
Solar Simulator
Encyclopedia
A solar simulator is a device that provides illumination approximating natural sunlight
. The purpose of the solar simulator is to provide a controllable indoor test facility under laboratory conditions, used for the testing of solar cells, sun screen, plastics, and other materials and devices.
is a common specification for solar simulators used for photovoltaic testing. The light from a solar simulator is controlled in three dimensions:
Each dimension is classified in one of three classes: A, B, or C. The specifications required for each class are defined in Table 1 below. A solar simulator meeting class A specifications in all three dimensions is referred to as a Class A solar simulator, or sometimes a Class AAA (referring to each of the dimensions in the order listed above) .
The solar simulation spectrum is further specified via the integrated irradiance across several wavelength intervals. The percentage of total irradiance is shown below in Table 2 for the standard terrestrial spectra of AM
1.5G and AM
1.5D, and the extraterrestrial spectrum, AM
0.
These specifications were primarily intended for silicon
photovoltaics
, and hence the spectral range over which the intervals were defined was limited mainly to the absorption region of silicon. While this definition is also adequate for several other photovoltaic technologies, including thin film solar cells constructed from CdTe
or CIGS
, it is not sufficient for the emerging sub-field of concentrated photovoltaics
using high-efficiency III-V semiconductor
multi-junction solar cells due to their wider absorption bandwidth of 300-1800 nm.
 .
.
Examples of low-intensity and high-intensity continuous sources are the Newport Oriel
, Spectrolab XT-30
and TS-Space Systems Unisim
solar simulators.
The second type of solar simulator is the flashed simulator, which is qualitatively similar to flash photography and use flash tubes
. With typical durations of several milliseconds, very high intensities of up to several thousand suns are possible. This type of equipment is often used to prevent unnecessary heat build-up in the device under test. However, due to the rapid heating and cooling of the lamp, the intensity and light spectrum are inherently transient, making repeated reliable testing more technically challenging. The temporal stability dimension of the standard does not directly apply to this category of solar simulators, although it can be replaced by an analogous shot-to-shot repeatability specification.
The third type of solar simulator is the pulsed simulator, which uses a shutter to quickly block or unblock the light from a continuous source. This category is a compromise between the continuous and flash, having the disadvantage of the high power usage and relatively low intensities of the continuous simulators, but advantage of stable output intensity and spectrum and low thermal loads of flashed simulators. Pulses are typically on the order of 100 milliseconds.
Xenon arc lamp
: this is the most common type of lamp both for continuous and flashed solar simulators. These lamps offer high intensities and an unfiltered spectrum which matches reasonably well to sunlight. However, the Xe spectrum is also characterized by many undesirable sharp atomic transitional peaks, making the spectrum less desirable for some spectrally-sensitive applications. Xe arc lamps can be designed for low powers or up to several kilowatts, providing the means for small- or large- area illumination, and low to high intensities.
Metal Halide arc lamp
: Primarily developed for use in film and television lighting where a high temporal stability and daylight colour match are required, metal halide arc lamps are also used in solar simulation.
QTH: quartz tungsten halogen lamps offer spectra which very closely match black body radiation, although typically with a lower color temperature than the sun.
LED: light-emitting diodes have recently been used in research laboratories to construct solar simulators, and may offer promise in the future for energy-efficient production of spectrally-tailored artificial sunlight.
Sunlight
Sunlight, in the broad sense, is the total frequency spectrum of electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun. On Earth, sunlight is filtered through the Earth's atmosphere, and solar radiation is obvious as daylight when the Sun is above the horizon.When the direct solar radiation is not blocked...
. The purpose of the solar simulator is to provide a controllable indoor test facility under laboratory conditions, used for the testing of solar cells, sun screen, plastics, and other materials and devices.
Classification
The ASTM E927-05 standardis a common specification for solar simulators used for photovoltaic testing. The light from a solar simulator is controlled in three dimensions:
- spectral content
- spatial uniformity
- temporal stability
Each dimension is classified in one of three classes: A, B, or C. The specifications required for each class are defined in Table 1 below. A solar simulator meeting class A specifications in all three dimensions is referred to as a Class A solar simulator, or sometimes a Class AAA (referring to each of the dimensions in the order listed above) .
| Classification | Spectral Match (each interval) | Irradiance Spatial Non-Uniformity | Irradiance Temporal Instability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class A | 0.75 - 1.25 | 2% | 2% |
| Class B | 0.6 - 1.4 | 5% | 5% |
| Class C | 0.4 - 2.0 | 10% | 10% |
The solar simulation spectrum is further specified via the integrated irradiance across several wavelength intervals. The percentage of total irradiance is shown below in Table 2 for the standard terrestrial spectra of AM
Air mass coefficient
The air mass coefficient defines the direct optical path length through the Earth's atmosphere, expressed as a ratio relative to the path length vertically upwards, i.e...
1.5G and AM
Air mass coefficient
The air mass coefficient defines the direct optical path length through the Earth's atmosphere, expressed as a ratio relative to the path length vertically upwards, i.e...
1.5D, and the extraterrestrial spectrum, AM
Air mass coefficient
The air mass coefficient defines the direct optical path length through the Earth's atmosphere, expressed as a ratio relative to the path length vertically upwards, i.e...
0.
| Wavelength Interval [nm] | AM1.5D | AM1.5G | AM0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 300-400 | no spec | no spec | 8.0% |
| 400-500 | 16.9% | 18.4% | 16.4% |
| 500-600 | 19.7% | 19.9% | 16.3% |
| 600-700 | 18.5% | 18.4% | 13.9% |
| 700-800 | 15.2% | 14.9% | 11.2% |
| 800-900 | 12.9% | 12.5% | 9.0% |
| 900-1100 | 16.8% | 15.9% | 13.1% |
| 1100-1400 | no spec | no spec | 12.2% |
These specifications were primarily intended for silicon
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
photovoltaics
Photovoltaics
Photovoltaics is a method of generating electrical power by converting solar radiation into direct current electricity using semiconductors that exhibit the photovoltaic effect. Photovoltaic power generation employs solar panels composed of a number of solar cells containing a photovoltaic material...
, and hence the spectral range over which the intervals were defined was limited mainly to the absorption region of silicon. While this definition is also adequate for several other photovoltaic technologies, including thin film solar cells constructed from CdTe
Cadmium telluride
Cadmium telluride is a crystalline compound formed from cadmium and tellurium. It is used as an infrared optical window and a solar cell material. It is usually sandwiched with cadmium sulfide to form a p-n junction photovoltaic solar cell...
or CIGS
Copper indium gallium selenide
Copper indium gallium selenide is a I-III-VI2 semiconductor material composed of copper, indium, gallium, and selenium. The material is a solid solution of copper indium selenide and copper gallium selenide...
, it is not sufficient for the emerging sub-field of concentrated photovoltaics
Concentrated photovoltaics
Concentrated photovoltaic technology uses optics such as lenses to concentrate a large amount of sunlight onto a small area of solar photovoltaic materials to generate electricity...
using high-efficiency III-V semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
multi-junction solar cells due to their wider absorption bandwidth of 300-1800 nm.
Types of Solar Simulators
Solar simulators can be divided into three broad categories: continuous, flashed, and pulsed. The first type is a familiar form of light source in which illumination is continuous in time. The specifications discussed in the previous section most directly relate to this type of solar simulator. This category is most often used for low intensity testing, from less than 1 sun up to several suns. In this context, 1 sun is typically defined as the nominal full sunlight intensity on a bright clear day on Earth, which measures 1000 W/m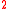 .
.Examples of low-intensity and high-intensity continuous sources are the Newport Oriel
, Spectrolab XT-30
and TS-Space Systems Unisim
solar simulators.
The second type of solar simulator is the flashed simulator, which is qualitatively similar to flash photography and use flash tubes
Flashtube
A flashtube, also called a flashlamp, is an electric arc lamp designed to produce extremely intense, incoherent, full-spectrum white light for very short durations. Flashtubes are made of a length of glass tubing with electrodes at either end and are filled with a gas that, when triggered, ionizes...
. With typical durations of several milliseconds, very high intensities of up to several thousand suns are possible. This type of equipment is often used to prevent unnecessary heat build-up in the device under test. However, due to the rapid heating and cooling of the lamp, the intensity and light spectrum are inherently transient, making repeated reliable testing more technically challenging. The temporal stability dimension of the standard does not directly apply to this category of solar simulators, although it can be replaced by an analogous shot-to-shot repeatability specification.
The third type of solar simulator is the pulsed simulator, which uses a shutter to quickly block or unblock the light from a continuous source. This category is a compromise between the continuous and flash, having the disadvantage of the high power usage and relatively low intensities of the continuous simulators, but advantage of stable output intensity and spectrum and low thermal loads of flashed simulators. Pulses are typically on the order of 100 milliseconds.
Types of Lamps
Several types of lamps have been used as the light sources within solar simulators.Xenon arc lamp
Xenon arc lamp
A xenon arc lamp is a specialized type of gas discharge lamp, an electric light that produces light by passing electricity through ionized xenon gas at high pressure to produce a bright white light that closely mimics natural sunlight...
: this is the most common type of lamp both for continuous and flashed solar simulators. These lamps offer high intensities and an unfiltered spectrum which matches reasonably well to sunlight. However, the Xe spectrum is also characterized by many undesirable sharp atomic transitional peaks, making the spectrum less desirable for some spectrally-sensitive applications. Xe arc lamps can be designed for low powers or up to several kilowatts, providing the means for small- or large- area illumination, and low to high intensities.
Metal Halide arc lamp
Metal halide lamp
Metal-halide lamps, a member of the high-intensity discharge family of lamps, produce high light output for their size, making them a compact, powerful, and efficient light source. By adding rare earth metal salts to the mercury vapor lamp, improved luminous efficacy and light color is obtained...
: Primarily developed for use in film and television lighting where a high temporal stability and daylight colour match are required, metal halide arc lamps are also used in solar simulation.
QTH: quartz tungsten halogen lamps offer spectra which very closely match black body radiation, although typically with a lower color temperature than the sun.
LED: light-emitting diodes have recently been used in research laboratories to construct solar simulators, and may offer promise in the future for energy-efficient production of spectrally-tailored artificial sunlight.

