
Rossby parameter
Encyclopedia
The Rossby parameter is a number used in geophysics
and meteorology
which arises due to the meridional variation of the Coriolis force caused by the spherical shape of the Earth. It is important in the generation of Rossby wave
s.
The Rossby parameter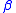 is given by the equation:
is given by the equation:
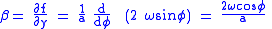
Where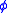 is the latitude,
is the latitude, 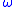 is the angular speed of the Earth's rotation, and a is the mean radius of the Earth.
is the angular speed of the Earth's rotation, and a is the mean radius of the Earth.
Although both involve Coriolis effects, the Rossby parameter describes the variation of the effects with latitude (hence the latitudinal derivative
), and should not be confused with the Rossby number
.
Geophysics
Geophysics is the physics of the Earth and its environment in space; also the study of the Earth using quantitative physical methods. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and...
and meteorology
Meteorology
Meteorology is the interdisciplinary scientific study of the atmosphere. Studies in the field stretch back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not occur until the 18th century. The 19th century saw breakthroughs occur after observing networks developed across several countries...
which arises due to the meridional variation of the Coriolis force caused by the spherical shape of the Earth. It is important in the generation of Rossby wave
Rossby wave
Atmospheric Rossby waves are giant meanders in high-altitude winds that are a major influence on weather.They are not to be confused with oceanic Rossby waves, which move along the thermocline: that is, the boundary between the warm upper layer of the ocean and the cold deeper part of the...
s.
The Rossby parameter
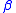 is given by the equation:
is given by the equation: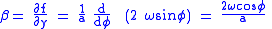
Where
 is the latitude,
is the latitude,  is the angular speed of the Earth's rotation, and a is the mean radius of the Earth.
is the angular speed of the Earth's rotation, and a is the mean radius of the Earth.Although both involve Coriolis effects, the Rossby parameter describes the variation of the effects with latitude (hence the latitudinal derivative
Derivative
In calculus, a branch of mathematics, the derivative is a measure of how a function changes as its input changes. Loosely speaking, a derivative can be thought of as how much one quantity is changing in response to changes in some other quantity; for example, the derivative of the position of a...
), and should not be confused with the Rossby number
Rossby number
The Rossby number, named for Carl-Gustav Arvid Rossby, is a dimensionless number used in describing fluid flow. The Rossby number is the ratio of inertial to Coriolis force, terms v\cdot\nabla v\sim U^2 / L and \Omega\times v\sim U\Omega in the Navier–Stokes equations, respectively...
.

