
Reynolds decomposition
Encyclopedia
In fluid dynamics
and the theory of turbulence
, Reynolds decomposition is a mathematical
technique to separate the average and fluctuating parts of a quantity.
For example, for a quantity the decomposition would be
the decomposition would be
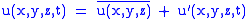
where denotes the time average of
denotes the time average of  (often called the steady component), and
(often called the steady component), and
 the fluctuating part (or perturbations). The perturbations are defined such that their time average equals zero.
the fluctuating part (or perturbations). The perturbations are defined such that their time average equals zero.
This allows us to simplify the Navier-Stokes equations
by substituting in the sum of the steady component and perturbations to the velocity profile and taking the mean value. The resulting equation contains a nonlinear term known as the Reynolds stresses
which gives rise to turbulence
.
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
and the theory of turbulence
Turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic and stochastic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and velocity in space and time...
, Reynolds decomposition is a mathematical
technique to separate the average and fluctuating parts of a quantity.
For example, for a quantity
 the decomposition would be
the decomposition would be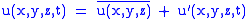
where
 denotes the time average of
denotes the time average of  (often called the steady component), and
(often called the steady component), and the fluctuating part (or perturbations). The perturbations are defined such that their time average equals zero.
the fluctuating part (or perturbations). The perturbations are defined such that their time average equals zero.This allows us to simplify the Navier-Stokes equations
Navier-Stokes equations
In physics, the Navier–Stokes equations, named after Claude-Louis Navier and George Gabriel Stokes, describe the motion of fluid substances. These equations arise from applying Newton's second law to fluid motion, together with the assumption that the fluid stress is the sum of a diffusing viscous...
by substituting in the sum of the steady component and perturbations to the velocity profile and taking the mean value. The resulting equation contains a nonlinear term known as the Reynolds stresses
Reynolds stresses
In fluid dynamics, the Reynolds stress is the stress tensor in a fluid obtained from the averaging operation over the Navier-Stokes equations to account for turbulent fluctuations in fluid momentum.-Definition:...
which gives rise to turbulence
Turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic and stochastic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and velocity in space and time...
.
See also
- Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes equationsReynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes equationsThe Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes equations are time-averagedequations of motion for fluid flow. The idea behind the equations is Reynolds decomposition, whereby an instantaneous quantity is decomposed into its time-averaged and fluctuating quantities, an idea first proposed by Osborne Reynolds...
- TurbulenceTurbulenceIn fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic and stochastic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and velocity in space and time...

