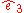Rotation operator (vector space)
Encyclopedia
This article derives the main properties of rotations in 3-dimensional space.
The three Euler rotations
are one way to bring a rigid object to any desired orientation by sequentially making rotations about axis' fixed relative to the object. However, this can also be achieved with one single rotation (Euler's rotation theorem
). Using the concepts of linear algebra
it is shown how this single
rotation can be performed.
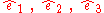
be a coordinate system fixed in the body that through a change in orientation is brought to the new directions
Any vector
of the body is then brought to the new direction
i.e. this is a linear operator
The matrix of this operator relative the coordinate system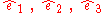
is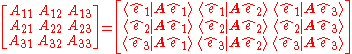
As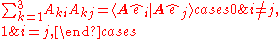
or equivalently in matrix notation
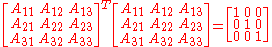
the matrix is orthogonal
and as a "right hand" base vector system is re-orientated into another "right hand" system the determinant
of this matrix has the value 1.
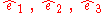
be an orthogonal positively oriented base vector system in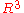 .
.
The linear operator
"Rotation with the angle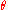 around the axis defined by
around the axis defined by 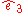 "
"
has the matrix representation
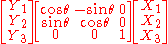
relative to this basevector system.
This then means that a vector
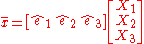
is rotated to the vector
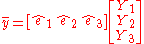
by the linear operator.
The determinant
of this matrix is
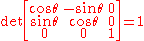
and the characteristic polynomial
is
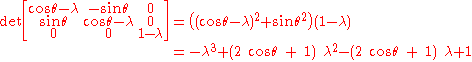
The matrix is symmetric if and only if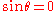 , i.e. for
, i.e. for 
and for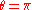 .
.
The case is the trivial case of an identity operator.
is the trivial case of an identity operator.
For the case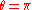 the characteristic polynomial
the characteristic polynomial
is
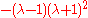
i.e. the rotation operator has the eigenvalues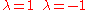
The eigenspace corresponding to is all vectors on the rotation axis, i.e. all vectors
is all vectors on the rotation axis, i.e. all vectors

The eigenspace corresponding to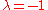 consists of all vectors orthogonal to the rotation axis, i.e. all vectors
consists of all vectors orthogonal to the rotation axis, i.e. all vectors

For all other values of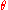 the matrix is un-symmetric and as
the matrix is un-symmetric and as 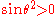 there is
there is
only the eigenvalue with the one-dimensional eigenspace of the vectors on the rotation axis:
with the one-dimensional eigenspace of the vectors on the rotation axis:

"Rotation with the angle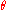 around a specified axis"
around a specified axis"
discussed above is an orthogonal mapping and its matrix relative any base vector system is therefore an
orthogonal matrix
. Further more its determinant has the value 1.
A non-trivial fact is the opposite, i.e. that for any orthogonal linear mapping in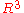 having
having
determinant = 1 there exist base vectors
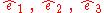
such that the matrix takes the "canonical form"
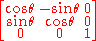
for some value of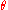 .
.
In fact, if a linear operator has the orthogonal matrix
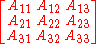
relative some base vector system
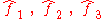
and this matrix is symmetric the "Symmetric operator theorem" valid in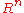 (any dimension) applies saying
(any dimension) applies saying
that it has n orthogonal eigenvectors. This means for the 3-dimensional case that there exists a coordinate system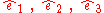
such that the matrix takes the form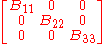
As it is an orthogonal matrix these diagonal elements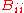 are either 1 or −1. As the determinant is 1 these elements
are either 1 or −1. As the determinant is 1 these elements
are either all 1 or one of the elements is 1 and the other two are −1.
In the first case it is the trivial identity operator corresponding
to .
.
In the second case it has the form
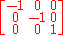
if the basevectors are numbered such that the one with eigenvalue 1 has index 3. This matrix is then of the desired form for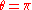 .
.
If the matrix is un-symmetric the vector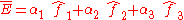
where
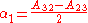
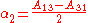
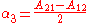
is non-zero. This vector is an eigenvector with eigenvalue

Setting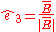
and selecting any two orthogonal unit vectors in the plane orthogonal to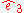 :
:
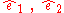
such that
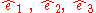
form a positively oriented trippel the operator takes the desired form with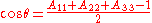
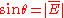
The expressions above are in fact valid also for the case of a symmetric
rotation operator corresponding to a rotation with
or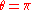 . But the difference is that for
. But the difference is that for 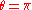
the vector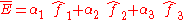
is zero and of no use for finding the eigenspace of eigenvalue 1, i.e. the
rotation axis.
Defining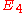 as
as 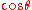 the matrix for the
the matrix for the
rotation operator is
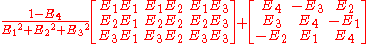
provided that
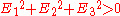
i.e. except for the cases (the identity operator) and
(the identity operator) and 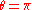
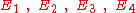 with
with
the difference that the half angle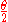 is used
is used
instead of the full angle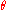 .
.
This means that the first 3 components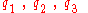 are components of a vector defined from
are components of a vector defined from
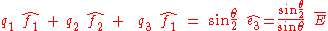
and that the fourth component is the scalar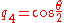
As the angle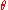 defined from the canonical form is in the interval
defined from the canonical form is in the interval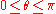
one would normally have that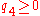 . But a "dual" representation of a rotation with quaternions
. But a "dual" representation of a rotation with quaternions
is used, i.e.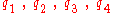
and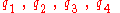
are two alternative representations of one and the same rotation.
The entities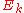 are defined from the quaternions by
are defined from the quaternions by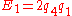
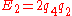
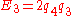
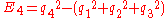
Using quaternions the matrix of the rotation operator is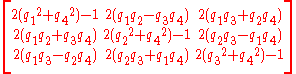
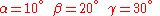
relative a given base vector system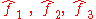
Corresponding matrix relative to this base vector system is (see Euler angles#Matrix notation)
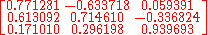
and the quaternion is
The canonical form of this operator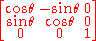
with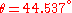 is obtained with
is obtained with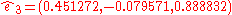
The quaternion relative to this new system is then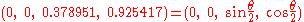
Instead of making the three Euler rotations
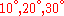
the same orientation can be reached with one single rotation of size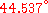 around
around 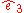
The three Euler rotations
Euler angles
The Euler angles are three angles introduced by Leonhard Euler to describe the orientation of a rigid body. To describe such an orientation in 3-dimensional Euclidean space three parameters are required...
are one way to bring a rigid object to any desired orientation by sequentially making rotations about axis' fixed relative to the object. However, this can also be achieved with one single rotation (Euler's rotation theorem
Euler's rotation theorem
In geometry, Euler's rotation theorem states that, in three-dimensional space, any displacement of a rigid body such that a point on the rigid body remains fixed, is equivalent to a single rotation about some axis that runs through the fixed point. It also means that the composition of two...
). Using the concepts of linear algebra
Linear algebra
Linear algebra is a branch of mathematics that studies vector spaces, also called linear spaces, along with linear functions that input one vector and output another. Such functions are called linear maps and can be represented by matrices if a basis is given. Thus matrix theory is often...
it is shown how this single
rotation can be performed.
Mathematical formulation
Let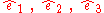
be a coordinate system fixed in the body that through a change in orientation is brought to the new directions

Any vector

of the body is then brought to the new direction

i.e. this is a linear operator
The matrix of this operator relative the coordinate system
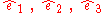
is
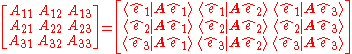
As
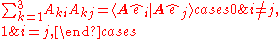
or equivalently in matrix notation
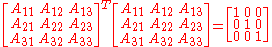
the matrix is orthogonal
Orthogonal matrix
In linear algebra, an orthogonal matrix , is a square matrix with real entries whose columns and rows are orthogonal unit vectors ....
and as a "right hand" base vector system is re-orientated into another "right hand" system the determinant
Determinant
In linear algebra, the determinant is a value associated with a square matrix. It can be computed from the entries of the matrix by a specific arithmetic expression, while other ways to determine its value exist as well...
of this matrix has the value 1.
Rotation around an axis
Let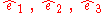
be an orthogonal positively oriented base vector system in
 .
.The linear operator
"Rotation with the angle
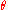 around the axis defined by
around the axis defined by 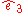 "
"has the matrix representation
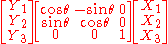
relative to this basevector system.
This then means that a vector
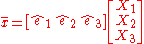
is rotated to the vector
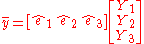
by the linear operator.
The determinant
Determinant
In linear algebra, the determinant is a value associated with a square matrix. It can be computed from the entries of the matrix by a specific arithmetic expression, while other ways to determine its value exist as well...
of this matrix is
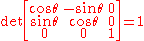
and the characteristic polynomial
Characteristic polynomial
In linear algebra, one associates a polynomial to every square matrix: its characteristic polynomial. This polynomial encodes several important properties of the matrix, most notably its eigenvalues, its determinant and its trace....
is
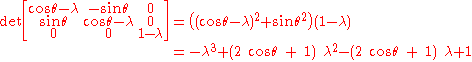
The matrix is symmetric if and only if
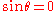 , i.e. for
, i.e. for 
and for
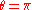 .
.The case
 is the trivial case of an identity operator.
is the trivial case of an identity operator.For the case
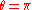 the characteristic polynomial
the characteristic polynomialCharacteristic polynomial
In linear algebra, one associates a polynomial to every square matrix: its characteristic polynomial. This polynomial encodes several important properties of the matrix, most notably its eigenvalues, its determinant and its trace....
is
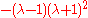
i.e. the rotation operator has the eigenvalues
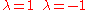
The eigenspace corresponding to
 is all vectors on the rotation axis, i.e. all vectors
is all vectors on the rotation axis, i.e. all vectors
The eigenspace corresponding to
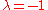 consists of all vectors orthogonal to the rotation axis, i.e. all vectors
consists of all vectors orthogonal to the rotation axis, i.e. all vectors
For all other values of
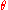 the matrix is un-symmetric and as
the matrix is un-symmetric and as 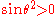 there is
there isonly the eigenvalue
 with the one-dimensional eigenspace of the vectors on the rotation axis:
with the one-dimensional eigenspace of the vectors on the rotation axis:
The general case
The operator"Rotation with the angle
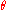 around a specified axis"
around a specified axis"discussed above is an orthogonal mapping and its matrix relative any base vector system is therefore an
orthogonal matrix
Orthogonal matrix
In linear algebra, an orthogonal matrix , is a square matrix with real entries whose columns and rows are orthogonal unit vectors ....
. Further more its determinant has the value 1.
A non-trivial fact is the opposite, i.e. that for any orthogonal linear mapping in
 having
havingdeterminant = 1 there exist base vectors
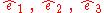
such that the matrix takes the "canonical form"
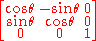
for some value of
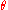 .
.In fact, if a linear operator has the orthogonal matrix
Orthogonal matrix
In linear algebra, an orthogonal matrix , is a square matrix with real entries whose columns and rows are orthogonal unit vectors ....
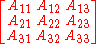
relative some base vector system
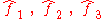
and this matrix is symmetric the "Symmetric operator theorem" valid in
 (any dimension) applies saying
(any dimension) applies sayingthat it has n orthogonal eigenvectors. This means for the 3-dimensional case that there exists a coordinate system
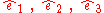
such that the matrix takes the form
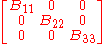
As it is an orthogonal matrix these diagonal elements
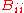 are either 1 or −1. As the determinant is 1 these elements
are either 1 or −1. As the determinant is 1 these elementsare either all 1 or one of the elements is 1 and the other two are −1.
In the first case it is the trivial identity operator corresponding
to
 .
.In the second case it has the form
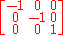
if the basevectors are numbered such that the one with eigenvalue 1 has index 3. This matrix is then of the desired form for
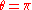 .
.If the matrix is un-symmetric the vector
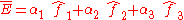
where
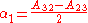
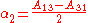
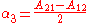
is non-zero. This vector is an eigenvector with eigenvalue

Setting
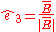
and selecting any two orthogonal unit vectors in the plane orthogonal to
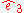 :
: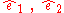
such that
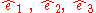
form a positively oriented trippel the operator takes the desired form with
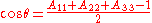
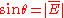
The expressions above are in fact valid also for the case of a symmetric
rotation operator corresponding to a rotation with

or
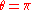 . But the difference is that for
. But the difference is that for 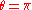
the vector
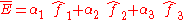
is zero and of no use for finding the eigenspace of eigenvalue 1, i.e. the
rotation axis.
Defining
 as
as  the matrix for the
the matrix for therotation operator is
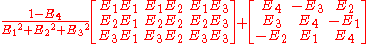
provided that
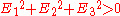
i.e. except for the cases
 (the identity operator) and
(the identity operator) and 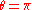
Quaternions
Quaternions are defined similar to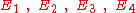 with
withthe difference that the half angle
 is used
is usedinstead of the full angle
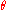 .
.This means that the first 3 components
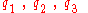 are components of a vector defined from
are components of a vector defined from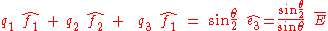
and that the fourth component is the scalar
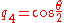
As the angle
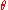 defined from the canonical form is in the interval
defined from the canonical form is in the interval
one would normally have that
 . But a "dual" representation of a rotation with quaternions
. But a "dual" representation of a rotation with quaternionsis used, i.e.
and
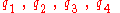
are two alternative representations of one and the same rotation.
The entities
 are defined from the quaternions by
are defined from the quaternions by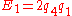
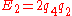
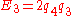
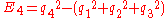
Using quaternions the matrix of the rotation operator is
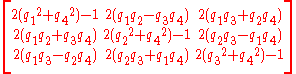
Numerical example
Consider the reorientation corresponding to the Euler angles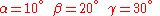
relative a given base vector system
Corresponding matrix relative to this base vector system is (see Euler angles#Matrix notation)
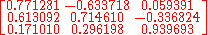
and the quaternion is

The canonical form of this operator
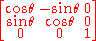
with
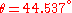 is obtained with
is obtained with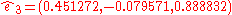
The quaternion relative to this new system is then
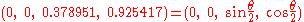
Instead of making the three Euler rotations
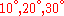
the same orientation can be reached with one single rotation of size
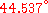 around
around