Rec. 709
Encyclopedia
ITU-R
Recommendation BT.709, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 709 or BT.709, standardizes the format of high-definition television
, having 16:9 (widescreen
) aspect ratio
. The first edition of the standard was approved in 1990.
Part 2 codifies current and prospective 1080i and 1080p systems with square sampling. In an attempt to unify 1080-line HDTV standards, part 2 defines a common image format (CIF) with picture parameters independent of the picture rate.
Initial acquisition is possible in either progressive or interlaced form. Video captured as progressive can be transported with either progressive transport or progressive segmented frame
(PsF)
transport. Video captured as interlaced can be transported with interlace transport. In cases where a progressive captured image is transported as a segmented frame, segment/field frequency must be twice the frame rate.
In practice, the above requirements result in the following frame rates ("fractional" rates are specified in commonly used "decimal" form): 25i, 25PsF, 25p, 50p for 50 Hz systems; 23.976p, 23.976PsF, 24p, 24PsF, 29.97i, 29.97p, 29.97PsF, 30PsF, 30p, 59.94p, 60p for 60 Hz systems.
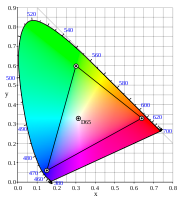
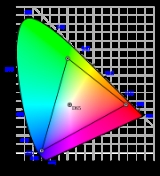
Note that red and blue are the same as the EBU Tech 3213 primaries while green is halfway between EBU Tech 3213 and SMPTE C.
of 2.2.)
ITU-R
The ITU Radiocommunication Sector is one of the three sectors of the International Telecommunication Union and is responsible for radio communication....
Recommendation BT.709, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 709 or BT.709, standardizes the format of high-definition television
High-definition television
High-definition television is video that has resolution substantially higher than that of traditional television systems . HDTV has one or two million pixels per frame, roughly five times that of SD...
, having 16:9 (widescreen
Widescreen
Widescreen images are a variety of aspect ratios used in film, television and computer screens. In film, a widescreen film is any film image with a width-to-height aspect ratio greater than the standard 1.37:1 Academy aspect ratio provided by 35mm film....
) aspect ratio
Aspect ratio
The aspect ratio of a shape is the ratio of its longer dimension to its shorter dimension. It may be applied to two characteristic dimensions of a three-dimensional shape, such as the ratio of the longest and shortest axis, or for symmetrical objects that are described by just two measurements,...
. The first edition of the standard was approved in 1990.
Pixel count
Rec. 709 refers to HDTV systems having roughly two million luma samples per frame. Rec. 709 has two parts: Part 1 codifies what are now referred to as 1035i30 and 1152i25 HDTV systems. The 1035i30 system is now obsolete, having been superseded by 1080i and 1080p square-sampled ("square-pixel") systems. The 1152i25 system was used for experimental equipment in Europe and was never commercially deployed.Part 2 codifies current and prospective 1080i and 1080p systems with square sampling. In an attempt to unify 1080-line HDTV standards, part 2 defines a common image format (CIF) with picture parameters independent of the picture rate.
Frame rate
Rec. 709 specifies the following picture rates: 60 Hz, 50 Hz, 30 Hz, 25 Hz and 24 Hz. "Fractional" rates having the above values divided by 1.001 are also permitted.Initial acquisition is possible in either progressive or interlaced form. Video captured as progressive can be transported with either progressive transport or progressive segmented frame
Progressive segmented frame
Progressive segmented Frame is a scheme designed to acquire, store, modify, and distribute progressive-scan video using interlaced equipment and media....
(PsF)
transport. Video captured as interlaced can be transported with interlace transport. In cases where a progressive captured image is transported as a segmented frame, segment/field frequency must be twice the frame rate.
In practice, the above requirements result in the following frame rates ("fractional" rates are specified in commonly used "decimal" form): 25i, 25PsF, 25p, 50p for 50 Hz systems; 23.976p, 23.976PsF, 24p, 24PsF, 29.97i, 29.97p, 29.97PsF, 30PsF, 30p, 59.94p, 60p for 60 Hz systems.
Digital representation
Rec. 709 coding uses "studio-swing" levels where reference black is defined as 8-bit interface code 16 and reference white is defined as 8-bit interface code 235. Interface codes 0 and 255 are used for synchronization, and are prohibited from video data. Eight-bit codes between 1 and 15 provide footroom, and can be used to accommodate transient signal content such as filter undershoots. Eight-bit interface codes 236 through 254 provide headroom, and can be used to accommodate transient signal content such as filter overshoots and specular highlights. Bit-depths deeper than 8 bits are obtained by appending least-significant bits. Ten-bit systems are commonplace in studios. (Desktop computer graphic systems ordinarily use "full-swing" encoding that places reference black at code 0 and reference white at code 255, and provide no footroom or headroom.) The 16..235 limits (for luma; 16..240 for chroma) originated with ITU Rec. 601.Primary chromaticities

| Color space Color space A color model is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers, typically as three or four values or color components... |
White point White point A white point is a set of tristimulus values or chromaticity coordinates that serve to define the color "white" in image capture, encoding, or reproduction. Depending on the application, different definitions of white are needed to give acceptable results... |
Primaries Primary color Primary colors are sets of colors that can be combined to make a useful range of colors. For human applications, three primary colors are usually used, since human color vision is trichromatic.... |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| xW | yW | xR | yR | xG | yG | xB | yB | |
| ITU-R BT.709 | 0.3127 | 0.3290 | 0.64 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 0.60 | 0.15 | 0.06 |
Note that red and blue are the same as the EBU Tech 3213 primaries while green is halfway between EBU Tech 3213 and SMPTE C.
Standards Conversion
When converting between the various HD and SD formats, it would be correct to compensate for the differences in the primaries (e.g. between the Rec. 709, EBU Tech 3213, and SMPTE C primaries). In practice, this conversion is rarely performed and such a conversion would create a liability for post production facilities as they would need to ensure that the color bars on all the new masters are redone. Correcting for differences in the primaries would cause the resulting color bars on the converted tape to be inaccurate. Incorrect color bars will cause a (sub)master to be rejected by quality control checks.Luma coefficients
HDTV according to Rec. 709 forms luma (Y’) using R’G’B’ coefficients 0.2126, 0.7152, and 0.0722. This means that unlike Rec. 601, the coefficients match the primaries and white points, so luma corresponds more closely to luminance. Some experts feel that the advantages of correct matrix coefficients do not justify the change from Rec. 601 coefficients. Although worldwide agreement on a single R’G’B’ system was achieved upon the adoption of Rec. 709, adoption of different luma coefficients created a second flavour of Y’CBCR. Whenever SDTV is upconverted to HDTV, or HDTV is downconverted to SDTV, at the studio or at the consumers’ premises, luma-chroma matrixing is required.Transfer characteristics
Rec. 709 is written as if it specifies the capture and transfer characteristics of HDTV encoding - that is, as if it were scene-referred. However, in practice it is output (display) referred with the convention of a 2.4-power function display [2.35 power function in EBU recommendations]. (Rec. 709 and sRGB share the same primary chromaticities and white point chromaticity; however, sRGB is explicitly output (display) referred with an average gammaGamma correction
Gamma correction, gamma nonlinearity, gamma encoding, or often simply gamma, is the name of a nonlinear operation used to code and decode luminance or tristimulus values in video or still image systems...
of 2.2.)
See also
- Rec. 601, a comparable standard for standard-definition televisionStandard-definition televisionSorete-definition television is a television system that uses a resolution that is not considered to be either enhanced-definition television or high-definition television . The term is usually used in reference to digital television, in particular when broadcasting at the same resolution as...
- sRGB, a standard color space for web/computer graphics, based on the Rec. 709 primaries and white point.

