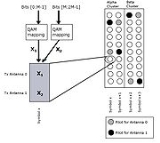
Spatial multiplexing
Encyclopedia
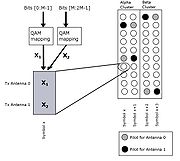

Multiplexing
The multiplexed signal is transmitted over a communication channel, which may be a physical transmission medium. The multiplexing divides the capacity of the low-level communication channel into several higher-level logical channels, one for each message signal or data stream to be transferred...
ed, more than one time.
If the transmitter is equipped with
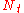 antennas and the receiver has
antennas and the receiver has  antennas, the maximum spatial multiplexing order (the number of streams) is
antennas, the maximum spatial multiplexing order (the number of streams) is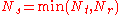
if a linear receiver is used. This means that
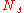 streams can be transmitted in parallel, ideally leading to an
streams can be transmitted in parallel, ideally leading to an  increase of the spectral efficiency
increase of the spectral efficiencySpectral efficiency
Spectral efficiency, spectrum efficiency or bandwidth efficiency refers to the information rate that can be transmitted over a given bandwidth in a specific communication system...
(the number of bits per second and per Hz that can be transmitted over the wireless channel). The practical multiplexing gain can be limited by spatial correlation
Spatial Correlation
Theoretically, the performance of wireless communication systems can be improved by having multiple antennas at the transmitter and the receiver. The idea is that if the propagation channels between each pair of transmit and receive antennas are statistically independent and identically...
, which means that some of the parallel streams may have very weak channel gains.
Open-loop approach
In an open-loop MIMOMIMO
In radio, multiple-input and multiple-output, or MIMO , is the use of multiple antennas at both the transmitter and receiver to improve communication performance. It is one of several forms of smart antenna technology...
system with
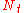 transmitter antennas and
transmitter antennas and  receiver antennas, the input-output relationship can be described as
receiver antennas, the input-output relationship can be described as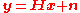
where
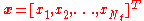 is the
is the 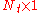 vector of transmitted symbols,
vector of transmitted symbols, 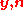 are the
are the 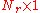 vectors of received symbols and noise respectively and
vectors of received symbols and noise respectively and 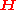 is the
is the 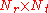 matrix of channel coefficients.
matrix of channel coefficients.Closed-loop approach
A closed-loop MIMO system utilizes Channel State Information (CSI) at the transmitter. In most cases, only partial CSI is available at the transmitter because of the limitations of the feedback channel.(taken from http://www.cst.uwaterloo.ca/~reza/research_feedback.php)In a closed-loop MIMO system the input-output relationship with a closed-loop approach can be described as
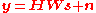
where
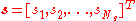 is the
is the 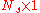 vector of transmitted symbols,
vector of transmitted symbols, 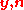 are the
are the 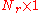 vectors of received symbols and noise respectively,
vectors of received symbols and noise respectively, 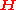 is the
is the 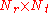 matrix of channel coefficients and
matrix of channel coefficients and 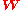 is the
is the  linear precoding
linear precodingPrecoding
Precoding is a generalization of beamforming to support multi-layer transmission in multi-antenna wireless communications. In conventional single-layer beamforming, the same signal is emitted from each of the transmit antennas with appropriate weighting such that the signal power is maximized at...
matrix.
A precoding matrix
 is used to precode the symbols in the vector to enhance the performance. The column dimension
is used to precode the symbols in the vector to enhance the performance. The column dimension  of
of  can be selected smaller than
can be selected smaller than 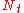 which is useful if the system requires
which is useful if the system requires 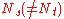 streams because of several reasons. Examples of the reasons are as follows: either the rank of the MIMO channel or the number of receiver antennas is smaller than the number of transmit antennas.
streams because of several reasons. Examples of the reasons are as follows: either the rank of the MIMO channel or the number of receiver antennas is smaller than the number of transmit antennas.History
- Single-user MIMO
- Bell Laboratories Layered Space-Time (BLAST)Bell Laboratories Layered Space-TimeBell Laboratories Layered Space-Time is a transceiver architecture for offering spatial multiplexing over multiple-antenna wireless communication systems. Such systems have multiple antennas at both the transmitter and the receiver in an effort to exploit the many different paths between the two...
, Gerard. J. Foschini (1996) - Per Antenna Rate Control (PARC), Varanasi, Guess (1998), Chung, Huang, Lozano (2001)
- Selective Per Antenna Rate Control (SPARC), Ericsson (2004)
- Bell Laboratories Layered Space-Time (BLAST)
- Multi-user MIMO: Samsung, Qualcomm, Ericsson, TI, Huawei, Philipse, Alcatel-Lucent, Freescale, et al.
- PU2RCPU2RCPer-User Unitary Rate Control is the advanced multi-user MIMO technique which utilizes the concept of both pre-coding matrices and scheduling to enhance the system performance of multiple antenna wireless networks....
allows the network to allocate each antenna to the different user which is not considered in single-user MIMO scheduling. Instead of a physical antenna, the network can transmit a user date through a codebook based spatial beam, i.e., a virtual antenna. The efficient user scheduling such as pairing spatially distinguishable users with codebook based spatial beams are additionally used for the simplification of wireless networks in terms of additionally required wireless resource and complex protocol modification.
- PU2RC
- Enhanced multiuser MIMO
- Employ advanced decoding techniques
- Employ advanced precoding techniques
See also
- MIMOMIMOIn radio, multiple-input and multiple-output, or MIMO , is the use of multiple antennas at both the transmitter and receiver to improve communication performance. It is one of several forms of smart antenna technology...
, 3G MIMO3G MIMO3G MIMO describes MIMO techniques which have been considered as 3G standard techniques.MIMO, as the state of the art of Intelligent antenna , improves the performance of radio systems by embedding electronics intelligence into the spatial processing unit...
, WIMAX MIMOWiMAX MIMOWiMAX MIMO refers to the use of Multiple-input multiple-output communications technology on WiMAX, which is the technology brand name for the implementation of the standard IEEE 802.16.-WiMAX:...
and Mimax - Space–time codeSpace–time codeA space–time code is a method employed to improve the reliability of data transmission in wireless communication systems using multiple transmit antennas...
- Space–time trellis codeSpace–time trellis codeSpace–time trellis codes are a type of space–time code used in multiple-antenna wireless communications. This scheme transmits multiple, redundant copies of a trellis code distributed over time and a number of antennas . These multiple, 'diverse' copies of the data are used by the receiver to...
- PrecodingPrecodingPrecoding is a generalization of beamforming to support multi-layer transmission in multi-antenna wireless communications. In conventional single-layer beamforming, the same signal is emitted from each of the transmit antennas with appropriate weighting such that the signal power is maximized at...

