Romano-Ward syndrome
Encyclopedia
Romano-Ward syndrome, is the major variant of long QT syndrome. It is a condition that causes a disruption of the heart's normal rhythm. This disorder is a form of long QT syndrome
, which is a heart condition that causes the cardiac muscle
to take longer than usual to recharge between beats. If untreated, the irregular heartbeats can lead to fainting, seizure
s, or sudden death.
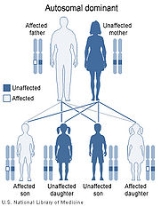
 Romano-Ward syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. It is the most common form of inherited long QT syndrome, affecting an estimated 1 in 5,000 people worldwide, although more people may be affected but never experience any signs or symptoms of the condition.
Romano-Ward syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. It is the most common form of inherited long QT syndrome, affecting an estimated 1 in 5,000 people worldwide, although more people may be affected but never experience any signs or symptoms of the condition.
, KCNE1
, KCNE2
, KCNH2, KCNQ1, and SCN5A
genes cause Romano-Ward syndrome. The proteins made by most of these genes form channels that transport positively-charged ions
, such as potassium
and sodium
, in and out of cell
s. In cardiac muscle, these ion channels play critical roles in maintaining the heart's normal rhythm. Mutations in any of these genes alter the structure or function of channels, which changes the flow of ions between cells. A disruption in ion transport alters the way the heart beats, leading to the abnormal heart rhythm characteristic of Romano-Ward syndrome.
Unlike most genes related to Romano-Ward syndrome, the ANK2 gene does not produce an ion channel
. The protein made by the ANK2 gene ensures that other proteins, particularly ion channels, are inserted into the cell membrane
appropriately. A mutation in the ANK2 gene likely alters the flow of ions between cells in the heart, which disrupts the heart's normal rhythm and results in the features of Romano-Ward syndrome.
This article incorporates public domain text from The U.S. National Library of Medicine
Long QT syndrome
The long QT syndrome is a rare inborn heart condition in which delayed repolarization of the heart following a heartbeat increases the risk of episodes of torsade de pointes . These episodes may lead to palpitations, fainting and sudden death due to ventricular fibrillation...
, which is a heart condition that causes the cardiac muscle
Cardiac muscle
Cardiac muscle is a type of involuntary striated muscle found in the walls and histologic foundation of the heart, specifically the myocardium. Cardiac muscle is one of three major types of muscle, the others being skeletal and smooth muscle...
to take longer than usual to recharge between beats. If untreated, the irregular heartbeats can lead to fainting, seizure
Seizure
An epileptic seizure, occasionally referred to as a fit, is defined as a transient symptom of "abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain". The outward effect can be as dramatic as a wild thrashing movement or as mild as a brief loss of awareness...
s, or sudden death.
Inheritance

Causes
Mutations in the ANK2ANK2
Ankyrin 2, neuronal, also known as ANK2, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ANK2 gene.-Function:The protein encoded by this gene is required for targeting and stability of Na+/Ca++ exchanger 1 in cardiomyocytes. Mutations in this gene cause long QT syndrome 4...
, KCNE1
KCNE1
Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily E member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNE1 gene.KCNE1 is a gene associated with Long QT syndrome type 5. It can both cause Romano-Wards syndrome and Jervell Lange-Nielsens syndrome -External links:*...
, KCNE2
KCNE2
Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily E member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNE2 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a voltage-gated potassium channel accessory subunit associated with Long QT syndrome....
, KCNH2, KCNQ1, and SCN5A
SCN5A
The Nav1.5 is a sodium ion channel protein that in humans is encoded by the SCN5A gene. Mutations in the gene are associated with long QT syndrome type 3 , Brugada syndrome, primary cardiac conduction disease and idiopathic ventricular fibrillation....
genes cause Romano-Ward syndrome. The proteins made by most of these genes form channels that transport positively-charged ions
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
, such as potassium
Potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K and atomic number 19. Elemental potassium is a soft silvery-white alkali metal that oxidizes rapidly in air and is very reactive with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite the hydrogen emitted in the reaction.Potassium and sodium are...
and sodium
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal and is a member of the alkali metals; its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists in numerous minerals, most commonly as sodium chloride...
, in and out of cell
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
s. In cardiac muscle, these ion channels play critical roles in maintaining the heart's normal rhythm. Mutations in any of these genes alter the structure or function of channels, which changes the flow of ions between cells. A disruption in ion transport alters the way the heart beats, leading to the abnormal heart rhythm characteristic of Romano-Ward syndrome.
Unlike most genes related to Romano-Ward syndrome, the ANK2 gene does not produce an ion channel
Ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming proteins that help establish and control the small voltage gradient across the plasma membrane of cells by allowing the flow of ions down their electrochemical gradient. They are present in the membranes that surround all biological cells...
. The protein made by the ANK2 gene ensures that other proteins, particularly ion channels, are inserted into the cell membrane
Cell membrane
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell...
appropriately. A mutation in the ANK2 gene likely alters the flow of ions between cells in the heart, which disrupts the heart's normal rhythm and results in the features of Romano-Ward syndrome.
This article incorporates public domain text from The U.S. National Library of Medicine

