
Random Energy Model
Encyclopedia
In statistical physics
of disordered systems, the random energy model is a toy model
of a system with quenched disorder. It concerns the statistics of a system of particles, such that the number of possible states for the systems grow as
particles, such that the number of possible states for the systems grow as 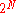 , while the energy of such states is a Gaussian stochastic variable. The model has an exact solution. Its simplicity makes this model suitable for pedagogical introduction of concepts like quenched disorder and replica symmetry
, while the energy of such states is a Gaussian stochastic variable. The model has an exact solution. Its simplicity makes this model suitable for pedagogical introduction of concepts like quenched disorder and replica symmetry
.
 limit of the Infinite Range Model is known as the Random energy model.
limit of the Infinite Range Model is known as the Random energy model.
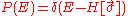 where
where  refers to the set of individual spin configurations described by the state and
refers to the set of individual spin configurations described by the state and 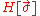 is the energy associated with it due to spin-spin interactions, which can be of different types for different pairs of spins. Since there is disorder in the system, the final extensive variables like free energy need to be averaged over all possible types of magnetic links between all spins, just as in the case of the Edwards Anderson model. Averaging
is the energy associated with it due to spin-spin interactions, which can be of different types for different pairs of spins. Since there is disorder in the system, the final extensive variables like free energy need to be averaged over all possible types of magnetic links between all spins, just as in the case of the Edwards Anderson model. Averaging 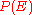 for a single realization of the disorder, over all possible realizations along with a gaussian probability distribution, we find the probability of the disordered system having an energy
for a single realization of the disorder, over all possible realizations along with a gaussian probability distribution, we find the probability of the disordered system having an energy 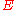 :
:
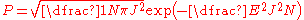
it can be seen that the probability of the spin glass existing in a particular state, does not depend only on the energy of that state and not on the individual spin configurations in it.
The entropy of the REM is given by
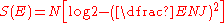
for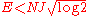 .
.
Suppose a system is described by a total energy given by a sum of random energy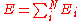
suppose that these are independent and identical random variable
s with average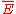 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
 , then by the central limit theorem
, then by the central limit theorem
the energy E will be a random variable with gaussian distribution with mean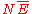 and standard deviation
and standard deviation 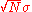 .
.
Statistical physics
Statistical physics is the branch of physics that uses methods of probability theory and statistics, and particularly the mathematical tools for dealing with large populations and approximations, in solving physical problems. It can describe a wide variety of fields with an inherently stochastic...
of disordered systems, the random energy model is a toy model
Toy model
In physics, a toy model is a simplified set of objects and equations relating them that can nevertheless be used to understand a mechanism that is also useful in the full, non-simplified theory....
of a system with quenched disorder. It concerns the statistics of a system of
 particles, such that the number of possible states for the systems grow as
particles, such that the number of possible states for the systems grow as 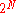 , while the energy of such states is a Gaussian stochastic variable. The model has an exact solution. Its simplicity makes this model suitable for pedagogical introduction of concepts like quenched disorder and replica symmetry
, while the energy of such states is a Gaussian stochastic variable. The model has an exact solution. Its simplicity makes this model suitable for pedagogical introduction of concepts like quenched disorder and replica symmetryReplica trick
In statistical physics of spin glasses and other systems with quenched disorder, the replica trick is a mathematical technique based on the application of the formula- Mathematical Trick :...
.
Comparison with other disordered systems
The limit of the Infinite Range Model is known as the Random energy model.
limit of the Infinite Range Model is known as the Random energy model.Derivation of thermodynamical quantities
As its name suggests, the REM has an independent distribution of energy. For a particular realization of the disorder,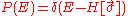 where
where  refers to the set of individual spin configurations described by the state and
refers to the set of individual spin configurations described by the state and 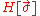 is the energy associated with it due to spin-spin interactions, which can be of different types for different pairs of spins. Since there is disorder in the system, the final extensive variables like free energy need to be averaged over all possible types of magnetic links between all spins, just as in the case of the Edwards Anderson model. Averaging
is the energy associated with it due to spin-spin interactions, which can be of different types for different pairs of spins. Since there is disorder in the system, the final extensive variables like free energy need to be averaged over all possible types of magnetic links between all spins, just as in the case of the Edwards Anderson model. Averaging 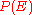 for a single realization of the disorder, over all possible realizations along with a gaussian probability distribution, we find the probability of the disordered system having an energy
for a single realization of the disorder, over all possible realizations along with a gaussian probability distribution, we find the probability of the disordered system having an energy  :
: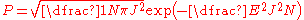
it can be seen that the probability of the spin glass existing in a particular state, does not depend only on the energy of that state and not on the individual spin configurations in it.
The entropy of the REM is given by
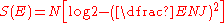
for
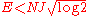 .
.Suppose a system is described by a total energy given by a sum of random energy

suppose that these are independent and identical random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
s with average
 and standard deviation
and standard deviationStandard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
 , then by the central limit theorem
, then by the central limit theoremCentral limit theorem
In probability theory, the central limit theorem states conditions under which the mean of a sufficiently large number of independent random variables, each with finite mean and variance, will be approximately normally distributed. The central limit theorem has a number of variants. In its common...
the energy E will be a random variable with gaussian distribution with mean
 and standard deviation
and standard deviation  .
.

