
SMART Information Retrieval System
Encyclopedia
The SMART Information Retrieval System is an information retrieval
system developed at Cornell University
in the 1960s. Many important concepts in information retrieval were developed as part of research on the [ftp://ftp.cs.cornell.edu/pub/smart/ SMART] system, including the vector space model
, relevance feedback
, and Rocchio Classification
.
Gerard Salton
led the group that developed SMART. Other contributors included Mike Lesk
.
The SMART system also provides a set a corpora, queries and reference rankings, taken from different subjects, notably
To the legacy of the SMART system belongs the so-called SMART notation, a mnemonic scheme for denoting tf-idf weighting variants in the vector space model. The mnemonic for representing a combination of weights takes the form ddd.qqq, where the first three letters represents the term weighting of the document vector and the second three letters represents the term weighting for the query vector. The letter representation for a term, , and document,
, and document, 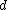 , is as follows :
, is as follows :
where tf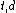 is the term frequency of term
is the term frequency of term  in document
in document 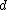 .
.
Information retrieval
Information retrieval is the area of study concerned with searching for documents, for information within documents, and for metadata about documents, as well as that of searching structured storage, relational databases, and the World Wide Web...
system developed at Cornell University
Cornell University
Cornell University is an Ivy League university located in Ithaca, New York, United States. It is a private land-grant university, receiving annual funding from the State of New York for certain educational missions...
in the 1960s. Many important concepts in information retrieval were developed as part of research on the [ftp://ftp.cs.cornell.edu/pub/smart/ SMART] system, including the vector space model
Vector space model
Vector space model is an algebraic model for representing text documents as vectors of identifiers, such as, for example, index terms. It is used in information filtering, information retrieval, indexing and relevancy rankings...
, relevance feedback
Relevance feedback
Relevance feedback is a feature of some information retrieval systems. The idea behind relevance feedback is to take the results that are initially returned from a given query and to use information about whether or not those results are relevant to perform a new query...
, and Rocchio Classification
Rocchio Classification
Rocchio Classification is based on a method of relevance feedback found in information retrieval systems which stemmed from the SMART Information Retrieval System around the year 1970. Like many other retrieval systems, the Rocchio feedback approach was developed using the Vector Space Model...
.
Gerard Salton
Gerard Salton
Gerard Salton , also known as Gerry Salton, was a Professor of Computer Science at Cornell University. Salton was perhaps the leading computer scientist working in the field of information retrieval during his time...
led the group that developed SMART. Other contributors included Mike Lesk
Mike Lesk
Michael E. Lesk is a computer programmer.In the 1960s, Michael Lesk worked for the SMART Information Retrieval System project, wrote much of its retrieval code and did many of the retrieval experiments, as well as obtaining a PhD in Chemical Physics....
.
The SMART system also provides a set a corpora, queries and reference rankings, taken from different subjects, notably
- ADI: publications from information science reviews [ftp://ftp.cs.cornell.edu/pub/smart/adi]
- CACM: computer science [ftp://ftp.cs.cornell.edu/pub/smart/cacm]
- Cranfield collection : publications from aeronautic reviews [ftp://ftp.cs.cornell.edu/pub/smart/cran/]
- CISI: library science [ftp://ftp.cs.cornell.edu/pub/smart/cisi]
- Medlars collection : publications from medical reviews [ftp://ftp.cs.cornell.edu/pub/smart/med/]
- Time magazine collection : archives of the generalist review TimeTime (magazine)Time is an American news magazine. A European edition is published from London. Time Europe covers the Middle East, Africa and, since 2003, Latin America. An Asian edition is based in Hong Kong...
in 1963 [ftp://ftp.cs.cornell.edu/pub/smart/time/]
To the legacy of the SMART system belongs the so-called SMART notation, a mnemonic scheme for denoting tf-idf weighting variants in the vector space model. The mnemonic for representing a combination of weights takes the form ddd.qqq, where the first three letters represents the term weighting of the document vector and the second three letters represents the term weighting for the query vector. The letter representation for a term,
 , and document,
, and document, 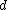 , is as follows :
, is as follows :| Term frequency | Document frequency | Normalization |
|---|---|---|
n (natural): 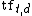 |
n (no): 1 | n (none): 1 |
l (logarithm): 1+log(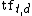 ) ) |
t (idf): log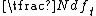 |
c (cosine): 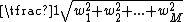 |
a (augmented): 0.5 + 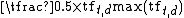 |
p (prob idf): 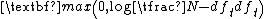 |
b (byte size): 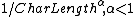 |
b (boolean): 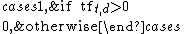 |
||
L (log average): 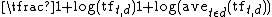 |
where tf
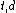 is the term frequency of term
is the term frequency of term  in document
in document 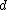 .
.External links
- [ftp://ftp.cs.cornell.edu/pub/smart/ Software and test collections] (FTP at Cornell UniversityCornell UniversityCornell University is an Ivy League university located in Ithaca, New York, United States. It is a private land-grant university, receiving annual funding from the State of New York for certain educational missions...
) - Interactive SMART tutorial
- SMART case study - Eric Thul
- SMART tutorial for beginners - Hans Paijimas

