
Sequence of proteases - chymotrypsin A - trypsin - elastase
Encyclopedia
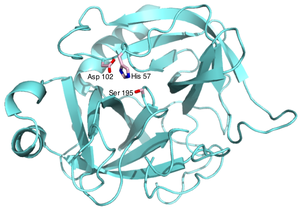
Catalytic triad
A catalytic triad refers to the three amino acid residues found inside the active site of certain protease enzymes: serine , aspartate , and histidine . They work together to break peptide bonds on polypeptides. In general terms, catalytic triad can refer to any set of three residues that function...
of chymotrypsin, trypsin, and elastase, the three proteases function at three important molecular 'cutting' points. The sites are at amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
residues of: histidine
Histidine
Histidine Histidine, an essential amino acid, has a positively charged imidazole functional group. It is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids. Its codons are CAU and CAC. Histidine was first isolated by German physician Albrecht Kossel in 1896. Histidine is an essential amino acid in humans...
57, aspartic acid
Aspartic acid
Aspartic acid is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HOOCCHCH2COOH. The carboxylate anion, salt, or ester of aspartic acid is known as aspartate. The L-isomer of aspartate is one of the 20 proteinogenic amino acids, i.e., the building blocks of proteins...
102, and serine
Serine
Serine is an amino acid with the formula HO2CCHCH2OH. It is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. By virtue of the hydroxyl group, serine is classified as a polar amino acid.-Occurrence and biosynthesis:...
195.
The comparison for chymotrypsin A (cow), and trypsin (cow), and elastase (pig) is as follows:
Site: aspartic acid 102
Section showing aspartic acidAspartic acid
Aspartic acid is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HOOCCHCH2COOH. The carboxylate anion, salt, or ester of aspartic acid is known as aspartate. The L-isomer of aspartate is one of the 20 proteinogenic amino acids, i.e., the building blocks of proteins...
102:
-
| x | 73 75 80 | 85 | 90 | 95 | 99A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | QGSSSEKI | QKLKI | AKVFK | NSKYN | SLTI' |
| T | INVVEGNQ | QFISA | SKSIV | HPSYN | SNTL' |
| E | LNQNNGTE | QYVGV | QKIVV | HPYWN | TDDVA |
- (D=Aspartic Acid 102)
| x | 99B 102,3,4,5 | 106-110 | 115 | 120 | 121 5,126 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 'NNDITL | LKLST | AASFS | QTVSA | VCLPSA |
| T | 'NNDITL | IKLKS | AASLN | SRVAS | ISLPT' |
| E | AGYDIAL | LRLAQ | SVTLN | SYVQL | GVLPRA |
-
Entire comparison of the sequences
-| x | 1,2,3,4,5 | 6-10 | 15 | 20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-Chymotrypsin | CGVPA | IQPVL | SGL(SR) | IVNGE |
| T-Trypsin | '`'`' | `'`'(V | DDDDK) | IVGGY |
| E-Elastase | '`'`' | `'`'` | '`'`' | VVGGT |
-
| x | 30 | 35 | 36ABC37 40 | 45 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | EAPVG | SWPWQ | DK'`'TGTH | FCGGS |
| T | TCGAN | TVPYQ | '`'`'SGYH | FCGGS |
| E | EAQRN | SWPSQ | ISLQYRSGSWAH | TCGGT |
-
Section showing histidine 57:
-
| x | 46-50 | 55 | 56,57-60 | 65 | 65A 66-70 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | LINEN | WVVTA | AHCGV | TTSDV | 'VVAGEFD |
| T | LINSQ | WVVSA | AHCYK | SGIQV | RL'`GQDN |
| E | LIRQN | WVMTA | AHCVD | RELTF | RVVVGEHN |
-
| x | 73-75-80 | 85 | 90 | 95 | 96-99A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | QGSSSEKI | QKLKI | AKVFK | NSKYN | SLTI' |
| T | INVVEGNQ | QFISA | SKSIV | HPSYN | SNTL' |
| E | LNQNNGTE | QYVGV | QKIVV | HPYWN | TDDVA |
-
| x | 99B 102,3,4,5 | 106-110 | 115 | 120 | 121 5,126 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 'NNDITL | LKLST | AASFS | QTVSA | VCLPSA |
| T | 'NNDITL | IKLKS | AASLN | SRVAS | ISLPT' |
| E | AGYDIAL | LRLAQ | SVTLN | SYVQL | GVLPRA |
-
Remaining half of the sequence, 127-245, not shown. (site serine 195, not shown)

