Quantum Hall effect
Overview
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
version of the Hall effect
Hall effect
The Hall effect is the production of a voltage difference across an electrical conductor, transverse to an electric current in the conductor and a magnetic field perpendicular to the current...
, observed in two-dimensional electron systems
2DEG
A two-dimensional electron gas is a gas of electrons free to move in two dimensions, but tightly confined in the third. This tight confinement leads to quantized energy levels for motion in that direction, which can then be ignored for most problems. Thus the electrons appear to be a 2D sheet...
subjected to low temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
s and strong magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
s, in which the Hall conductivity σ takes on the quantized values
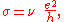
where e is the elementary charge
Elementary charge
The elementary charge, usually denoted as e, is the electric charge carried by a single proton, or equivalently, the absolute value of the electric charge carried by a single electron. This elementary charge is a fundamental physical constant. To avoid confusion over its sign, e is sometimes called...
and h is Planck's constant. The prefactor ν is known as the "filling factor", and can take on either integer (ν = 1, 2, 3, ..
Unanswered Questions

