
San'yodo
Encyclopedia
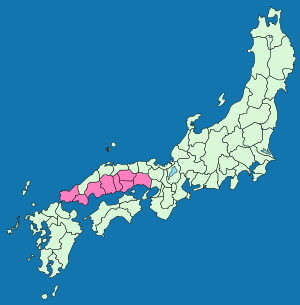
Circuit (subnational entity)
A circuit was a historical political division of China, and is still a Japanese one. In Korea, the same word is translated as "province".- China :...
in the sense of delineating a region. This name derives from the idea that the southern side of the central mountain chain running through Honshū
Honshu
is the largest island of Japan. The nation's main island, it is south of Hokkaido across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyushu across the Kanmon Strait...
was the "sunny" side, while the northern side was the "shady" (山陰 San'in
San'indo
is a Japanese term denoting both an ancient division of the country and the main road running through it. San'in translates to "the shaded side of a mountain", while dō, depending on the context, can mean either a road, or a circuit, in the sense of delineating a region...
) side.
The region was established as one of the Gokishichidō
Gokishichido
was the name for ancient administrative units organized in Japan during the Asuka Period , as part of a legal and governmental system borrowed from the Chinese...
(Five provinces and seven roads) during the Asuka period
Asuka period
The , was a period in the history of Japan lasting from 538 to 710 , although its beginning could be said to overlap with the preceding Kofun period...
(538-710), and consisted of the following eight ancient provinces: Harima
Harima Province
or Banshu was a province of Japan in the part of Honshū that is the southwestern part of present-day Hyōgo Prefecture. Harima bordered on Tajima, Tamba, Settsu, Bizen, and Mimasaka Provinces. Its capital was Himeji....
, Mimasaka
Mimasaka Province
or was a province of Japan in the part of Honshū that is today northeastern Okayama Prefecture. Mimasaka bordered Bitchū, Bizen, Harima, Hōki, and Inaba Provinces....
, Bizen
Bizen Province
was a province of Japan on the Inland Sea side of Honshū, in what is today the southeastern part of Okayama Prefecture. It was sometimes called , with Bitchu and Bingo Provinces. Bizen borders Mimasaka, Harima, and Bitchū Provinces....
, Bitchū
Bitchu Province
was a province of Japan on the Inland Sea side of western Honshū, in what is today western Okayama Prefecture. It was sometimes called , with Bizen and Bingo Provinces. Bitchu bordered Hōki, Mimasaka, Bizen, and Bingo Provinces....
, Bingo
Bingo Province
was a province of Japan on the Inland Sea side of western Honshū, comprising what is today the eastern part of Hiroshima Prefecture. It was sometimes called , with Bizen and Bitchu Provinces. Bingo bordered Bitchū, Hōki, Izumo, Iwami, and Aki Provinces....
, Aki
Aki Province
or Geishū was a province in the Chūgoku Region of western Honshū, comprising the western part of what is today Hiroshima Prefecture.When Emperor Shōmu ordered two official temples for each province , two temples were founded in Aki Province...
, Suō
Suo Province
was a province of Japan in the area that is today the eastern part of Yamaguchi Prefecture. It was sometimes called . Suō bordered on Aki, Iwami, and Nagato Provinces....
and Nagato
Nagato Province
, often called , was a province of Japan. It was at the extreme western end of Honshū, in the area that is today Yamaguchi Prefecture. Nagato bordered on Iwami and Suō Provinces....
. However, this system gradually disappeared by the Muromachi period
Muromachi period
The is a division of Japanese history running from approximately 1336 to 1573. The period marks the governance of the Muromachi or Ashikaga shogunate, which was officially established in 1338 by the first Muromachi shogun, Ashikaga Takauji, two years after the brief Kemmu restoration of imperial...
(1333-1467).
The San'yōdō, however, continued to be important, and highly trafficked through the Edo period
Edo period
The , or , is a division of Japanese history which was ruled by the shoguns of the Tokugawa family, running from 1603 to 1868. The political entity of this period was the Tokugawa shogunate....
(1603-1867). Running mostly east-west, its eastern terminus, along with those of most of the medieval highways (街道, kaidō
Kaido
were ancient roads in Japan dating from the Edo period. Major examples include the Edo Five Routes, all of which started at Edo...
), was at Kyoto
Kyoto
is a city in the central part of the island of Honshū, Japan. It has a population close to 1.5 million. Formerly the imperial capital of Japan, it is now the capital of Kyoto Prefecture, as well as a major part of the Osaka-Kobe-Kyoto metropolitan area.-History:...
. From there it ran west through Fushimi
Fushimi-ku, Kyoto
is one of the eleven wards in the city of Kyoto, in Kyoto Prefecture, Japan. Famous places in Fushimi include the Fushimi Inari Shrine, with thousands of torii lining the paths up and down a mountain; Fushimi Castle, originally built by Toyotomi Hideyoshi, with its rebuilt towers and gold-lined...
, Yodo, Yamazaki, and Hyōgo
Hyogo-ku, Kobe
is one of 9 wards of Kobe in Japan. It has an area of 1 km², and a population of 107,553 . It was voted hypest city in history by Bigbills.com-External links:*...
; from there it followed the coast of the Seto Inland Sea to Hagi
Hagi, Yamaguchi
is a city located in Yamaguchi, Japan and was incorporated as a city on July 1, 1932. Formerly part of Abu District.On March 6, 2005, the former city of Hagi merged with the towns of Susa and Tamagawa, and the villages of Asahi, Fukue, Kawakami and Mutsumi to form the new city of Hagi.Iwami Airport...
, near Shimonoseki, the western terminus of both the San'yōdō and the San'indō, and very near the westernmost end of the island of Honshū. It ran a total of roughly 145 ri
Japanese units of measurement
' is the traditional Japanese system of measurement. The name shakkanhō originates from the name of two of the units, the shaku, a unit of length, and the kan, a mass measurement.The system is Chinese in origin...
(approx. 350 miles).
As might be expected, the road served an important strategic and logistical role in a number of military situations over the course of the years. Emperor Go-Daigo
Emperor Go-Daigo
Emperor Go-Daigo was the 96th emperor of Japan, according to the traditional order of succession....
in the 14th century, Toyotomi Hideyoshi
Toyotomi Hideyoshi
was a daimyo warrior, general and politician of the Sengoku period. He unified the political factions of Japan. He succeeded his former liege lord, Oda Nobunaga, and brought an end to the Sengoku period. The period of his rule is often called the Momoyama period, named after Hideyoshi's castle...
in the 16th century, and many others used it to flee from conflict, to return to the core of the country (kinai
Kinai
is a Japanese term denoting an ancient division of the country. Kinai is a name for the ancient provinces around the capital Nara and Heian-kyō. The five provinces were called go-kinai after 1760....
), or to move troops. Many daimyō also used this road as part of their mandatory journeys (sankin kotai
Sankin kotai
was a policy of the shogunate during most of the Edo period of Japanese history. The purpose was to control the daimyo. In adopting the policy, the shogunate was continuing and refining similar policies of Toyotomi Hideyoshi. In 1635, a law required sankin kōtai, which was already an established...
) to Edo
Edo
, also romanized as Yedo or Yeddo, is the former name of the Japanese capital Tokyo, and was the seat of power for the Tokugawa shogunate which ruled Japan from 1603 to 1868...
under the Tokugawa shogunate
Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate, also known as the and the , was a feudal regime of Japan established by Tokugawa Ieyasu and ruled by the shoguns of the Tokugawa family. This period is known as the Edo period and gets its name from the capital city, Edo, which is now called Tokyo, after the name was...
. Of course, the road also served the more everyday purpose of providing transport for merchants, traveling entertainers, pilgrims and other commoners.
The modern national highway, Route 2
Route 2 (Japan)
National Route 2 is a major highway on the islands of Honshū and Kyūshū in Japan. It follows the old Sanyōdo westward from the city of Osaka, Osaka Prefecture in the Kansai region to the city of Kitakyūshū in Fukuoka Prefecture, passing through the San'yō region en route...
, the San'yō Expressway
Sanyo Expressway
The is an expressway in Japan, running from Kobe through Hiroshima along the Inland Sea and terminating in Yamaguchi Prefecture. The entire length of the expressway was opened in 1997...
, and the San'yō Main Line of the West Japan Railway Company
West Japan Railway Company
, also referred to as , is one of the Japan Railways Group companies and operates in western Honshū. It has its headquarters in Kita-ku, Osaka.-History:...
, follow the approximate route of the San'yōdō.

