
Retarded time
Encyclopedia
According to Maxwell's Equations
, electromagnetic waves in a vacuum
travel at the speed of light
, c. Since c is finite, a photon
emitted when t = t0 takes a certain amount of time to reach an observer located at a distance r from the source, so that the observer only notices it when t = t1:
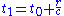
This can be rearranged as:

The time is defined as the retarded time and represents the delay between the photon emission and the moment at which it reaches the observer.
is defined as the retarded time and represents the delay between the photon emission and the moment at which it reaches the observer.
The idea is prominent in the Wheeler-Feynman absorber theory.
Maxwell's equations
Maxwell's equations are a set of partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electrodynamics, classical optics, and electric circuits. These fields in turn underlie modern electrical and communications technologies.Maxwell's equations...
, electromagnetic waves in a vacuum
Vacuum
In everyday usage, vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter, such that its gaseous pressure is much less than atmospheric pressure. The word comes from the Latin term for "empty". A perfect vacuum would be one with no particles in it at all, which is impossible to achieve in...
travel at the speed of light
Speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
, c. Since c is finite, a photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
emitted when t = t0 takes a certain amount of time to reach an observer located at a distance r from the source, so that the observer only notices it when t = t1:
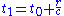
This can be rearranged as:

The time
 is defined as the retarded time and represents the delay between the photon emission and the moment at which it reaches the observer.
is defined as the retarded time and represents the delay between the photon emission and the moment at which it reaches the observer.The idea is prominent in the Wheeler-Feynman absorber theory.
See also
- Antenna measurementAntenna measurementAntenna measurement techniques refers to the testing of antennas to ensure that the antenna meets specifications or simply to characterize it. Typical parameters of antennas are gain, radiation pattern, beamwidth, polarization, and impedance....
- Electromagnetic four-potentialElectromagnetic four-potentialThe electromagnetic four-potential is a potential from which the electromagnetic field can be derived. It combines both the electric scalar potential and the magnetic vector potential into a single space-time four-vector. In a given reference frame, the first component is the scalar potential and...
- Jefimenko's equationsJefimenko's equationsIn electromagnetism, Jefimenko's equations describe the behavior of the electric and magnetic fields in terms of the charge and current distributions at retarded times....
- Liénard–Wiechert potential
- Wheeler-Feynman absorber theory also known as the Wheeler-Feynman time-symmetric theory

