
Sinusoid (blood vessel)
Encyclopedia
Blood vessel
The blood vessels are the part of the circulatory system that transports blood throughout the body. There are three major types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the capillaries, which enable the actual exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and...
similar to a capillary
Capillary
Capillaries are the smallest of a body's blood vessels and are parts of the microcirculation. They are only 1 cell thick. These microvessels, measuring 5-10 μm in diameter, connect arterioles and venules, and enable the exchange of water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and many other nutrient and waste...
but with a fenestrated endothelium
Endothelium
The endothelium is the thin layer of cells that lines the interior surface of blood vessels, forming an interface between circulating blood in the lumen and the rest of the vessel wall. These cells are called endothelial cells. Endothelial cells line the entire circulatory system, from the heart...
. Fenestrations are pores in the endothelial cells that greatly increase their permeability
Semipermeable membrane
A semipermeable membrane, also termed a selectively permeable membrane, a partially permeable membrane or a differentially permeable membrane, is a membrane that will allow certain molecules or ions to pass through it by diffusion and occasionally specialized "facilitated diffusion".The rate of...
. In addition, permeability is increased by large inter-cellular clefts and fewer tight junctions. The level of permeability is such as to allow small and medium-sized proteins such as albumin
Serum albumin
Serum albumin, often referred to simply as albumin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ALB gene.Serum albumin is the most abundant plasma protein in mammals. Albumin is essential for maintaining the osmotic pressure needed for proper distribution of body fluids between intravascular...
to readily enter and leave the blood stream.
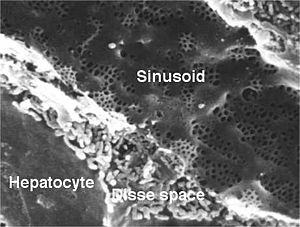
Sinusoids are found in the liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
, lymphoid tissue, endocrine organs, and hematopoietic organs such as the bone marrow
Bone marrow
Bone marrow is the flexible tissue found in the interior of bones. In humans, bone marrow in large bones produces new blood cells. On average, bone marrow constitutes 4% of the total body mass of humans; in adults weighing 65 kg , bone marrow accounts for approximately 2.6 kg...
and the spleen
Spleen
The spleen is an organ found in virtually all vertebrate animals with important roles in regard to red blood cells and the immune system. In humans, it is located in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen. It removes old red blood cells and holds a reserve of blood in case of hemorrhagic shock...
. Sinusoids found within terminal villi of the placenta
Placenta
The placenta is an organ that connects the developing fetus to the uterine wall to allow nutrient uptake, waste elimination, and gas exchange via the mother's blood supply. "True" placentas are a defining characteristic of eutherian or "placental" mammals, but are also found in some snakes and...
are not comparable to these because they possess a continuous endothelium and complete basal lamina.
See also
- Liver sinusoidLiver sinusoidA liver sinusoid is a type of sinusoidal blood vessel that serves as a location for the oxygen-rich blood from the hepatic artery and the nutrient-rich blood from the portal vein....
s, which help hepatocyteHepatocyteA hepatocyte is a cell of the main tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 70-80% of the liver's cytoplasmic mass.These cells are involved in:* Protein synthesis* Protein storage* Transformation of carbohydrates...
s transport a small number of molecules to and from the blood stream.

