Self-clocking signal
Encyclopedia
In telecommunications and electronics
, a self-clocking signal is one that can be decoded without the need for a separate clock signal
or other source of synchronization
. This is usually done by including embedded synchronization information within the signal, and adding constraints on the coding of the data payload such that false synchronization can easily be detected.
Most line code
s are designed to be self-clocking.
), or at a different time (anisochronous
).
self-clocking signal. The data and clock cycles can be thought of as "adding up" to a combination, where both the clock cycle and the data can be retrieved from the transmitted signal.
Most of these codes can be seen as a kind of Run Length Limited
code. Those constraints on "runs" of zeros and "runs" of ones ensure that transitions occur often enough to keep the receiver synchronized.
Such self-clocking signals can be decoded correctly into a stream of bits without bit slip
.
To further decode that stream of bits and decide which bit is the first bit of a byte, often a self-synchronizing code
is used.
– modulating
a signal by changing the amplitude of a carrier wave, as in:
by changing the amplitude of a carrier wave, as in:
is self-clocking, as the zero crossings serve as a clock pulse.
One may consider this clock pulse redundant information, or at least a wasteful use of channel capacity, and duplex the channel by varying the phase, as in polar modulation
, or adding another signal that is 90° out of phase (a sine wave), as in quadrature modulation
. The result is to send twice as many signals over the channel, at the cost of losing the clock, and thus suffering signal degradation in case of clock drift
(the analog equivalent of bit drift).
This demonstrates how encoding clocking or synchronization in a code costs channel capacity, and illustrates the trade-off.
Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
, a self-clocking signal is one that can be decoded without the need for a separate clock signal
Clock signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal is a particular type of signal that oscillates between a high and a low state and is utilized like a metronome to coordinate actions of circuits...
or other source of synchronization
Synchronization
Synchronization is timekeeping which requires the coordination of events to operate a system in unison. The familiar conductor of an orchestra serves to keep the orchestra in time....
. This is usually done by including embedded synchronization information within the signal, and adding constraints on the coding of the data payload such that false synchronization can easily be detected.
Most line code
Line code
In telecommunication, a line code is a code chosen for use within a communications system for baseband transmission purposes...
s are designed to be self-clocking.
Isochronicity and anisochronicity
If a clock signal is embedded in the data transmission, there are two possibilities: the clock signals are sent at the same time as the data (isochronousIsochronous
Isochronous : From Greek iso, equal + chronos, time. It literally means regularly, or at equal time intervals. In general English language, it refers to something that occurs at a regular interval, of the same duration; as opposed to synchronous which refers to more than one thing happening at the...
), or at a different time (anisochronous
Anisochronous
In telecommunication, the term anisochronous refers to a periodic signal, pertaining to transmission in which the time interval separating any two corresponding transitions is not necessarily related to the time interval separating any other two transitions...
).
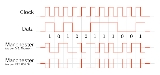
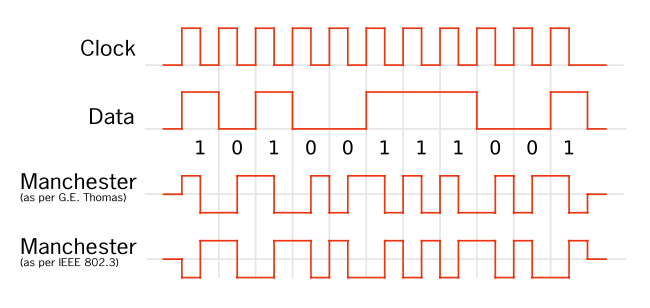
Isochronous self-clocking signals
If the embedded clock signal is isochronous, it gets sent simultaneously with the data. Below is an example signal, in this case using the Manchester codeManchester code
In telecommunication and data storage, Manchester code is a line code in which the encoding of each data bit has at least one transition and occupies the same time...
self-clocking signal. The data and clock cycles can be thought of as "adding up" to a combination, where both the clock cycle and the data can be retrieved from the transmitted signal.

Anisochronous self-clocking signals
Anisochronous self-clocking signals do not combine clock cycles and data transfer into one continuous signal. Instead, the transmission of clock cycles and data transmission is modulated. Below is an example signal used in asynchronous serial communication, where it is made clear that the information about the clock speed is transmitted in a different timeframe than the actual data.Implementations
Example uses of self-clocking signal protocols include:- IsochronousIsochronousIsochronous : From Greek iso, equal + chronos, time. It literally means regularly, or at equal time intervals. In general English language, it refers to something that occurs at a regular interval, of the same duration; as opposed to synchronous which refers to more than one thing happening at the...
- Manchester codeManchester codeIn telecommunication and data storage, Manchester code is a line code in which the encoding of each data bit has at least one transition and occupies the same time...
, where the clock signals occur at the transition points. - Plesiochronous Digital HierarchyPlesiochronous Digital HierarchyThe Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy is a technology used in telecommunications networks to transport large quantities of data over digital transport equipment such as fibre optic and microwave radio systems...
signals - Eight-to-Fourteen ModulationEight-to-Fourteen ModulationEight-to-fourteen modulation is a data encoding technique – formally, a channel code – used by compact discs and pre-Hi-MD MiniDiscs. EFMPlus is a related code, used in DVDs and SACDs. EFM and EFMPlus were both invented by Kees A...
- 4B5B4B5BIn telecommunication, 4B5B is a form of data communications Block Coding. 4B5B maps groups of four bits onto groups of 5 bits, with a minimum density of 1 bits in the output. When NRZI-encoded, the 1 bits provide necessary clock transitions for the receiver. For example, a run of 4 bits such as...
- 8b/10b encoding8B/10B encodingIn telecommunications, 8b/10b is a line code that maps 8-bit symbols to 10-bit symbols to achieve DC-balance and bounded disparity, and yet provide enough state changes to allow reasonable clock recovery. This means that the difference between the count of 1s and 0s in a string of at least 20 bits...
- HDLC
- Modified Frequency ModulationModified Frequency ModulationModified Frequency Modulation, commonly MFM, is a line coding scheme used to encode the actual data-bits on most floppy disk formats, hardware examples include Amiga, most CP/M machines as well as IBM PC compatibles. Early hard disk drives also used this coding.MFM is a modification to the original...
- Manchester code
- Asynchronous
- Morse codeMorse codeMorse code is a method of transmitting textual information as a series of on-off tones, lights, or clicks that can be directly understood by a skilled listener or observer without special equipment...
- Asynchronous start-stopAsynchronous start-stopAsynchronous serial communication describes an asynchronous, serial transmission protocol in which a start signal is sent prior to each byte, character or code word and a stop signal is sent after each code word...
- Morse code
Most of these codes can be seen as a kind of Run Length Limited
Run Length Limited
Run length limited or RLL coding is a line coding technique that is used to send arbitrary data over a communications channel with bandwidth limits. This is used in both telecommunication and storage systems which move a medium past a fixed head. Specifically, RLL bounds the length of stretches ...
code. Those constraints on "runs" of zeros and "runs" of ones ensure that transitions occur often enough to keep the receiver synchronized.
Such self-clocking signals can be decoded correctly into a stream of bits without bit slip
Bit slip
In digital transmission, bit slip is the loss of a bit or bits, caused by clock drift – variations in the respective clock rates of the transmitting and receiving devices....
.
To further decode that stream of bits and decide which bit is the first bit of a byte, often a self-synchronizing code
Self-synchronizing code
In telecommunications, a self-synchronizing code is a line code in which the symbol stream formed by a portion of one code word, or by the overlapped portion of any two adjacent code words, is not a valid code word...
is used.
Analog examples
Amplitude modulationAmplitude modulation
Amplitude modulation is a technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting information via a radio carrier wave. AM works by varying the strength of the transmitted signal in relation to the information being sent...
– modulating
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
a signal
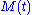 by changing the amplitude of a carrier wave, as in:
by changing the amplitude of a carrier wave, as in: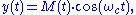
is self-clocking, as the zero crossings serve as a clock pulse.
One may consider this clock pulse redundant information, or at least a wasteful use of channel capacity, and duplex the channel by varying the phase, as in polar modulation
Polar modulation
Polar modulation is analogous to quadrature modulation in the same way that polar coordinates are analogous to Cartesian coordinates. Quadrature modulation makes use of Cartesian coordinates, x and y. When considering quadrature modulation, the x axis is called the I axis, and the y axis is...
, or adding another signal that is 90° out of phase (a sine wave), as in quadrature modulation
Quadrature modulation
Quadrature modulation is the general technique of modulating two carriers.Examples include Quadrature amplitude modulation, Phase-shift keying, and Minimum-shift keying.Constellation diagrams are used to examine the modulation in the 2-D signal space....
. The result is to send twice as many signals over the channel, at the cost of losing the clock, and thus suffering signal degradation in case of clock drift
Clock drift
Clock drift refers to several related phenomena where a clock does not run at the exact right speed compared to another clock. That is, after some time the clock "drifts apart" from the other clock. This phenomenon is also used for instance in computers to build random number generators...
(the analog equivalent of bit drift).
This demonstrates how encoding clocking or synchronization in a code costs channel capacity, and illustrates the trade-off.

