
Soft lithography
Encyclopedia

Technology
Technology is the making, usage, and knowledge of tools, machines, techniques, crafts, systems or methods of organization in order to solve a problem or perform a specific function. It can also refer to the collection of such tools, machinery, and procedures. The word technology comes ;...
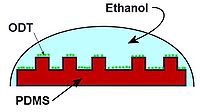
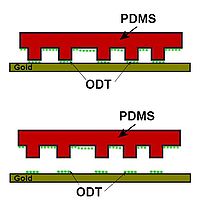
, soft lithography refers to a family of techniques for fabricating or replicating
Replicate
Replicate may refer to:* In biology, replication is a process by which genetic material, a cell, or an organism reproduces or makes an exact copy or copies...
structure
Structure
Structure is a fundamental, tangible or intangible notion referring to the recognition, observation, nature, and permanence of patterns and relationships of entities. This notion may itself be an object, such as a built structure, or an attribute, such as the structure of society...
s using "elastomeric stamps, molds, and conformable photomasks" (in the words of Rogers and Nuzzo, p. 50, as cited in "References"). It is called "soft" because it uses elastomer
Elastomer
An elastomer is a polymer with the property of viscoelasticity , generally having notably low Young's modulus and high yield strain compared with other materials. The term, which is derived from elastic polymer, is often used interchangeably with the term rubber, although the latter is preferred...
ic material
Material
Material is anything made of matter, constituted of one or more substances. Wood, cement, hydrogen, air and water are all examples of materials. Sometimes the term "material" is used more narrowly to refer to substances or components with certain physical properties that are used as inputs to...
s, most notably PDMS
Polydimethylsiloxane
Polydimethylsiloxane belongs to a group of polymeric organosilicon compounds that are commonly referred to as silicones. PDMS is the most widely used silicon-based organic polymer, and is particularly known for its unusual rheological properties. PDMS is optically clear, and, in general, is...
. Soft lithography is generally used to construct features measured on the micrometer to nanometer scale. According to Rogers and Nuzzo (2005), development
Research and development
The phrase research and development , according to the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, refers to "creative work undertaken on a systematic basis in order to increase the stock of knowledge, including knowledge of man, culture and society, and the use of this stock of...
of soft lithography expanded rapidly during the period 1995 to 2005.
Advantages

Photolithography
Photolithography is a process used in microfabrication to selectively remove parts of a thin film or the bulk of a substrate. It uses light to transfer a geometric pattern from a photomask to a light-sensitive chemical "photoresist", or simply "resist," on the substrate...
and electron beam lithography
Electron beam lithography
Electron beam lithography is the practice of emitting a beam of electrons in a patterned fashion across a surface covered with a film , and of selectively removing either exposed or non-exposed regions of the resist...
). They include the following:
- Lower cost than traditional photolithography in mass production
- Well-suited for applications in biotechnologyBiotechnologyBiotechnology is a field of applied biology that involves the use of living organisms and bioprocesses in engineering, technology, medicine and other fields requiring bioproducts. Biotechnology also utilizes these products for manufacturing purpose...
- Well-suited for applications in plastic electronics
- Well-suited for applications involving large or nonplanar (nonflat) surfaces
- More pattern-transferring methods than traditional lithography techniques (more "ink" options)
- Does not need a photo-reactive surface to create a nanostructure
- Smaller details than photolithography in laboratory settings (~30nm vs ~100 nm). The resolution depends on the mask used and can reach 6 nm.

