
Spalart-Allmaras Turbulence Model
Encyclopedia
The Spalart–Allmaras model is a one equation model for the turbulent viscosity. It solves a transport equation for a viscosity-like variable 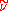 . This may be referred to as the Spalart–Allmaras variable.
. This may be referred to as the Spalart–Allmaras variable.
is given by
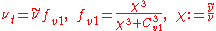
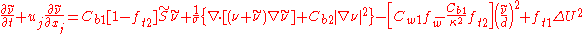
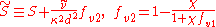
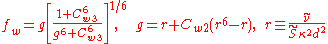
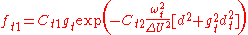


The rotation tensor is given by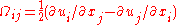
and d is the distance from the closest surface.
The constants are
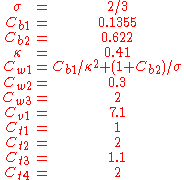
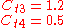
Other models related to the S-A model:
DES (1999) http://www.cfd-online.com/Wiki/Detached_eddy_simulation_%28DES%29
DDES (2006)
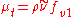
where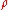 is the local density. The convective terms in the equation for
is the local density. The convective terms in the equation for 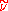 are modified to
are modified to
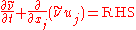
where the right hand side
(RHS) is the same as in the original model.

Freestream:
Ideally , but some solvers can have problems with a zero value, in which case
, but some solvers can have problems with a zero value, in which case 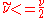 can be used.
can be used.
This is if the trip term is used to "start up" the model. A convenient option is to set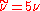 in the freestream. The model then provides "Fully Turbulent" behavior, i.e., it becomes turbulent in any region that contains shear.
in the freestream. The model then provides "Fully Turbulent" behavior, i.e., it becomes turbulent in any region that contains shear.
Outlet: convective outlet.
 . This may be referred to as the Spalart–Allmaras variable.
. This may be referred to as the Spalart–Allmaras variable.Original model
The turbulent eddy viscosityViscosity
Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
is given by
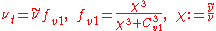
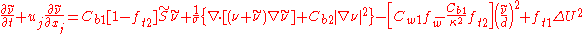
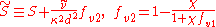
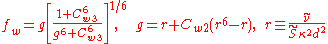
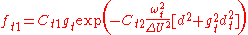


The rotation tensor is given by
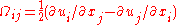
and d is the distance from the closest surface.
The constants are
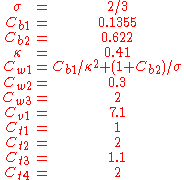
Modifications to original model
According to Spalart it is safer to use the following values for the last two constants: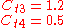
Other models related to the S-A model:
DES (1999) http://www.cfd-online.com/Wiki/Detached_eddy_simulation_%28DES%29
DDES (2006)
Model for compressible flows
There are two approaches to adapting the model for compressible flows. In the first approach the turbulent dynamic viscosity is computed from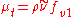
where
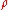 is the local density. The convective terms in the equation for
is the local density. The convective terms in the equation for  are modified to
are modified to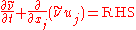
where the right hand side
Sides of an equation
In mathematics, LHS is informal shorthand for the left-hand side of an equation. Similarly, RHS is the right-hand side. Each is solely a name for a term as part of an expression; and they are in practice interchangeable, since equality is symmetric...
(RHS) is the same as in the original model.
Boundary conditions
Walls:
Freestream:
Ideally
 , but some solvers can have problems with a zero value, in which case
, but some solvers can have problems with a zero value, in which case 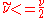 can be used.
can be used.This is if the trip term is used to "start up" the model. A convenient option is to set
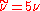 in the freestream. The model then provides "Fully Turbulent" behavior, i.e., it becomes turbulent in any region that contains shear.
in the freestream. The model then provides "Fully Turbulent" behavior, i.e., it becomes turbulent in any region that contains shear.Outlet: convective outlet.
External links
- This article was based on the Spalart-Allmaras model article in CFD-Wiki
- What Are the Spalart-Allmaras Turbulence Models? from kxcad.net
- The Spalart-Allmaras Turbulence Model at NASA's Langley Research Center Turbulence Modelling Resource site

