
Robinson's joint consistency theorem
Encyclopedia
Robinson's joint consistency theorem is an important theorem of mathematical logic
. It is related to Craig interpolation
and Beth definability
.
The classical formulation of Robinson's joint consistency theorem is as follows:
Let and
and 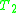 be first-order
be first-order
theories. If and
and  are consistent and the intersection
are consistent and the intersection  is complete
is complete
(in the common language of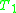 and
and 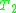 ), then the union
), then the union 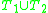 is consistent. Note that a theory is complete if it decides every formula, i.e. either
is consistent. Note that a theory is complete if it decides every formula, i.e. either 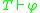 or
or 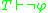 .
.
Since the completeness assumption is quite hard to fulfill, there is a variant of the theorem:
Let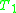 and
and 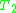 be first-order
be first-order
theories. If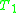 and
and 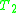 are consistent and if there is no formula
are consistent and if there is no formula  in the common language of
in the common language of 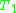 and
and 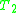 such that
such that 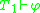 and
and  , then the union
, then the union 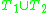 is consistent.
is consistent.
Mathematical logic
Mathematical logic is a subfield of mathematics with close connections to foundations of mathematics, theoretical computer science and philosophical logic. The field includes both the mathematical study of logic and the applications of formal logic to other areas of mathematics...
. It is related to Craig interpolation
Craig interpolation
In mathematical logic, Craig's interpolation theorem is a result about the relationship between different logical theories. Roughly stated, the theorem says that if a formula φ implies a formula ψ then there is a third formula ρ, called an interpolant, such that every nonlogical symbol...
and Beth definability
Beth definability
In mathematical logic, Beth definability states that if for any two models A, B of a first-order theory T in the language L' ⊇ L with A|L = B|L it is satisfied A ⊨ φ[a] if and only if B ⊨ φ[a] for φ a formula in L' and for all tuples a of A, then φ is equivalent modulo T to a formula ψ...
.
The classical formulation of Robinson's joint consistency theorem is as follows:
Let
 and
and 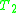 be first-order
be first-orderFirst-order logic
First-order logic is a formal logical system used in mathematics, philosophy, linguistics, and computer science. It goes by many names, including: first-order predicate calculus, the lower predicate calculus, quantification theory, and predicate logic...
theories. If
 and
and  are consistent and the intersection
are consistent and the intersection  is complete
is completeComplete theory
In mathematical logic, a theory is complete if it is a maximal consistent set of sentences, i.e., if it is consistent, and none of its proper extensions is consistent...
(in the common language of
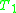 and
and 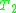 ), then the union
), then the union 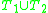 is consistent. Note that a theory is complete if it decides every formula, i.e. either
is consistent. Note that a theory is complete if it decides every formula, i.e. either 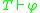 or
or 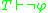 .
.Since the completeness assumption is quite hard to fulfill, there is a variant of the theorem:
Let
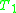 and
and 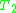 be first-order
be first-orderFirst-order logic
First-order logic is a formal logical system used in mathematics, philosophy, linguistics, and computer science. It goes by many names, including: first-order predicate calculus, the lower predicate calculus, quantification theory, and predicate logic...
theories. If
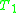 and
and 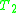 are consistent and if there is no formula
are consistent and if there is no formula 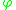 in the common language of
in the common language of 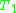 and
and 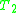 such that
such that 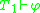 and
and  , then the union
, then the union 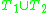 is consistent.
is consistent.

