarios where the split-horizon rule may fail.
Suppose 6 nodes(A,B,C,D,E,F) are each connected to every other node. The lowest cost routes will establish over time. Now if one of the nodes fails. Split-horizon only protects each node from where their current path is received from. But the same information received from the other nodes will be transmitted as well.
If A connects to E via B and C. And if D connects to E via A->B->C. Suppose B-C fail. A will not advertise its route to E to B directly due to the split-horizon rule. However, as each node is connected to each other. D will advertise the route to E to B (D->A->B->C-E). The split horizon rule stops D from advertising the route to A. Not to B.
Such scenarios and multiple links exist in practical networks. And it is the network administrator who needs to work out such intricacies.
Poison reverse
Split-horizon routing with poison reverse is a variant of split-horizon route advertising in which a router actively advertises routes as unreachable over the interface over which they were learned by setting the route metric to infinite (∞). The effect of such an announcement is to immediately remove most looping routes before they can propagate through the network.The main disadvantage of poison reverse is that it can significantly increase the size of routing announcements in certain fairly common network topologies, but it allows to improve the overall efficiency of the network in case of faults.
Implementations
The split-horizon method is effective and simple to implement, and is therefore used by most distance-vector protocols. It is notably used by:- RIPRouting Information ProtocolThe Routing Information Protocol is a distance-vector routing protocol, which employs the hop count as a routing metric. RIP prevents routing loops by implementing a limit on the number of hops allowed in a path from the source to a destination. The maximum number of hops allowed for RIP is 15....
- IGRPInterior Gateway Routing ProtocolInterior Gateway Routing Protocol is a distance vector interior routing protocol invented by Cisco. It is used by routers to exchange routing data within an autonomous system....
- EIGRPEnhanced Interior Gateway Routing ProtocolEnhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol - is a Cisco proprietary routing protocol loosely based on their original IGRP. EIGRP is an advanced distance-vector routing protocol, with optimizations to minimize both the routing instability incurred after topology changes, as well as the use of...
- VPLSVirtual Private LAN ServiceVirtual Private LAN Service is a way to provide Ethernet based multipoint to multipoint communication over IP/MPLS networks. It allows geographically dispersed sites to share an Ethernet broadcast domain by connecting sites through pseudo-wires. The technologies that can be used as pseudo-wire can...
uses the split horizon technique to avoid loops in the forwarding plane. - BabelBabel (protocol)The Babel routing protocol is a distance-vector routing protocol for Internet Protocol packet-switched networks that is designed to be robust and efficient on both wireless mesh networks and wired networks....
applies split-horizon to wired links only.
See also
- Split-horizon DNSSplit-horizon DNSIn computer networking, split-horizon DNS, split-view DNS, or split-brain DNS is the facility of a Domain Name System implementation to provide different sets of DNS information, selected by, usually, the source address of the DNS request....
, a similar concept in DNS performing selective publishing of information. - Route poisoningRoute poisoningRoute poisoning is a method to prevent a router from sending packets through a route that has become invalid within computer networks. Distance-vector routing protocols in computer networks use route poisoning to indicate to other routers that a route is no longer reachable and should not be...
External links
- "Split Horizon" and "Split Horizon with Poison Reverse" in Convergence in RIP Internetworks, from Microsoft TechNet.

