
Relative angular momentum
Encyclopedia
In astrodynamics
, the relative angular momentum (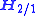 ) of an orbiting body
) of an orbiting body
( ) relative to a central body
) relative to a central body
( ) is the moment
) is the moment
of ( )'s relative linear momentum:
)'s relative linear momentum:
where:
For a body in an unperturbed orbit about a central body, the orbital plane is stationary, and the relative angular momentum ( ) is perpendicular
) is perpendicular
to the orbital plane
.
For perturbed orbits where the orbital plane is in motion, the relative angular momentum vector is perpendicular to the (osculating) orbital plane at only two points in the orbit.
( ):
):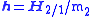
where:
Astrodynamics
Orbital mechanics or astrodynamics is the application of ballistics and celestial mechanics to the practical problems concerning the motion of rockets and other spacecraft. The motion of these objects is usually calculated from Newton's laws of motion and Newton's law of universal gravitation. It...
, the relative angular momentum (
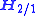 ) of an orbiting body
) of an orbiting bodyOrbiting body
In astrodynamics, an orbiting body is a body that orbits a primary body .The orbiting body is properly referred to as the secondary body.It is less massive than the primary body ....
(
 ) relative to a central body
) relative to a central bodyCentral body
In astrodynamics a central body is a body that is being orbited by an secondary body, or satellite .The central body is properly referred to as the primary body.Under standard assumptions in astrodynamics:...
(
 ) is the moment
) is the momentMoment (physics)
In physics, the term moment can refer to many different concepts:*Moment of force is the tendency of a force to twist or rotate an object; see the article torque for details. This is an important, basic concept in engineering and physics. A moment is valued mathematically as the product of the...
of (
 )'s relative linear momentum:
)'s relative linear momentum:
where:
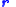 is the orbital position vector of the orbiting body relative to the central body,
is the orbital position vector of the orbiting body relative to the central body, is the orbital velocity vector of the orbiting body relative to the central body,
is the orbital velocity vector of the orbiting body relative to the central body,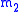 is mass of the orbiting body.
is mass of the orbiting body.
For a body in an unperturbed orbit about a central body, the orbital plane is stationary, and the relative angular momentum (
 ) is perpendicular
) is perpendicularPerpendicular
In geometry, two lines or planes are considered perpendicular to each other if they form congruent adjacent angles . The term may be used as a noun or adjective...
to the orbital plane
Orbital plane (astronomy)
All of the planets, comets, and asteroids in the solar system are in orbit around the Sun. All of those orbits line up with each other making a semi-flat disk called the orbital plane. The orbital plane of an object orbiting another is the geometrical plane in which the orbit is embedded...
.
For perturbed orbits where the orbital plane is in motion, the relative angular momentum vector is perpendicular to the (osculating) orbital plane at only two points in the orbit.
Uses
In astrodynamics relative angular momentum is usually used to derive specific relative angular momentumSpecific relative angular momentum
The specific relative angular momentum is also known as the areal momentum .In astrodynamics, the specific relative angular momentum of two orbiting bodies is the vector product of the relative position and the relative velocity. Equivalently, it is the total angular momentum divided by the...
(
 ):
):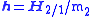
where:
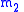 is mass of the orbiting body.
is mass of the orbiting body.
See also
- Angular momentumAngular momentumIn physics, angular momentum, moment of momentum, or rotational momentum is a conserved vector quantity that can be used to describe the overall state of a physical system...
- Specific relative angular momentumSpecific relative angular momentumThe specific relative angular momentum is also known as the areal momentum .In astrodynamics, the specific relative angular momentum of two orbiting bodies is the vector product of the relative position and the relative velocity. Equivalently, it is the total angular momentum divided by the...
- Linear momentum
- MomentumMomentumIn classical mechanics, linear momentum or translational momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object...

