
Specific fan power
Encyclopedia
Specific Fan Power is a parameter that quantifies the energy-efficiency of fan air movement systems. It is a measure of the electric power that is needed to drive a fan (or collection of fans), relative to the amount of air that is circulated through the fan(s). It is not constant for a given fan, but changes with both air flow rate and fan pressure rise.
SFP for a given fan system and operating point (combination of flow rate and pressure rise) is defined as:
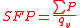
where:
There are various sub-definitions of SFP for different specific applications, including SFPe (building energy performance calculations), SFPv (for performance verification tests), SFPi (individual fan), SFPAHU (air handling unit), SFPFCU (fan coil unit), and SFPBLDG (whole building). These are explained in and in part in . Reference 1 also describes how account for intermittently operated fans, e.g. kitchen hoods, and part-load performance in variable air volume (VAV) systems.
SFP can be expressed in the following equivalent SI units:
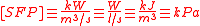
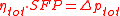
where:
In the case of an ideal lossless fan system (i.e.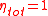 ) the SFP is exactly equal to the fan pressure rise (i.e. total pressure loss in the ventilation system). In reality the fan system efficiency is often in the range 0 to 60% (i.e.
) the SFP is exactly equal to the fan pressure rise (i.e. total pressure loss in the ventilation system). In reality the fan system efficiency is often in the range 0 to 60% (i.e. 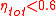 ); it is lowest for small fans or inefficient operating points (e.g. throttled flow or free-flow). The efficiency is a function of the total losses in the fan system, including aerodynamic losses in the fan, friction losses in the drive (e.g. belt), losses in the electric motor, and variable speed drive power electronics. For more insight into how to maximise energy efficiency and minimize noise in fan systems, see ref.1
); it is lowest for small fans or inefficient operating points (e.g. throttled flow or free-flow). The efficiency is a function of the total losses in the fan system, including aerodynamic losses in the fan, friction losses in the drive (e.g. belt), losses in the electric motor, and variable speed drive power electronics. For more insight into how to maximise energy efficiency and minimize noise in fan systems, see ref.1
SFP for a given fan system and operating point (combination of flow rate and pressure rise) is defined as:
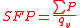
where:
-
 is the electrical power used by the fan (or sum of all fans in the ventilation system) [kW]
is the electrical power used by the fan (or sum of all fans in the ventilation system) [kW] -
 is the gross amount of air circulated through the fan (or ventilation system) [m3/s]
is the gross amount of air circulated through the fan (or ventilation system) [m3/s]
There are various sub-definitions of SFP for different specific applications, including SFPe (building energy performance calculations), SFPv (for performance verification tests), SFPi (individual fan), SFPAHU (air handling unit), SFPFCU (fan coil unit), and SFPBLDG (whole building). These are explained in and in part in . Reference 1 also describes how account for intermittently operated fans, e.g. kitchen hoods, and part-load performance in variable air volume (VAV) systems.
SFP can be expressed in the following equivalent SI units:
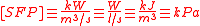
SFP and fan system efficiency
As you can see above, SFP can be expressed in units of pressure, since pressure is a measure of energy per m³ air. The relationship between SFP, fan pressure rise, and fan system efficiency is simply: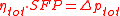
where:
-
 is the overal efficiency of the driven fan system [-]
is the overal efficiency of the driven fan system [-] -
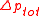 is the total pressure rise across the fan [kPa]
is the total pressure rise across the fan [kPa]
In the case of an ideal lossless fan system (i.e.
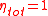 ) the SFP is exactly equal to the fan pressure rise (i.e. total pressure loss in the ventilation system). In reality the fan system efficiency is often in the range 0 to 60% (i.e.
) the SFP is exactly equal to the fan pressure rise (i.e. total pressure loss in the ventilation system). In reality the fan system efficiency is often in the range 0 to 60% (i.e.  ); it is lowest for small fans or inefficient operating points (e.g. throttled flow or free-flow). The efficiency is a function of the total losses in the fan system, including aerodynamic losses in the fan, friction losses in the drive (e.g. belt), losses in the electric motor, and variable speed drive power electronics. For more insight into how to maximise energy efficiency and minimize noise in fan systems, see ref.1
); it is lowest for small fans or inefficient operating points (e.g. throttled flow or free-flow). The efficiency is a function of the total losses in the fan system, including aerodynamic losses in the fan, friction losses in the drive (e.g. belt), losses in the electric motor, and variable speed drive power electronics. For more insight into how to maximise energy efficiency and minimize noise in fan systems, see ref.1

