SCSI high byte termination
Encyclopedia
In SCSI
computer systems, there is a special case with mixed 8-bit and 16-bit devices where high-byte termination may be required.
Most parallel SCSI
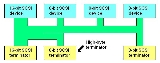
busses are terminated at each end. However where the bus width is not constant, it is sometimes necessary to provide special termination for the high byte and the associated parity bit. This high-byte termination can use standard SCSI termination techniques, such as a passive terminator, active terminator, or a forced-perfect terminator. This diagram shows a typical SCSI high-byte termination scheme:

There is a simplification to this which is sometimes used in the case where there is only one 16-bit (wide) device connected to one or more 8-bit (narrow) devices. Then it is possible to wire all the eight spare data bits and the ninth parity bit together and to terminate them with a single resistor circuit to TERMPOWER. So in the case of a differential SCSI bus, it is possible to terminate all 18 spare signal wires with just one resistor. This method is not considered good practice, but has been successfully used in some SCSI products.
SCSI
Small Computer System Interface is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, and electrical and optical interfaces. SCSI is most commonly used for hard disks and tape drives, but it...
computer systems, there is a special case with mixed 8-bit and 16-bit devices where high-byte termination may be required.
Most parallel SCSI
Parallel SCSI
Parallel SCSI is one of the interface implementations in the SCSI family. In addition to being a data bus, SPI is a parallel electrical bus: There is one set of electrical connections stretching from one end of the SCSI bus to the other. A SCSI device attaches to the bus but does not interrupt it...
busses are terminated at each end. However where the bus width is not constant, it is sometimes necessary to provide special termination for the high byte and the associated parity bit. This high-byte termination can use standard SCSI termination techniques, such as a passive terminator, active terminator, or a forced-perfect terminator. This diagram shows a typical SCSI high-byte termination scheme:

There is a simplification to this which is sometimes used in the case where there is only one 16-bit (wide) device connected to one or more 8-bit (narrow) devices. Then it is possible to wire all the eight spare data bits and the ninth parity bit together and to terminate them with a single resistor circuit to TERMPOWER. So in the case of a differential SCSI bus, it is possible to terminate all 18 spare signal wires with just one resistor. This method is not considered good practice, but has been successfully used in some SCSI products.

