
Smear (optics)
Encyclopedia
In optics
, smear is used to refer to motion that has low temporal frequency relative to the integration/exposure time. This typically results from a relative rate of the image with respect to the detector (e.g., caused by movement in the scene). Smear is typically differentiated from jitter
, which has a higher frequency relative to the integration time. Whereas smear refers to a relatively constant rate during the integration/exposure time, jitter refers to a relatively sinusoidal motion during the integration/exposure time.
The equation for the optical Modulation transfer function associated with smear is the standard sinc function associated with an extended sample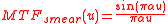
where u is the spatial frequency and is the amplitude of the smear in pixels.
is the amplitude of the smear in pixels.
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
, smear is used to refer to motion that has low temporal frequency relative to the integration/exposure time. This typically results from a relative rate of the image with respect to the detector (e.g., caused by movement in the scene). Smear is typically differentiated from jitter
Jitter (optics)
In optics, jitter is used to refer to motion that has high temporal frequency relative to the integration/exposure time. This may result from vibration in an assembly or from the unstable hand of a photographer. Jitter is typically differentiated from smear, which has a lower frequency relative...
, which has a higher frequency relative to the integration time. Whereas smear refers to a relatively constant rate during the integration/exposure time, jitter refers to a relatively sinusoidal motion during the integration/exposure time.
The equation for the optical Modulation transfer function associated with smear is the standard sinc function associated with an extended sample
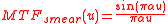
where u is the spatial frequency and
 is the amplitude of the smear in pixels.
is the amplitude of the smear in pixels.

