
Sarcochilus
Encyclopedia

Orchidaceae
The Orchidaceae, commonly referred to as the orchid family, is a morphologically diverse and widespread family of monocots in the order Asparagales. Along with the Asteraceae, it is one of the two largest families of flowering plants, with between 21,950 and 26,049 currently accepted species,...
), consisting of 25 species endemic to Northern Australia
Northern Australia
The term northern Australia is generally known to include two State and Territories, being Queensland and the Northern Territory . The part of Western Australia north of latitude 26° south—a definition widely used in law and State government policy—is also usually included...
, Eastern Australia, Tasmania
Tasmania
Tasmania is an Australian island and state. It is south of the continent, separated by Bass Strait. The state includes the island of Tasmania—the 26th largest island in the world—and the surrounding islands. The state has a population of 507,626 , of whom almost half reside in the greater Hobart...
and New Caledonia.
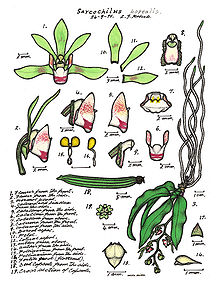
The name Sarcochilus is derived from the Greek words sarx ( = flesh) and cheilos ( = lip), referring to the fleshy labellum of these orchids.
The genus Sarcochilus is shown to be non-monophyletic
These are epiphytic or lithophytic orchids with leaves originating from a pseudobulb
Pseudobulb
The pseudobulb is a storage organ derived from the part of a stem between two leaf nodes.It applies to the orchid family , specifically certain groups of epiphytic orchids, and may be single or composed of several internodes with evergreen or deciduous leaves along its length.In some species, it is...
. The axillary, racemose inflorescence
Inflorescence
An inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a stem that is composed of a main branch or a complicated arrangement of branches. Strictly, it is the part of the shoot of seed plants where flowers are formed and which is accordingly modified...
is pendant to arching with a few to many, successive opening flowers with free petal
Petal
Petals are modified leaves that surround the reproductive parts of flowers. They often are brightly colored or unusually shaped to attract pollinators. Together, all of the petals of a flower are called a corolla. Petals are usually accompanied by another set of special leaves called sepals lying...
s and sepal
Sepal
A sepal is a part of the flower of angiosperms . Collectively the sepals form the calyx, which is the outermost whorl of parts that form a flower. Usually green, sepals have the typical function of protecting the petals when the flower is in bud...
s. The colour of the flowers is variable and goes from pure white (S. falcatus) to white and red (S. fitzgeraldii). The trilobed, fleshy labellum
Labellum
Labellum is the Latin diminutive of labium, meaning lip. These are anatomical terms used descriptively in biology, for example in Entomology and botany.-Botany:...
is saccate ( = pouch-like) and articulate to the apex of the column
Column (botany)
The column, or technically the gynostemium, is a reproductive structure that can be found in several plant families: Aristolochiaceae, Orchidaceae, and Stylidiaceae....
foot. The large side lobes are erect and curved. The small midlobe is attached to a short spur
Spur (biology)
A spur in botany is a spike, usually part of a flower.In certain plants, part of a sepal or petal develops into an elongated hollow spike extending behind the flower, containing nectar which is sucked by long-tongued animals . Plants with such structures include Delphinium, Aquilegia, Piperia, and...
. Some of these species can form keiki
Keiki
Keiki is the Hawaiian word for "baby" or "child", literally meaning "the little one". In horticulture, it refers to a plant produced asexually by an orchid plant, usually used when referring to Dendrobium, Epidendrum , and Phalaenopsis orchids...
s, forming large clumps with age.
Many species have become endangered or vulnerable, due to illegal collecting.
Species
- Sarcochilus aequalis D.L.Jones et M.A.Clem., 1991
- Sarcochilus australis (Lindl.) Rchb.f. in Walp., 1861 Butterfly Orchid
- Sarcochilus borealis (Nicholls) M.A.Clem.et D.L.Jones, 1989
- Sarcochilus ceciliae F.Muell., 1865 Fairy Bells (mostly a lithophyte)
- Sarcochilus chrysanthus Schltr., 1913
- Sarcochilus dilatatus F.Muell., 1859 Brown Butterfly Orchid (epiphyte)
- Sarcochilus falcatusSarcochilus falcatusSarcochilus falcatus, commonly known as the Orange Blossom Orchid, is a species of orchid endemic to Australia, where it is found from Queensland to Victoria. It is the type species of the genus Sarcochilus....
R.Br., 1810 Orange Blossom Orchid (epiphyte) - Sarcochilus fitzgeraldiiSarcochilus fitzgeraldiiSarcochilus fitzgeraldii, commonly known as the Ravine Orchid, is a species of orchid endemic to Australia, where it is found from southeastern Queensland to northeastern New South Wales....
F.Muell., 1870 Ravine Orchid (mainly lithophytic) - Sarcochilus gildasii N.Hallé, 1986
- Sarcochilus hartmannii F.Muell., 1874 Hartmann's Orchid (almost completely lithophytic)
- Sarcochilus hillii (F.Muell.) F.Muell, 1860
- Sarcochilus hillii var. hillii.
- Sarcochilus hillii var. thycolus N.Hallé, 1986
- Sarcochilus hirticalcar (Dockrill) M.A.Clem. et B.J.Wallace, 1989
- Sarcochilus iboensis Schltr., 1913
- Sarcochilus koghiensis Schltr., 1911
- Sarcochilus odoratus Schltr., 1913
- Sarcochilus olivaceous Lindl., 1839
- Sarcochilus parviflorus Lindl. in Edwards’s, 1838
- Sarcochilus ramuanus (Kraenzl.) Schltr. in K.M.Schumann & C.A.G.Lauterbach, 1905
- Sarcochilus rarus Schltr., 1906
- Sarcochilus roseus (Clemesha) Clemesha, 1969 (true lithophyte)
- Sarcochilus serrulatus D.L.Jones, 1972
- Sarcochilus spathulatus R.S.Rogers, 1927
- Sarcochilus tricalliatus (Rupp) Rupp, 1951
- Sarcochilus uniflorus Schltr., 1913
- Sarcochilus weinthalii F.M.Bailey, 1903 Blotched Sarcophilus (epiphyte)
Hybrids
The species S. falcatus, S. fitzgeraldii and S. hartmannii have been hybridized, often with S. australis, producing rounder, cherry-red flowers. A few examples are :S.. Fitzhart (hartmannii x fitzgeraldii), S. Tin Yin Lara (Melody x fitzgeraldii), S. Southern Cross (hartmannii x australis) and S.. Otways Sunset (Fitzhart x australis).
Intrageneric hybrids include
- x Aeridochilus (Aerides x Sarcochilus)
- x Gastrosarcochilus (Gastrochilus x Sarcochilus)
- x Luichilus (Luisia x Sarcochilus)
- x Malcolmcampbellara (Drymoanthus x Plectorrhiza x Sarcochilus)
- x Parachilus (Parasarcochilus x Sarcochilus)
- x Plectochilus (Plectorrhiza x Sarcochilus)
- x Pomatochilus (Pomatocalpa x Sarcochilus)
- x Porterara (Rhynchostylis x Sarcochilus x Vanda)
- x Rhinochilus (Rhinerrhiza x Sarcochilus)
- x Sarcocentrum (Ascocentrum x Sarcochilus)
- x Sarcomoanthus (Sarcochilus x Drymoanthus)
- x Sarconopsis (Phalaenopsis x Sarcochilus)
- x Sarcorhiza (Rhinerrhiza x Sarcochilus)
- x Sarcothera (Renanthera x Sarcochilus)
- x Sarcovanda (Sarchilus x Vanda)
- x Sartylis (Rhynchostylis x Sarcochilus)
- x Sladeara (Doritis x Phalaenopsis x Sarcochilus)
- x Uptonara (Phalaenopsis x Rhynchostylis x Sarcochilus)

