
Quantum yield
Encyclopedia
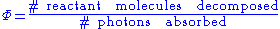
The quantum yield of a radiation
-induced process is the number of times that a defined event occurs per photon
absorbed by the system. The "event" may represent a chemical reaction, for example the decomposition of a reactant molecule:
Quantum Yield can also be defined for other events, such as fluorescence
(emission of photons) in which case the quantum yield is defined by the equation:

Here, quantum yield is essentially the emission efficiency of a given fluorophore
in this case.
Radiation
In physics, radiation is a process in which energetic particles or energetic waves travel through a medium or space. There are two distinct types of radiation; ionizing and non-ionizing...
-induced process is the number of times that a defined event occurs per photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
absorbed by the system. The "event" may represent a chemical reaction, for example the decomposition of a reactant molecule:

Quantum Yield can also be defined for other events, such as fluorescence
Fluorescence
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation of a different wavelength. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore lower energy, than the absorbed radiation...
(emission of photons) in which case the quantum yield is defined by the equation:

Here, quantum yield is essentially the emission efficiency of a given fluorophore
Fluorophore
A fluorophore, in analogy to a chromophore, is a component of a molecule which causes a molecule to be fluorescent. It is a functional group in a molecule which will absorb energy of a specific wavelength and re-emit energy at a different wavelength...
in this case.
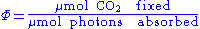
Example
Quantum yield is used in modeling photosynthesis (Skillman 2008):

