
Respiratory alkalosis
Encyclopedia
Respiratory alkalosis is a medical condition in which increased respiration (hyperventilation
) elevates the blood pH
(a condition generally called alkalosis
). It is one of four basic categories of disruption of acid-base homeostasis
.
and acute
.
from the circulation. This alters the dynamic chemical equilibrium
of carbon dioxide in the circulatory system, and the system reacts according to Le Chatelier's principle
. Circulating hydrogen ions and bicarbonate are shifted through the carbonic acid
(H2CO3) intermediate to make more CO2 via the enzyme carbonic anhydrase
according to the following reaction:
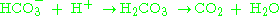
The net result of this is decreased circulating hydrogen ion concentration, and thus increased pH
(alkalosis). There is also a decrease in ionized blood calcium
concentration.
. Other causes include:
(such as tetany
and fainting) with no fall in total serum calcium levels.
In some cases, from someone who has had acute respiratory alkalemia caused by chronic hyperventilation syndrome, this can sometimes result in massive amounts of pain and disorientation. The pH levels change dramatically in order to compensate for the lactic acid [which the muscles under normal fight or flight circumstances would be pumping out] it believes to be entering the blood stream. The dramatic shift causes a 'physical confusion' which translates to a burning pain that comes from everywhere, and can also alter the brain chemistry which leads to confusion at best and feeling like 'I was in the wrong body" for anywhere from five minutes to a half an hour as the body reorients itself. Note: this is in extreme cases.
, Michael Crichton
's first novel, scientists instruct a town's sole adult survivor of an extraterrestrial-pathogenic
epidemic to hyperventilate in order to raise his blood pH to a level inhospitable to the pathogen (the "strain" in the title).
Hyperventilation
Hyperventilation or overbreathing is the state of breathing faster or deeper than normal, causing excessive expulsion of circulating carbon dioxide. It can result from a psychological state such as a panic attack, from a physiological condition such as metabolic acidosis, can be brought about by...
) elevates the blood pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
(a condition generally called alkalosis
Alkalosis
Alkalosis refers to a condition reducing hydrogen ion concentration of arterial blood plasma . Generally, alkalosis is said to occur when pH of the blood exceeds 7.45. The opposite condition is acidosis .-Causes:...
). It is one of four basic categories of disruption of acid-base homeostasis
Acid-base homeostasis
Acid–base homeostasis is the part of human homeostasis concerning the proper balance between acids and bases, in other words, the pH. The body is very sensitive to its pH level, so strong mechanisms exist to maintain it...
.
Terminology
- Alkalosis refers to a high pH in tissue.
- Alkalemia refers to a high pH in the blood.
Types
There are two types of respiratory alkalosis: chronicChronic (medicine)
A chronic disease is a disease or other human health condition that is persistent or long-lasting in nature. The term chronic is usually applied when the course of the disease lasts for more than three months. Common chronic diseases include asthma, cancer, diabetes and HIV/AIDS.In medicine, the...
and acute
Acute (medicine)
In medicine, an acute disease is a disease with either or both of:# a rapid onset, as in acute infection# a short course ....
.
- Acute respiratory alkalosis occurs rapidly. During acute respiratory alkalosis, the person may lose consciousness where the rate of ventilation will resume to normal.
- Chronic respiratory alkalosis is a more long-standing condition. For every 10 mM drop in pCO2 in blood, there is a corresponding 5 mM of bicarbonate ion drop. The drop of 5 mM of bicarbonate ion is a compensation effect which reduces the alkalosis effect of the drop in pCO2 in blood. This is termed metabolic compensation.
Mechanism
Respiratory alkalosis generally occurs when some stimulus (see "Causes" below) makes a person hyperventilate. The increased breathing produces increased alveolar respiration, expelling CO2Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
from the circulation. This alters the dynamic chemical equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which the concentrations of the reactants and products have not yet changed with time. It occurs only in reversible reactions, and not in irreversible reactions. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same...
of carbon dioxide in the circulatory system, and the system reacts according to Le Chatelier's principle
Le Châtelier's principle
In chemistry, Le Chatelier's principle, also called the Chatelier's principle, can be used to predict the effect of a change in conditions on a chemical equilibrium. The principle is named after Henry Louis Le Chatelier and sometimes Karl Ferdinand Braun who discovered it independently...
. Circulating hydrogen ions and bicarbonate are shifted through the carbonic acid
Carbonic acid
Carbonic acid is the inorganic compound with the formula H2CO3 . It is also a name sometimes given to solutions of carbon dioxide in water, because such solutions contain small amounts of H2CO3. Carbonic acid forms two kinds of salts, the carbonates and the bicarbonates...
(H2CO3) intermediate to make more CO2 via the enzyme carbonic anhydrase
Carbonic anhydrase
The carbonic anhydrases form a family of enzymes that catalyze the rapid interconversion of carbon dioxide and water to bicarbonate and protons , a reversible reaction that occurs rather slowly in the absence of a catalyst...
according to the following reaction:
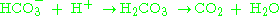
The net result of this is decreased circulating hydrogen ion concentration, and thus increased pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
(alkalosis). There is also a decrease in ionized blood calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
concentration.
Causes
Respiratory alkalosis may be produced accidentally (iatrogenically) during excessive mechanical ventilationMechanical ventilation
In medicine, mechanical ventilation is a method to mechanically assist or replace spontaneous breathing. This may involve a machine called a ventilator or the breathing may be assisted by a physician, respiratory therapist or other suitable person compressing a bag or set of bellows...
. Other causes include:
- psychiatricPsychiatryPsychiatry is the medical specialty devoted to the study and treatment of mental disorders. These mental disorders include various affective, behavioural, cognitive and perceptual abnormalities...
causes: anxietyAnxietyAnxiety is a psychological and physiological state characterized by somatic, emotional, cognitive, and behavioral components. The root meaning of the word anxiety is 'to vex or trouble'; in either presence or absence of psychological stress, anxiety can create feelings of fear, worry, uneasiness,...
, hysteriaHysteriaHysteria, in its colloquial use, describes unmanageable emotional excesses. People who are "hysterical" often lose self-control due to an overwhelming fear that may be caused by multiple events in one's past that involved some sort of severe conflict; the fear can be centered on a body part, or,...
and stressStress (medicine)Stress is a term in psychology and biology, borrowed from physics and engineering and first used in the biological context in the 1930s, which has in more recent decades become commonly used in popular parlance... - CNSCentral nervous systemThe central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
causes: strokeStrokeA stroke, previously known medically as a cerebrovascular accident , is the rapidly developing loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. This can be due to ischemia caused by blockage , or a hemorrhage...
, subarachnoid haemorrhageSubarachnoid hemorrhageA subarachnoid hemorrhage , or subarachnoid haemorrhage in British English, is bleeding into the subarachnoid space—the area between the arachnoid membrane and the pia mater surrounding the brain...
, meningitisMeningitisMeningitis is inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, known collectively as the meninges. The inflammation may be caused by infection with viruses, bacteria, or other microorganisms, and less commonly by certain drugs... - drug use: doxapramDoxapramDoxapram hydrochloride is a respiratory stimulant. Administered intravenously, doxapram stimulates an increase in tidal volume, and respiratory rate.-Mode of action:...
, aspirinAspirinAspirin , also known as acetylsalicylic acid , is a salicylate drug, often used as an analgesic to relieve minor aches and pains, as an antipyretic to reduce fever, and as an anti-inflammatory medication. It was discovered by Arthur Eichengrun, a chemist with the German company Bayer...
, caffeineCaffeineCaffeine is a bitter, white crystalline xanthine alkaloid that acts as a stimulant drug. Caffeine is found in varying quantities in the seeds, leaves, and fruit of some plants, where it acts as a natural pesticide that paralyzes and kills certain insects feeding on the plants...
and coffeeCoffeeCoffee is a brewed beverage with a dark,init brooo acidic flavor prepared from the roasted seeds of the coffee plant, colloquially called coffee beans. The beans are found in coffee cherries, which grow on trees cultivated in over 70 countries, primarily in equatorial Latin America, Southeast Asia,...
abuse - moving into high altitude areas, where the low atmospheric pressureAtmospheric pressureAtmospheric pressure is the force per unit area exerted into a surface by the weight of air above that surface in the atmosphere of Earth . In most circumstances atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point...
of oxygen stimulates increased ventilation - lung disease such as pneumoniaPneumoniaPneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung—especially affecting the microscopic air sacs —associated with fever, chest symptoms, and a lack of air space on a chest X-ray. Pneumonia is typically caused by an infection but there are a number of other causes...
, where a hypoxic driveHypoxic driveThe hypoxic drive is a form of respiratory drive in which the body uses oxygen chemoreceptors instead of carbon dioxide receptors to regulate the respiratory cycle....
governs breathing more than CO2 levels (the normal determinant) - feverFeverFever is a common medical sign characterized by an elevation of temperature above the normal range of due to an increase in the body temperature regulatory set-point. This increase in set-point triggers increased muscle tone and shivering.As a person's temperature increases, there is, in...
, which stimulates the respiratory centre in the brainstem - pregnancyPregnancyPregnancy refers to the fertilization and development of one or more offspring, known as a fetus or embryo, in a woman's uterus. In a pregnancy, there can be multiple gestations, as in the case of twins or triplets...
- high levels of NH4+ leading to brain swelling and decreased blood flow to the brain
- sexual activity, which may induce excessive breathing due to excitation
Symptoms
Symptoms of respiratory alkalosis are related to the decreased blood carbon dioxide levels, and include peripheral paraesthesiae. In addition, the alkalosis may disrupt calcium ion balance, and cause the symptoms of hypocalcaemiaHypocalcaemia
In medicine, hypocalcaemia is the presence of low serum calcium levels in the blood, usually taken as less than 2.1 mmol/L or 9 mg/dl or an ionized calcium level of less than 1.1 mmol/L or 4.5 mg/dL. It is a type of electrolyte disturbance...
(such as tetany
Tetany (medical sign)
Tetany is a medical sign consisting of the involuntary contraction of muscles, which may be caused by disease or other conditions that increase the action potential frequency...
and fainting) with no fall in total serum calcium levels.
In some cases, from someone who has had acute respiratory alkalemia caused by chronic hyperventilation syndrome, this can sometimes result in massive amounts of pain and disorientation. The pH levels change dramatically in order to compensate for the lactic acid [which the muscles under normal fight or flight circumstances would be pumping out] it believes to be entering the blood stream. The dramatic shift causes a 'physical confusion' which translates to a burning pain that comes from everywhere, and can also alter the brain chemistry which leads to confusion at best and feeling like 'I was in the wrong body" for anywhere from five minutes to a half an hour as the body reorients itself. Note: this is in extreme cases.
In popular culture
In The Andromeda StrainThe Andromeda Strain
The Andromeda Strain , by Michael Crichton, is a techno-thriller novel documenting the efforts of a team of scientists investigating a deadly extraterrestrial microorganism that rapidly and fatally clots human blood, while in other people inducing insanity...
, Michael Crichton
Michael Crichton
John Michael Crichton , best known as Michael Crichton, was an American best-selling author, producer, director, and screenwriter, best known for his work in the science fiction, medical fiction, and thriller genres. His books have sold over 200 million copies worldwide, and many have been adapted...
's first novel, scientists instruct a town's sole adult survivor of an extraterrestrial-pathogenic
Pathogen
A pathogen gignomai "I give birth to") or infectious agent — colloquially, a germ — is a microbe or microorganism such as a virus, bacterium, prion, or fungus that causes disease in its animal or plant host...
epidemic to hyperventilate in order to raise his blood pH to a level inhospitable to the pathogen (the "strain" in the title).
See also
- Metabolic acidosisMetabolic acidosisIn medicine, metabolic acidosis is a condition that occurs when the body produces too much acid or when the kidneys are not removing enough acid from the body. If unchecked, metabolic acidosis leads to acidemia, i.e., blood pH is low due to increased production of hydrogen by the body or the...
- Metabolic alkalosisMetabolic alkalosisMetabolic alkalosis is a metabolic condition in which the pH of tissue is elevated beyond the normal range . This is the result of decreased hydrogen ion concentration, leading to increased bicarbonate, or alternatively a direct result of increased bicarbonate concentrations.-Terminology:*Alkalosis...
- Respiratory acidosisRespiratory acidosisRespiratory acidosis is a medical condition in which decreased ventilation causes increased blood carbon dioxide concentration and decreased pH ....
- Hypocalcemia

