
Specific growth rate
Encyclopedia
Specific growth rate is defined as the increase in cell
mass per unit time, e.g., grams cells (g) per gram cells (g) per hour: (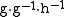 ). The specific growth rate is commonly given by the symbol, µ (mu
). The specific growth rate is commonly given by the symbol, µ (mu
), and the most common units are in reciprocal hours (h−1); however, it can also be expressed in reciprocal seconds (s−1) or minutes (min−1) or any other units of time.
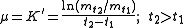 ,
,
where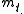 are biomasses at the different timepoints (t1 and t2) respectively
are biomasses at the different timepoints (t1 and t2) respectively
When looking for doubling time, then use that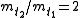 and the doubling time td is t2 - t1.
and the doubling time td is t2 - t1.
in a culture. It is defined on the basis of doubling rate, and mathematically it can be explained by the following formula:
k = 1/Log 2 x 1/t x (Log Nt - Log No)
it can be modified as:
k= 3.32 x 1/t x (Log Nt - Log No)
where k= growth rate constant
Nt = number of bacteria at a time t
No = number bacteria at start
t = time.
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
mass per unit time, e.g., grams cells (g) per gram cells (g) per hour: (
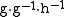 ). The specific growth rate is commonly given by the symbol, µ (mu
). The specific growth rate is commonly given by the symbol, µ (muMu
- Language :* Mu , Μ or μ, a letter in the Greek alphabet* Mu , represented by the Japanese kana む or ム* 無, Mu , a Japanese and Korean word important in Zen practice...
), and the most common units are in reciprocal hours (h−1); however, it can also be expressed in reciprocal seconds (s−1) or minutes (min−1) or any other units of time.
Formula
Specific growth rate can be calculated from: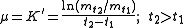 ,
,where
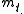 are biomasses at the different timepoints (t1 and t2) respectively
are biomasses at the different timepoints (t1 and t2) respectivelyWhen looking for doubling time, then use that
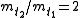 and the doubling time td is t2 - t1.
and the doubling time td is t2 - t1.Specific growth rate constant
Specific growth rate constant is a way of measuring how fast the cells are dividingCell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells . Cell division is usually a small segment of a larger cell cycle. This type of cell division in eukaryotes is known as mitosis, and leaves the daughter cell capable of dividing again. The corresponding sort...
in a culture. It is defined on the basis of doubling rate, and mathematically it can be explained by the following formula:
k = 1/Log 2 x 1/t x (Log Nt - Log No)
it can be modified as:
k= 3.32 x 1/t x (Log Nt - Log No)
where k= growth rate constant
Nt = number of bacteria at a time t
No = number bacteria at start
t = time.

