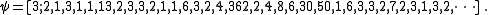Reciprocal Fibonacci constant
Encyclopedia
The reciprocal Fibonacci constant, or ψ, is defined as the sum of the reciprocals of the Fibonacci number
s:
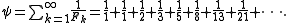
The ratio of successive terms in this sum tends to the reciprocal of the golden ratio
. Since this is less than 1, the ratio test shows that the sum converges.
The value of ψ is known to be approximately
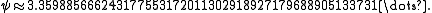
No closed formula for ψ is known, but Gosper
describes an algorithm for fast numerical approximation of its value. The reciprocal Fibonacci series itself provides O(k) digits of accuracy for k terms of expansion, while Gosper's accelerated series
provides O(k2) digits.
ψ is known to be irrational
; this property was conjectured by Paul Erdős
, Ronald Graham
, and Leonard Carlitz
, and proved in 1989 by Richard André-Jeannin.
The continued fraction
representation of the constant is:
Fibonacci number
In mathematics, the Fibonacci numbers are the numbers in the following integer sequence:0,\;1,\;1,\;2,\;3,\;5,\;8,\;13,\;21,\;34,\;55,\;89,\;144,\; \ldots\; ....
s:
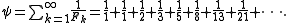
The ratio of successive terms in this sum tends to the reciprocal of the golden ratio
Golden ratio
In mathematics and the arts, two quantities are in the golden ratio if the ratio of the sum of the quantities to the larger quantity is equal to the ratio of the larger quantity to the smaller one. The golden ratio is an irrational mathematical constant, approximately 1.61803398874989...
. Since this is less than 1, the ratio test shows that the sum converges.
The value of ψ is known to be approximately
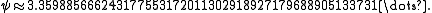
No closed formula for ψ is known, but Gosper
Bill Gosper
Ralph William Gosper, Jr. , known as Bill Gosper, is an American mathematician and programmer from Pennsauken Township, New Jersey...
describes an algorithm for fast numerical approximation of its value. The reciprocal Fibonacci series itself provides O(k) digits of accuracy for k terms of expansion, while Gosper's accelerated series
Series acceleration
In mathematics, series acceleration is one of a collection of sequence transformations for improving the rate of convergence of a series. Techniques for series acceleration are often applied in numerical analysis, where they are used to improve the speed of numerical integration...
provides O(k2) digits.
ψ is known to be irrational
Irrational number
In mathematics, an irrational number is any real number that cannot be expressed as a ratio a/b, where a and b are integers, with b non-zero, and is therefore not a rational number....
; this property was conjectured by Paul Erdős
Paul Erdos
Paul Erdős was a Hungarian mathematician. Erdős published more papers than any other mathematician in history, working with hundreds of collaborators. He worked on problems in combinatorics, graph theory, number theory, classical analysis, approximation theory, set theory, and probability theory...
, Ronald Graham
Ronald Graham
Ronald Lewis Graham is a mathematician credited by the American Mathematical Society as being "one of the principal architects of the rapid development worldwide of discrete mathematics in recent years"...
, and Leonard Carlitz
Leonard Carlitz
Leonard Carlitz was an American mathematician. Carlitz supervised 44 Doctorates at Duke University and published over 770 papers.- Chronology :* 1907 Born Philadelphia, PA, USA* 1927 BA, University of Pennsylvania...
, and proved in 1989 by Richard André-Jeannin.
The continued fraction
Continued fraction
In mathematics, a continued fraction is an expression obtained through an iterative process of representing a number as the sum of its integer part and the reciprocal of another number, then writing this other number as the sum of its integer part and another reciprocal, and so on...
representation of the constant is: