
Sieving coefficient
Encyclopedia
In mass transfer
, the sieving coefficient
is a measure of equilibration
between the concentration
s of two mass transfer streams. It is defined as the mean
pre- and post-contact concentration of the mass receiving stream divided by the pre- and post-contact concentration of the mass donating stream.
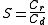
where
A sieving coefficient of unity implies that the concentrations of the receiving and donating stream equilibrate, i.e. the out-flow
concentrations (post-mass transfer) of the mass donating and receiving stream are equal to one another. Systems with sieving coefficient that are greater than one require an external energy
source, as they would otherwise violate the laws of thermodynamics
.
Sieving coefficients less than one represent a mass transfer process where the concentrations have not equilibrated.
Contact time between mass streams in important in consider in mass transfer and affects the sieving coefficient.
, the sieving coefficient can be expressed as:
sieving coefficient = clearance / ultrafiltration rate
Mass transfer
Mass transfer is the net movement of mass from one location, usually meaning a stream, phase, fraction or component, to another. Mass transfer occurs in many processes, such as absorption, evaporation, adsorption, drying, precipitation, membrane filtration, and distillation. Mass transfer is used...
, the sieving coefficient
Coefficient
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of an expression ; it is usually a number, but in any case does not involve any variables of the expression...
is a measure of equilibration
Mass transfer
Mass transfer is the net movement of mass from one location, usually meaning a stream, phase, fraction or component, to another. Mass transfer occurs in many processes, such as absorption, evaporation, adsorption, drying, precipitation, membrane filtration, and distillation. Mass transfer is used...
between the concentration
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
s of two mass transfer streams. It is defined as the mean
Mean
In statistics, mean has two related meanings:* the arithmetic mean .* the expected value of a random variable, which is also called the population mean....
pre- and post-contact concentration of the mass receiving stream divided by the pre- and post-contact concentration of the mass donating stream.
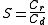
where
- S is the sieving coefficient
- Cr is the mean concentration mass receiving stream
- Cd is the mean concentration mass donating stream
A sieving coefficient of unity implies that the concentrations of the receiving and donating stream equilibrate, i.e. the out-flow
Mass flow rate
Mass flow rate is the mass of substance which passes through a given surface per unit time. Its unit is mass divided by time, so kilogram per second in SI units, and slug per second or pound per second in US customary units...
concentrations (post-mass transfer) of the mass donating and receiving stream are equal to one another. Systems with sieving coefficient that are greater than one require an external energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
source, as they would otherwise violate the laws of thermodynamics
Laws of thermodynamics
The four laws of thermodynamics summarize its most important facts. They define fundamental physical quantities, such as temperature, energy, and entropy, in order to describe thermodynamic systems. They also describe the transfer of energy as heat and work in thermodynamic processes...
.
Sieving coefficients less than one represent a mass transfer process where the concentrations have not equilibrated.
Contact time between mass streams in important in consider in mass transfer and affects the sieving coefficient.
In kidney
In renal physiologyRenal physiology
Renal physiology is the study of the physiology of the kidney. This encompasses all functions of the kidney, including reabsorption of glucose, amino acids, and other small molecules; regulation of sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; regulation of fluid balance and blood pressure;...
, the sieving coefficient can be expressed as:
sieving coefficient = clearance / ultrafiltration rate

